Diapositiva 1
advertisement

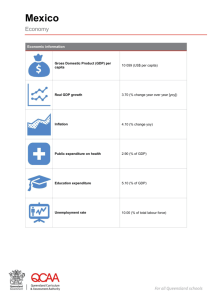
Mexico – country of opportunities for the Slovenian companies March 2015 Mexico: The 14th biggest country Corresponds to the surface of Europe‘s 4 biggest countries: Germany = Spain France Sweden 2 Mexico is the 11th country in terms of population México tiene Mexico una has población de 118 118millones Million de inhabitants habitantes Equal to the population of Colombia, Spanien and Australia 3 A country with great infrastructure Mexico has: • • • • • 63 border crossings. 68 international ports. 64 international airports. 16,700 miles of railroads. 230,000 miles of roads. Monterrey Altamira SLP Tampico Guanajuato Guadalajara Veracruz Manzanillo Lázaro Cárdenas Source: SCT. 4 2013 15th biggest economy amongst 189 countries Economic Indicator Real GDP Growthl (%, constant prices) GDP(Billion of current US dollars, BD) GDP per capita (current dollars) PPP GDP (Billion of international dollars) PPP GDP per capita (international dollars) Inflation (%, end of period) Unemployment Rate (% of total labor force) Population (million persons) General Government Revenue (as % of GDP) General Government Expenditure (as % of GDP) General government net lending/borrowing (as % of GDP) General Government Gross Debt (as % of GDP) Current Account (BD) Current Account Balance (as % of GDP) Exchange Rate (pesos/US dollar, end of period) 28-day CETES Interest Rate (%, yield, end of period) 2009 -4.7 895.0 7,947 1,678.4 14,904 3.6 5.5 112.6 22.1 27.2 -5.1 43.9 -8.2 -0.9 13.06 4.51 2010 5.1 1,051.1 9,197 1,785.7 15,624 4.4 5.4 114.3 22.4 26.7 -4.3 42.2 -3.9 -0.4 12.36 4.45 2011 4.0 1,171.2 10,124 1,896.3 16,392 3.8 5.2 115.7 22.9 26.2 -3.3 43.2 -12.6 -1.1 13.99 4.31 2012 4.0 1,185.7 10,129 2,007.2 17,147 3.6 5.0 117.1 23.4 27.1 -3.7 43.2 -15.1 -1.3 13.01 3.91 2013 1.4 1,260.9 10,650 2,058.9 17,390 4.0 4.9 118.4 23.3 27.1 -3.8 46.4 -25.9 -2.1 13.08 3.18 2014 2.1 1,295.9 10,837 2,143.5 17,925 4.1 4.8 119.6 22.2 26.4 -4.2 48.0 -25.2 -1.9 14.72 2.74 2015f 3.3 1,367.3 11,321 2,260.2 18,714 3.2 4.5 120.8 21.6 25.6 -4.0 49.0 -27.7 -2.0 14.18 3.51 2016f 3.8 1,436.6 11,777 2,389.7 19,590 3.5 4.3 122.0 22.5 26.0 -3.5 49.0 -33.1 -2.3 14.18 4.48 Source: Elaboration of the Representative Office in Europe of the Ministry of Economy with IMF and Banco de Mexico data and forecasts and Survey of Expectiations of Private Sector Economist: January 2015. 5 Mexico will be one of the top 10 economies 2013 World's largest GDP measured by PPP Gross Domestic Product (Billion Dollars) 18,000 16,000 Goldman Sachs estimates that Mexico will be the 5th largest economy by 2050. 14,000 14th place 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 Corea del… According to Accenture, Mexico will be one of the Big Six in 2025. Gross Domestic Product (Billion Dollars) Vietnam Turquía Corea Francia Nigeria Alemania Reino Unido Japón Indonesia According to HSBC, Mexico will be the 8th largest economy in the world by 2050. Rusia México Brasil India EU China 5th place Goldman Sach’s Forecast México España Australia Canadá India Italia Rusia Brasil Francia Alemania Japón 20501 China EU 0 Reino… 2,000 Source: Goldman Sachs. The N-11: More Than an Acronym. Documento de economía mundial No: 153. Marzo de 2007/ HSBC/ ACCENTURE.1/ Pronóstico de Goldman Sachs / Fondo Monetario Internacional. 6 We are commited to free trade Mexico has access to 45 countries through its free trade agreements (1.2 billion people). 45 Number of countries Number of countries with privileged access* 20 17 12 8 1 Our FTAs give privileged access to 61% of the world’s GDP. Sources: Brazil; China: Colombia:; United States: ; Chile: Direcon; Mexico: Ministry of Economy. 