Antipyretic, analgesic and anti
advertisement

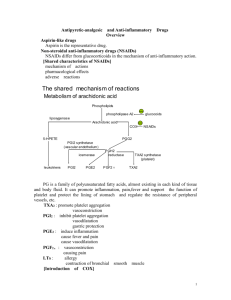
Antipyretic, analgesic and antiinflammatory drugs Liming Zhou (周黎明) Department of pharmacology Huxi medical center Sichuan university Contents • Overview • History • Common pharmacological effects • Aspirin 阿斯匹林 • Selective COS-2 inhibitor • Other Drugs Overview • This kind of drug is a group of chemically dissimilar agents that have antipyretic, analgesic and antiinflammatory effects. • The structure of this kind of drug differs from that of steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. • Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDs • History • In ancient Egypt & Greece, dried leaves of myrtle, the bark of willow & poplar tree • In England, active component from willow bark was identified as salicin (水杨苷), which is metabolized to salicylate (水杨酸盐)in 1763. • In Germany, salicylic acid (水杨酸) was synthesized in 1860. • In 1875, acetylsalicylic acid (乙酰水杨酸) was synthesized. History • In 1899, “Aspirin“ (acetylsalicylic acid) was named; the "a" --- acetyl grouping and the "spirin" --- botanical genus spiraea, from which salicylates could be extracted. • Now, more than 30 million people consume NSAIDs daily and of these 40% of the patients are more than 60 years of age. • The consumption of NSAIDs is No. 1 among all drugs. History • In 1969 the first association between prostaglandin production and the actions of aspirin- like drugs • In 1992 new enzyme was cloned & was called cyclooxygenase 2 (COX- 2) or PGH 2 synthase 2 Common pharmacological effects These drugs show the same pharmacological effects • -- antipyretic effect (解热) • -- analgesic effect (镇痛) • -- anti-inflammatory effect (抗炎) 1. Antipyretic Effects • "normal" temperature: slightly affected • "elevated" temperature: reduced • The higher temperature, the more potent • Mechanisms of Antipyretic Action Blocks pyrogen-induced prostaglandin production in thermoregulatory center (CNS) Prostaglandins pGE2 thermoregulatory center Pyrogen NSAIDs • Antipyretic Mechanism set point ↑ heat production ↑ Heat dissipation ↓ Fever Block prostaglandins production • Sites of action: Central Nervous System 2. Analgesic Effects • Effective to mild to moderate pain 0.5g of aspirin is a weak or mild analgesic that is effective in short, intermittent types of pain as encountered in neuralgia, myalgia (肌 肉痛), toothache. Analgesic Effects • Pain may arise from: Musculature, dental work , vascular , postpartum conditions, arthritis , bursitis • Sites of action: peripherally -- sites of inflammation subcortical sites NSAIDs Prostaglandins factors pGE2 pGF2 + Bradrkinin histamine Nerve ending of pain Pain • block prostaglandins production • Sites of action: peripheral tissue 3. Anti-inflammatory Effects • NSAIDs only inhibit the symptoms of inflammation • But they neither arrest the progress of the disease nor do they induce remission Anti-inflammatory Effects • Reduced synthesis: --eicosanoid mediators • Interference: --kallikrein system mediators --inhibits granulocyte adherence --stabilizes lysosomes --inhibits leukocyte migration How can NSAIDs inhibit the prostaglandin production? The Mechanism of NSAIDs Mechanism of action The principal pharmacological effect of NSAIDs is due to their ability to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis by blocking the cyclooxygenase (COX) activity of both COX-1 and COX-2. NSAIDs----- acetylation of COX (reversible or irreversible) NSAIDs Prostaglandins Inflammatory factors pGE2 pGF2 + Bradrkinin Histamine Symptoms of inflammation Red, swelling, Heating, Pain 5-HT • block prostaglandins production • Sites of action: peripheral tissue Phospholipids Phospholipase Arachidonic Acid 5-lipoxygenase cyclooxygenase 5-HPTE LTB4 PGG 2 peroxidase LTC4 PGH2 TXA 2 PGI2 PGE2 PGF2 PGD2 • PGE2 vasodilatation, pain sensitization, gastric cytoprotection [mucous/HCO3 secretion], fever • PGF2 bronchoconstriction, uterine contraction • PGI2 inhibition of platelet aggregation, gastric cytoprotection • TXA2 platelet aggregation Salicylates 水杨酸类 • Acetylsalicyclic acid 乙酰水杨酸 Aspirin 阿斯匹林 • Sadium Salicylate 水杨酸钠 Pharmacokinetics • Rapidly absorbed: stomach and upper small intestine • Distribution:through the body rapidly hydrolyzed --------- acetic acid + salicylate, catalyzed by tissue/blood esterases Elimination----- Pharmacokinetics • metabolite in liver dose <1g/day:one-order elimination T1/2: 3--5 hrs dose >1g/day:zero-order elimination >4g/day T1/2: • Excretion: kidney, influenced by pH of urine Pharmacodynamics 1. Analgesic Effects (300-600mg) 2. Antipyretic Effects (300-600mg) 3. Anti-inflammatory Effects (3-6g) do not influence the progress of disease 4. Effects on Platelets (40-100mg) Reduced platelet aggregation reduces thromboxane A2 (TXA2) formation •Effects on Platelets (40-100mg) 血 管 壁 磷脂 血小板 磷脂 花生四烯酸 花生四烯酸 环氧化酶 抑 cAMP 制血小 PGH2 PGH2 板集聚 收缩 松弛血 管平滑肌 PGI2 血管平滑肌 TXA2 (-) cAMP 阿斯匹林 血小板释 放ADP 促进血小板集聚 Low doses 40-100mg/day • Platelets • Endothelial cell • No nuclei • Has nuclei • No new COX1 • New COX1 produce produce • TXA2 production ↓ • Lifetime: 8-11 days Pharmacodynamics 5. Other effects • Immune inhibition • Effect on metabolism of connective tissue • Effects on metabolism of glucose, fat, protein ---- catabolism ↑ • ACTH release ↑ Clinical Uses 1. Commonly used for management of mild to moderate pain (300-600mg) 2. Combination agents (cold) 3. Used for reducing fever (300-600mg) 4. Useful in treatment of: (high doses 3-6g) T1/2 > 12 hours 0 rheumatic fever 0 rheumatoid arthritis 0 other inflammatory joint diseases Clinical Uses 5. Antiplatelet: (low doses) 40-100mg reduce incidence of transient ischemic attacks (prophylaxis) reduce incidence of unstable angina (prophylaxis) may reduce incidents of coronary artery thrombosis Clinical Uses 6. Hypertension in pregnancy : (low doses) 60-100mg TXA2↓ 7. Local indication GI inflammation : 5-amido-salicylic acid SIDE EFFECTS 1. CNS: excitation----inhibition salicylic acid reaction: Headaches; confusion; hallucinations; tremors; vertigo; behavior disturbance 2. GI effects: direct stimulation PGE2 & PGI2 ↓ Esophagitis; gastric ulcerations; GI hemorrhage SIDE EFFECTS 3. Liver & renal toxicity Dose dependence toxicity Reye's syndrome a potentially fatal disease that causes numerous detrimental effects to many organs, especially the brain and liver. The disease causes hepatitis with jaundice and encephalopathy SIDE EFFECTS 4. Other reaction Hematologic: decreased platelet aggregation; prolonged bleeding time. Exacerbations of asthma Hypersensitivity: rashes Acid-base Imbalance Acetaminophen 乙酰氨基酚(醋氨酚,扑 热息痛) Phenacetin 非拉西丁 • Rapidly absorbed from GI • Phenacetin is largely converted to Acetaminophen • Similar antipyretic, analgesia to aspirin • Weak anti-inflammatory properties • used to reduce fever and pains (a major ingredient in numerous cold and flu medications) (choice for child) • used appropriately, side effects are rare Indomethacin 吲哚美辛(消炎痛) • More potent than aspirin • As an anti-inflammatory agent • More adverse reaction Ibuprofen 布洛芬 • More analgesia • Fewer adverse reaction • Brufen;Benzeneacetic acid; Fenbid; Emodin;Motrin 异丁苯丙酸;异丁洛芬;拔 怒风;芬必得;炎痛停; Phenylbutazone 保泰松 羟基保泰松 • • • • Powerful anti-inflammatory effects Weak analgesic & antipyretic activities Promote excretion of uric acid Used for acute gout, rheumatic & rheumatoid arthritis • More adverse reaction • Can induce activities of drug metabolize-E • Can displace other drugs from plasma proteins Selective COX-2 inhibitors Less adverse reactions Do not impact platelet aggregation • • • • • Meloxicam 美洛昔康 Celecoxib 塞来昔布 Nimesulide 尼美舒力 Rofecoxib Valdecoxib Acetaminophen Anti pyretic analges Antiic inflammatory Side action ++ ++ + Indomethacin ++++ ++++ sulindac ++++ ++ + ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ +++ + + tolmetin + diclofenac Ibuprofen + meloxicam ---- Phenylbutazone ketorolac +++ +++ cox2 +++ i.m 常用感冒药组成 • 解热镇痛药:对乙酰氨基酚、布洛芬 • H1受体阻断药:氯苯那敏、苯海拉明 • 止咳药:右美沙芬等 • 缩血管药:伪麻黄碱 • 抗病毒药:金刚烷胺 • 中枢兴奋药:咖啡因 • 其他:中草药、人工牛黄