Teacher
advertisement

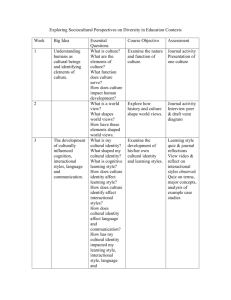
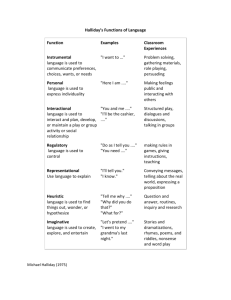
Teacher talk and classroom interaction Your trainer Wendy Arnold • • • • • MA in Teaching English to Young Learners (TEYL) Freelance teacher, trainer, writer, researcher IATEFL’s YL SIG committee Specialist in reading for young learner literacy 15 years experience teaching Chinese young learners What do you know? Teacher talk Interaction • Features of teacher talk • Principles of giving instruction and feedback • Name the different types of classroom interaction • Explain the role of interaction, input, output questions and answers dialogue role play PAIRWORK projects GROUPWORK games songs/chants WHOLE CLASS surveys DID YOUR LIST LOOK LIKE THIS? TEACHER TALK giving instructions asking and answering questions Comprehensible input (可理解性输入) Comprehensible output (可理解性输出) Interaction Interaction Input Output Language Acquisition(语言习 得) Summary of the relationship between interactions, comprehensible input, output and language acquisition Example of pairwork (video) Students Teacher • What are they doing? • Are they engaged? • Do they understand what they are doing? • What are they doing? • Are they supporting anyone? How? WHAT MAKES THE INTERACTION EFFECTIVE(有效)? WHAT ARE THE PROBLEMS(问题) OF THE INTERACTION? Example of groupwork (video) Students Teacher • What are they doing? • Are they all engaged? • What are they doing? • Are they helping anyone? WHAT MAKES THE INTERACTION EFFECTIVE? WHAT ARE THE PROBLEMS OF THE INTERACTION? Example of whole class activity (video) Students Teacher • What they doing? • Does everyone know how to do it? • How successful are they? • What are they doing? • Are the instructions clear? • Are they supporting anyone? How? WHAT MAKES THE INTERACTION EFFECTIVE? WHAT ARE THE PROBLEMS OF THE INTERACTION? Feedback Teacher • How are the teachers giving feedback? The Nature of interaction a. The teacher’s “interactional” adjustment b. The pupils’ “interactional” behaviors Input and interactional adjustments (交互性调整) The most commonly used strategies to make the language input more comprehensible are: 1. Repeating 2. Simplifying questions 3. Switching to Chinese 4. Setting an example What do you think of these strategies? Have you identified other strategies in the video clips? Atkinson (1987:426) worries that the teacher and/or the students will feel that “they have not ‘really understood any item of language until it has been translated.” Output and interactional adjustments The most commonly used strategies to elicit language output are: 1. Provide the beginning of a sentence and let pupils continue. Elicit by starting the sentence: For example: “Here’s the……” 2. Set a model and ask pupils to repeat. Give requirement: “You must say ……” or provide the expected answer. 3. Use rhetorical (反问)questions: Example: Ss: Where’s the marker? S: Here’s the pencil sharpener. T: Pencil sharpener? Have you identified other strategies in the video clips? Walsh (2002, cited Wacaro, 2003:198) identified a number of features which obstructed(阻碍) learning potential(潜力). • The teacher completes the turn for the student. • The teacher interrupts(打断) the student’s turn in order to correct. • No negotiation(商量) of meaning is detectable via clarification requests(澄清), confirmation checks(确认). • The teacher echoes(重复) the student response even if it is correct. • IRF (Initiate-Response-Feedback) turn-taking structure as the dominant (主要)pattern. Can you give examples in the video clips? The pupils “interactional” behaviors: • the “reduction” behavior • the “achievement” behavior (Faerch and Kaspar, 1980, cited in Ellis, 1985). Did you see both behaviors in the video clips? the “reduction” behavior: the learner missing a turn by keeping silent, choosing to be out of the task by saying “no” or “I don’t know”, and other similar utterances, switching topics or imitating part or the whole of the teacher’s previous utterance. the “achievement” behavior: learners respond actively to the teacher’s utterance by using their first language, miming, requesting assistance or guessing. A demonstration lesson Work in groups and complete one of the following tasks: • Group 1: Count the time used for different types of interaction: PW, GW, IW, CW • Group 2: Find out teachers’ interactional adjustment strategies • Group 3: Find out pupils’ interactional behaviours A demonstration lesson • Group 4: Write down all the questions asked by the teacher and find out the features of this teacher. • Group 5: Write down the language used for praise and feedback and comment on it. Cross group discussion Each person: 2’ Time limit: 15’ Let’s discuss what makes effective and dynamic interaction! Theory into practice: Krashen Comprehensible input Vygotsky ZPD (最近发展区) social interaction Bruner Scaffolding (支架) Want to have another look...? The slides of this presentation will be published at