7 Acuerdos de Complementación Económica Tratados de Libre Comercio NAFTA: Canadá y Estados Unidos FTA EU-MX: Unión Europea EFTA: Noruega, Islandia, Suiza y Liechtenstein G3-FTA: Colombia y Venezuela NTFTA: El Salvador, Guatemala y Honduras EPA: Japón FTA: Bolivia FTA: Chile FTA: Costa Rica FTA: Israel FTA: Uruguay ACE: Argentina ACE: Bolivia ACE: Brasil ACE: Cuba ACE: Paraguay ACE: Perú ACE: Uruguay ACE: Mercosur Acuerdos de Alcance Parcial PSA: Ecuador PSA: Panamá PSA: Paraguay Acuerdos para la Promoción y Protección Recíproca de las Inversiones: América Latina y el Caribe Argentina, Cuba, Panamá, Trinidad and Tobago, Uruguay Europa Alemania, Austria, Bélgica-Luxemburgo, Bielorrusia, Dinamarca, Eslovaquia, España, Finlandia, Francia, Grecia, Islandia, Italia, Países Bajos, Portugal, Reino Unido, República Checa, Suecia, Suiza Asia-Pacífico Australia, China, India, Corea, Singapur Pacto de Alianza Trans-Pacífica: Chile, Colombia y Perú 8 Pacific Alliance • Elimination of 100% of tariffs. • 92% immediately and the other 8% in the next 15 years or sooner. • Elimination of visas between members. • Platform for student and academic mobility. • Unification of stock exchanges. • Homologation of health and regulatory certifications. 9 México And the TPP In negotiation P4 (Brunei, Chile, New Zealand and Singapore) The 12 countries of the TPP represent: • 38% of global GDP. • 23% of world exports. • 28% of world imports. • 11% of the world’s population. 10 Mexico Slovenia GDP $1,261 Billion USD* (1.1%) $47.99 Billion USD* (-0.1%) GDP per capita $10,307 USD* $23,289 USD* Population 118 Million Inhabitants* 2 Million Inhabitants* Inflation 4.08% Inflation Rate 0.2% Inflation Rate 11 Source: Information obtained from World Bank, *Information from 2013 Bilateral Trade between Mexico and Slovenia Value in Thousands of USD 80,000 7,892 30,000 0 -20,000 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 /1 293 116,514 -70,000 -120,000 Exports Source: ProMéxico, Information from Ministry of Economic Affairs. Imports Balance of payments 12 From Mexico to Slovenia • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Polyvinyl chloride (plastic components) Digital processing units Memory Units Elements for vibration control (in vehicles) Propionic acid Tequila Toothpaste Beer Magnetic tapes Deodorants and antiperspirants Washers, valves or other parts of technical use for shock absorbers Harnesses and electrical cables for current conduction Mandrels or tool holder Spirituous beverages containing hard liquor or distilled agave Circuit boards Scale models for assembling 13 Source: ProMéxico, Information from Ministry of Economic Affairs. From Slovenia to Mexico • • • • • • • • • • • • Brush holder for starters Camshaft to transmit rotary motion in cars Starters (engine), less than 24V Synchronous Motors Alternators Rheostats Hop made into crushed cones or pellets Antennas with electric drive Waxing tools Multilayers for turn signals or rear lights Compressors Sunglasses 14 Source: ProMéxico, Information from Ministry of Economic Affairs. Industries Strategic & Main Industries Mexico Slovenia Automotive, Aerospace, ICTs, Life Sciences, Chemical, Food & Beverage, Energy Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals, Machining & Metalworking, ICTs, Logistics & Distribution, Wood-procesing, Electronics & Electrical, Automotive 15 Opportunities between Mexico & Slovenia • • Opportunities (Export) Automotive Wood processing • Medical Equipment • Information & Communication Technologies • Processed Foods & Beverages • Construction & Infraestructure • Pharmaceuticals & chemicals 16 NAFTAs Value Chain Automotive Parts cross the border 8 times during the production process. Der Learjet 85 is developed in Canada, but produced in Mexico and assembled in the USA. 17 A country part of NAFTA • +50 border crossings with the US. • NAFTA market = 18 trillion USD. • Bilateral trade with the U.S. = 1 million dollars per minute. • 1 million people and 300 thousand vehicles crossing the border daily. Source: SCT/ US Department of Transportation. 