Measurement Notes
advertisement

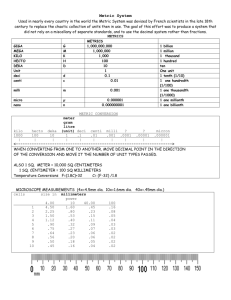
Scientific Method & Measurement Unit Unit EQ: Why is it important to know how to use chemistry skills? Identifying Laboratory Equipment EQ: Why is it important to know how to use different types of laboratory equipment? Identifying Laboratory Equipment Notes Notes at stations Move from station to station to complete notes No more than 2 students at a station at a time Reading Scientific Instruments EQ: How do significant figures relate to measurements in chemistry? Reading a Meterstick or Metric Ruler Each number represents a centimeter (cm) Each small line represents a millimeter (mm) Always estimate to one digit beyond the smallest line marker Reading a Meterstick or Metric Ruler a. 0.00 cm b. 1.49 cm c. 2.26 cm d. 3.20 cm Reading a Graduated Cylinder Meniscus – curved surface of water caused by adhesion of water to glass When reading a meniscus, Stoop so that the water is at your eye level Read the volume from the bottom of the meniscus Reading a Graduated Cylinder Significant Figures Contain all certain digits and one estimated (uncertain) digit Example: 36.4 mL The 3 and the 6 are certain; there is no doubt there are at least 36 mL The 4 is uncertain; this digit is estimated, but tells us there is close to half of another mL Metric Units and Prefixes EQ: Why is the metric system the most useful system for measurements in chemistry? Why the Metric System? The metric, or SI system of measurement is based on multiples of 10. Devised in 18th century France by Lavoisier Standard system to be used in all countries Sizes in other systems differed, causing disputes among merchants Based on properties of water On liter of water has a mass of 1 kilogram and a volume of 1 cubic decimeter. Base Units in the SI System Length = meter (m) Mass = gram (g) Volume = liter (L) Prefix tells you how much larger or smaller the unit is than the base Writing Abbreviations in the Metric System Write abbreviation for prefix Deciliters = dL Write abbreviation for base Millimeter = mm Micrograms = μg Megagrams = Mg Hectometers = hm Nanoliters - nL Metric Conversions Find the starting unit Count the steps to the ending unit Move the decimal the same number of spaces in the same direction Metric Conversions Convert 65 meters to centimeters Starting = meters (base) Ending = centi Move decimal 2 places to the right 65 m = 6500 cm Metric Conversions Convert 130 dekagrams to decigrams Starting = deka Ending = deci Move decimal 2 places to the right 130 dag = 13 000 dg Metric Conversions Convert 17 hectometers to kilometers Starting = hecto Ending = kilo Move decimal 1 place to the left 17 hm = 1.7 km Metric Conversions Convert 4.58 mL to L Starting = milli Ending = base Move decimal 3 places to the left 4.58 mL = 0.00458 L Metric Conversions Convert 4.998 mg to kg Starting = milli Ending = kilo Move decimal 6 places to the left 4.998 mg = 0.000 004 998 kg Metric Conversions Convert 34 cL to hL Starting = centi Ending = hecto Move decimal 4 places to the left 34 cL = 0.003 4 hL Precision and Accuracy EQ: Compare and contrast precision and accuracy. Accuracy How close a measurement or calculation is to the actual value In lab, measurements are accurate if they have less than 10% error. Percent Error Determines the accuracy of lab data Don’t forget the absolute value! Percent error is never negative. Theoretical = what you should have gotten Actual = what you got Precision How close together two measurements are Or The number of significant digits in a measurement Precision vs. Accuracy