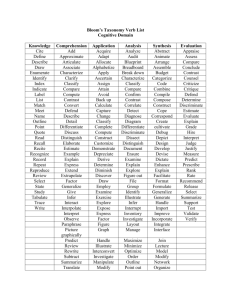
File
advertisement
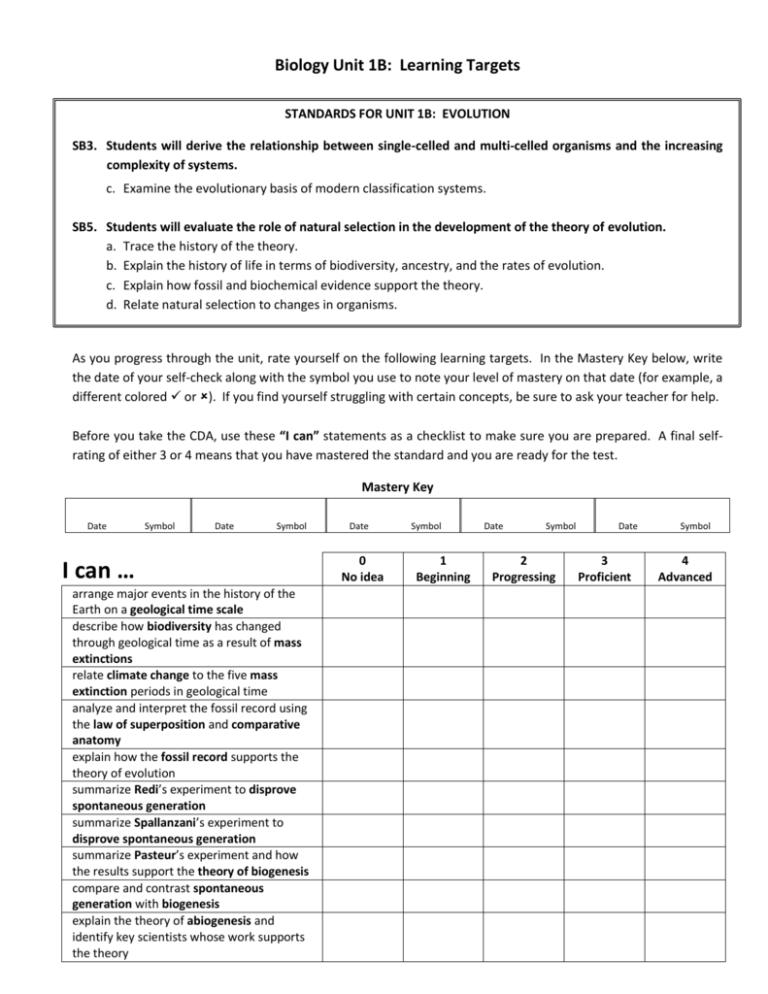
Biology Unit 1B: Learning Targets STANDARDS FOR UNIT 1B: EVOLUTION SB3. Students will derive the relationship between single-celled and multi-celled organisms and the increasing complexity of systems. c. Examine the evolutionary basis of modern classification systems. SB5. Students will evaluate the role of natural selection in the development of the theory of evolution. a. Trace the history of the theory. b. Explain the history of life in terms of biodiversity, ancestry, and the rates of evolution. c. Explain how fossil and biochemical evidence support the theory. d. Relate natural selection to changes in organisms. As you progress through the unit, rate yourself on the following learning targets. In the Mastery Key below, write the date of your self-check along with the symbol you use to note your level of mastery on that date (for example, a different colored or ). If you find yourself struggling with certain concepts, be sure to ask your teacher for help. Before you take the CDA, use these “I can” statements as a checklist to make sure you are prepared. A final selfrating of either 3 or 4 means that you have mastered the standard and you are ready for the test. Mastery Key Date Symbol Date Symbol I can … arrange major events in the history of the Earth on a geological time scale describe how biodiversity has changed through geological time as a result of mass extinctions relate climate change to the five mass extinction periods in geological time analyze and interpret the fossil record using the law of superposition and comparative anatomy explain how the fossil record supports the theory of evolution summarize Redi’s experiment to disprove spontaneous generation summarize Spallanzani’s experiment to disprove spontaneous generation summarize Pasteur’s experiment and how the results support the theory of biogenesis compare and contrast spontaneous generation with biogenesis explain the theory of abiogenesis and identify key scientists whose work supports the theory Date 0 No idea Symbol 1 Beginning Date Symbol 2 Progressing Date 3 Proficient Symbol 4 Advanced Biology Unit 1B: Learning Targets I can … summarize the primordial soup hypothesis as proposed by Oparin & Haldane summarize the Miller-Urey experiment explain how the results of the Miller-Urey experiment support the primordial soup hypothesis describe the conditions of the early Earth (atmospheric and terrestrial) prior to the appearance of life explain why scientists believe that Domain Archae are the closest relatives to the first life on Earth predict the types of organisms that would have evolved first in the conditions of the early Earth correlate early life forms with changes in the early Earth’s atmospheric conditions explain why prokaryotic cells probably appeared before eukaryotic cells explain the endosymbiotic theory sequence the hypothesized events that led from a lifeless Earth to the presence of eukaryotic cells summarize Darwin’s theory of natural selection generate examples for each of Darwin’s Four Postulates of natural selection describe Wallace’s contribution to evolutionary theory summarize Larmack’s theory of inheritance of acquired characteristics compare and contrast Darwin’s and Lamarck’s theories concerning evolution compare and contrast artificial selection with natural selection differentiate between inherited and acquired traits relate natural variation within a species to genetic and environmental factors explain the role of natural variation in a species in natural selection relate adaptation and fitness in terms of natural selection generate examples of adaptations explain the importance of the amniotic egg as an evolutionary adaptation compare and contrast camouflage & mimicry explain the development of antibiotic resistance explain how comparative anatomy 0 No idea 1 Beginning 2 Progressing 3 Proficient 4 Advanced Biology Unit 1B: Learning Targets I can … supports the theory of evolution differentiate between homologous, analogous, and vestigial structures generate examples of homologous, analogous, and vestigial structures relate homologous and vestigial structures to divergent evolution (adaptive radiation and common ancestry) relate analogous structures and convergent evolution compare and contrast the patterns of divergent and convergent evolution generate examples of pairs of organisms which exhibit divergent, convergent, and co-evolution explain how comparative embryology supports the theory of evolution analyze and interpret biochemical data (e.g., DNA or amino acid sequences) to determine evolutionary relationships differentiate between stabilizing, directional, and disruptive selection analyze a graph of trait frequencies in a population over time to identify a selective pressure as stabilizing, directional, or disruptive differentiate between gradualism and punctuated equilibrium as two theories explaining the tempo (rate) of evolution explain the basis for modern classification systems explain the biological and phylogenetic concepts of species analyze and interpret a cladogram in terms of evolutionary relationships (ancestral and derived traits) 0 No idea 1 Beginning 2 Progressing 3 Proficient 4 Advanced