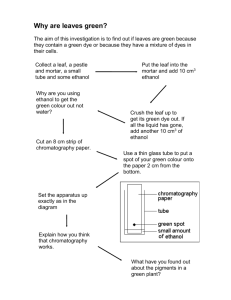
Biofuels - fieldbio
advertisement
Biofuels By: Micki & Kelly General Description Two main types: • Ethanol: • Alcohol made of oxygen, hydrogen and carbon. • Obtained from fermentation of cellulose (sugars) of plants .. Continued Biodiesel: Vegetable oils (canola, corn, sunflower, etc.) and recycled grease Non-toxic and biodegradable Obtained from transesterification, where oils react with an alcohol (ex: ethanol) mixed with a catalyst (ex: sodium hydroxide) Ethanol Is produced and consumed in U.S. more than any other countries in the world Produced from a variety of crops such as: Sugar cane bagasse miscathus sugar beet sorghum barley potatoes grain sorghum hemp kenaf cassava switchgrass potatoes sweet sunflower fruit molasses corn stover grain wheat straw cotton and more Ethanol again… Energy balance- energy used to produce fuel is comparable to energy released when burned. Corn is the most preferred source in the U.S. Fossil fuels are used to also use ethanol Ethanol is mixed in with petrol to power cars How it can be used • Ethanol: • Blended with petrol for transportation • Biodiesel: • Can replace diesel fuels or use in combination with traditional diesel fuels. • Can be used in any diesel engine Advantages Reduce Greenhouse Gas Potential to be CO2 efficient Readily Available Doesn’t require changes to current fueling ways Gives new opportunities to farmers Disadvantages Biodiversity- taking land to produce crop, loses land used by animals and wild plants Example: Asian countries replacing rainforests with oil plantations Food vs. Fuel Debate- if biofuels become profitable to farmers they might reduce the of crops they produce. Less food = higher prices and inflation (may be countered by 2nd Gen. biofuels which use waste biomass but this may also impact Disadvantages Continued.. Carbon emissions- machinery used to cultivate crops and plants emit hefty amount of emissions Water use- Enormous quantities are required to properly irrigate crops as well as manufacture fuel strains local and regional water sources Carbon Neutral? Companies try to offset carbon output by planting trees but this only helps for a little time; to be truly carbon neutral they would have to be locked in for millions of years. With biofuels there is a cycle- plants are used, which release CO2 converted into biofuel CO2 stored in plants (removed from atmosphere) SOURCES http://greenliving.lovetoknow.com/Advant ages_and_Disadvantages_of_Biofuels http://www.thegreencarwebsite.co.uk/biof uels.asp#disadvantages http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ethanol_fuel# United_States http://ezinearticles.com/?Carbon-Neutral--What-Does-It-Mean?&id=339090 Sources http://biofuels.croplife.org/index.php?pag e=biofuel-basics http://www.thegreencarwebsite.co.uk/biof uels http://biofuelguide.net