5. XII QP - WordPress.com
advertisement

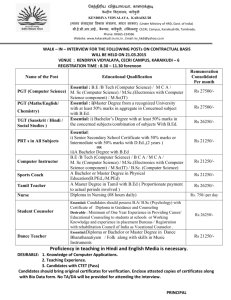
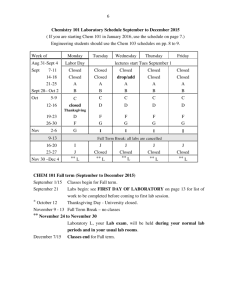
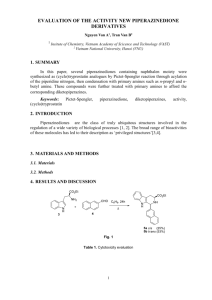
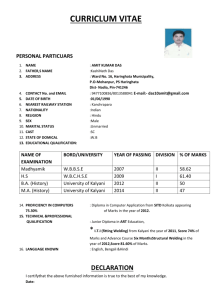
MUKESH KUMAR PGT CHEM KV GARHARA PATNA REGION MODEL QUESTION PAPER CLASS-XII Sub: Chemistry (Theory) MM:70 Time : 3 hrs General Instructions (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) Marks for each question are indicated against it. (iii) Question Number 01 to 05 are very short answer question carrying 1 mark each. (iv) Question Number 6 to 10 are short answer questions carrying 2 marks each. (v) Question Number 11 to 22 are also short answer question carrying 3 marks each. (vi) Question Number 23 is value based question carrying 4 marks. (vii) Question Number 24 to 26 are long answer carrying 5 marks each. (viii) Use log tables if necessary, use of calculators is not permitted. 1. What is doping in a semiconductor? 2. What is meant by shape selective catalysis of reactions? 3. State Satzef’s rule. 4. Write the IUPAC name of the following- CH3—CH2—CH=CH—CHO 5. Write the zwitter ion structure of sulphanilic acid. 6. State Kohlrausch law of independent migrations of ions. How will you calculate degree of dissociation of week electrolyte using this law. 7. What is the effect of temp on the rate constant of a reaction?How can this temp effect on the rate constant be represented quantitatively? 8. Explain(a)Helium is used in diving equipment. MUKESH KUMAR PGT CHEM KV GARHARA PATNA REGION (b)NH3 is a better proton accepter than PH3 9. Explain the mechanism of acid catalysed hydration of an alkene to form alcohol. 10. (a)O-nitrophenol is more acidic than o-methoxyphenol (b)Alcohols have higher boiling point than hydrocarbons of comparable molecular mass. 11. Analysis shows that Iron(II) oxide has formula Fe 0.95O1.00.Whatfractions of iron exist as Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions 12. The cell in which the following rkn occurs 2Fe3+ + 2I- = 2Fe2+ + I2 has Eo cell =0.236V at 298K. Calculate the standard free energy and equilibrium constant of the cell reaction 13. In a reaction between A and B the initial rate of reaction was measured for different initial concentrations of A and B as given below A mole/ lit 0.10 0.20 0.20 B mole/ lit 0.10 0.20 0.40 R mol/lit/sec 1.5 x 10-3 3.0 x 10-3 6.0x 10-3 What is the order of reaction with respect to A and B 14. Explain the following term(a) Dialysis(b)Tyndal effect (c) Electrophoresis 15. List the reaction occurred in a blast furnace. 16. Draw the molecular structure of the following:SF4 , BrF3, IBr217. (i)Ozone is thermodyanimically unstable. Give reason. (ii) Silver nitrate solution is added to potassium iodide solution. Write the observation. (iii)NF3 is an exothermic compound where as NCl3 is not. Explain MUKESH KUMAR PGT CHEM KV GARHARA PATNA REGION 18. Define the crystal field splitting energy .How does magnitude of it and pairing energy decide the actual confg of d-orbitals in coordination compound? Or For the complex [Ni(CO)4], write (1) The IUPAC name (2) The hybridization type (3) The shape of the complex (At no of Ni = 28) 19. Answer: a) what is meant by enantiomers. Give an example b) Which one of the following compound is more easily hydrolysed by KOH and why? CH3CHClCH2CH3 OR CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl c) Which one undergoes SN2 substitution faster and why? 20. Write the relevant chemical equation to represent (a)Reimer-Tiemann rkn. (b)Kolbe’s rkn (C) H V Z rkn MUKESH KUMAR PGT CHEM KV GARHARA PATNA REGION 21. Write the name and structure of monomers for the following polymers (a)Buna-s (b)Nylon-6 (c)Glyptal 22. (a)What is main constituent of dettol? (b)What are the artificial sweeting agents? (c) write one example of anionic dergent. 23. Nita observed that her mother got tired after doingevery little work. She felt lethargic and did not have the energy to do the work.She took her motherto a doctor . The doctor diagonosed her mother with pernicious anemia. Nita helped her mother I household work till she recovered and took her care. (i) Name the vitamin whose deficiency caused pernicious anemia. (ii) Name the source which will provide this vitamin (iii) Mention the values shown by Nita 24. Define(a) (i)mole fraction(II)colligative properties (b)Addition of 1.3g 0f a solute B to 169 g of water raises its boiling point to 100.025 C o at 1 atm. Compute MB when Kb is 0.52 K kg mol-1 or (i) Explain the following (a) Henry’s Law about dissolution of a gas in a liquid MUKESH KUMAR PGT CHEM KV GARHARA PATNA REGION (b) Boiling point elevation constant for solvent. (ii) A solution of glycerol (c3H8O3) in water was prepared by dissolving some glycerol in 500 g of water. This solution has a boiling point 100.42 0C what mass of glycerol was dissolved to make this solution. (kb for water = 0.5 KK Kg mol-1) 25. Explain (i)The highest oxidation state is exhibited in the oxo-anions of metal (ii)Of the d4 - confg Cr is strongly reducing while Mn is strongly oxidizing (iii)There is greater range of oxidation states among the actinoids than among the lanthanoids (iv)enthalpies of atomization of transition metals are high (v)most of the transition metals are coloured Or (i) Give reasons for the following observations. (a) Cu+ ion is not stable in aqueous solution. (b) Mn(ii) ion shows maximum paramagnetic character amongst the bivalent ions of first transition series. (c) Scandium (at no.21) salts are white. (ii) Describe the reactions involved in the preparation of K2Cr2O7 from chromite ore. 26. (a)How will you carry out following conversions (i)Aniline to nitrobenzene (II)Chloroethane to propan-1-amine MUKESH KUMAR PGT CHEM KV GARHARA PATNA REGION (iii)Ethanamine to N-ethylethanamide (b)Give chemical test to distinguish between (i)aniline and benzylamine (ii)secondary and tertiary amine