18 5.4% 8.5% Cars Parts & Accesories 1.2% Refrigerators & Freezers 1.3% Medical equipment & surgical intstruments 4.7% 4.6% Phones and Cargo trucks Telecommunications 12 Mexico’s most important Car seats & their parts 1.5% Partially processed gold Quelle: ProMéxico with Information from Global Trade Atlas 2013. * Share of total exports in %. Computers & Accesories 4.4% exported products * 1.4% 4.6% Receiver 1.5% Tractors 2.7% Electrical conductors 19 Mexico is an exporter of sophisticated products Mexico ranks 20th in Harvard and MIT's Atlas of Economic Complexity. • It acknowledges that Mexico can retain large amounts of productive knowledge. • Mexico manufactures and exports a large number of sophisticated products. • Manufacturing accounts for 80% of our exports. Source: INEGI/ Presidency/ Harvard and MIT, Atlas of Economic Complexity/ OECD. 20 We are leaders in key sectors AUTOMOTIVE AND AUTOPARTS • 8th producer and 4th exporter globally of new light vehicles in the world. AEROSPACE • Mexico is the 6th supplier to the American aerospace industry. 370 billions in exports 50% medium and high tech manufactures MEDICAL DEVICES • We are the largest exporter in Latin America and main supplier to the US. Source: FEMIA/ GTA/ AMIA/ OICA. . ELECTRIC-ELECTRONIC • Leading flat television screen exporter in the world. 21 A COUNTRY WITH COMPETITIVE SECTORS 22 Aerospace Aerospace part manufacture (US=100) • There are 270 aerospace companies in Mexico. Japan Australia Germani USA Italy United Kingdom France Canada The Netherlands Brazil Russia Mexico • In 2013, exports from this sector exceeded 5 billion dollars. • Mexico has the second largest fleet of business jets in the world (after the US). • Every two minutes takes-off an airplane with Mexican technology. 0 20 Cost Index 40 60 80 100 120 According to KPMG, aerospace parts manufacturing costs in Mexico are approximately 16% lower than in the United States. Source: KPMG/ US Census Bureau/ Ministry of Economy/ Bombardier. • Mexico is the 6th supplier to the American aerospace industry. 23 Automotive • Mexico is the 8th vehicle producer in the world. • And the 4th exporter globally of new light vehicles in the world. • We export almost three times more than Brazil and India combined. Ford’s plant in Hermosillo, Mexico, is the only facility in the world to produce the new Fusion model and the Lincoln MKZ. • We are a strategic supplier to the North and Latin American automotive markets. • In 2011, Mexico was the leading autoparts supplier to the United States. • Eleven of every 100 light automobiles sold in the United States are manufactured in Mexico. • 84 of the top 100 auto parts companies in the world have production facilities in Mexico. 24 Source: OICA/ Global Trade Atlas/ AMIA/ Ward’s Automotive Reports/ AASA, 2011. Electric-Electronic • Mexico is the leading home appliance exporter in Latin America. • And the 6th globally. • It is the leading flat television screen exporter in the world. • The second refrigerator exporter. • The 4th global exporter of computers. • 8 of the top 10 transnational electronics manufacturing services (CM’s) have operations in Mexico. Electronics assembling (US=100) Japan Australia Germany USA Italy United Kingdom France The Netherlands Canada Brazil Russia Mexico 0 20 Cost Index 40 60 80 100 120 According to KPMG, electronics assembling costs in Mexico are 15% lower than in the United States. 25 Source: Global Trade Atlas/ KPMG/ Manufacturer Market Insider. Medical devices • Medical devices manufacturing (US=100) Japan Australia Germany USA Italy Canada France The Netherlands United Kingdom Brazil Russia Mexico • • • 0 20 Cost Index 40 60 80 100 According to KPMG, medical device manufacturing costs in Mexico are 23% lower than in the United States. 120 • Mexico is the 5th global exporter of medical instruments and devices. We are the largest exporter in the medical device industry in Latin America. The 3rd global exporter of suture needles in the world. And the 6th exporter of respiratory and mechanic therapy equipment in the world. Our country is the leading exporter of orthopedic items and gauzes and bandages in Latin America. 26 Source: Global Trade Atlas/ KPMG. Agrifood Food processing (US=100) • Mexico is the leading exporter of • Avocado. • Mango. • Guava. • Papaya. • Processed peppers. • Sweetened, powdered cocoa. • Fresh tomato. • Beer. Japón Australia EU Alemania Canadá Francia Italia Países Bajos Reino Unido Brasil México 75.0 80.0 85.0 90.0 95.0 100.0 • And the second exporter of • Watermelon. According to KPMG, processed food costs in • Limes. Mexico are 15% lower than in the United • Raspberry, blackberry and mulberry. States. Cost index 27 Source: Global Trade Atlas/ KPMG. ProMéxico’s strategies 28 What Do We Offer in ProMéxico? Brings companies together and link them to private or public organizations and academia, among others, with specific goals that are usually project-related. ProMéxico Simplifies the execution or increases the appeal of a project, whether for export, FDI or internationalization, through incentives, studies or by opening markets. Boosts activities aimed to present an overview of international business and trade. It also seeks to encourage enterprises and strategic sectors to reach international markets and promote the country's image. Assists clients to reach a specific goal, through training, personal assistance or consulting. Development of programs and projects DCC/ ACT Model/ Softlanding/ Aftercare/ Roadmaps/ Clusters articulation/ MOMA/ PROCEI 29 The ACT Model: global value added 2 LINKAGE FDI ATTRACTION Exports 1 National supplier Multinational company National supplier Multinational company FDI 3 Foreign supplier EXPORTS 30 Thank You for Your attention! Fernanda Alvarez Deputy Trade and Investment Commissioner ProMéxico Germany www.promexico.gob.mx fernanda.alvarez@promexico.gob.mx 31 Current reform projects Energy Telecommunications Education Labor Economic Competition PoliticalElectoral Criminal Procedure Source: ProMéxico with Infomation from http://reformas.gob.mx Financial Tax Appeal Law Transparency 32 Energy Reform The efficient use of our natural resources will make it possible to harness the potential of the energy sector to generate greater well-being for the population. Energy Reform is designed to attract investment and modernize the energy sector in order to achieve the following: • • • • • • • Support for the family economy. Social development. Caring for the environment and ensuring worker protection and the well-being of the population. Increased transparency in the energy sector, to provide Mexicans with detailed information. The competitiveness of the country. Increasing the availability of lower-cost energy inputs produced in the country. Energy exports will be strengthened while our growing dependence on imported energy will be reduced. The country will transition toward a dynamic energy modelbased on the principles of competition, openness, transparency, sustainability and long-term fiscal responsibility. 33