Cluster-Based Semi-Asynchronous Power
advertisement

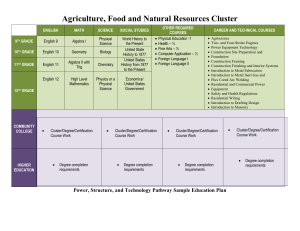
Cluster-Based Semi-Asynchronous Power-Saving Protocols for Multi-hop Ad Hoc Networks Chih-Shun Hsu Department of Information Management Nanya Institute of Technology Yu-Chee Tseng Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Chiao Tung University ICC 2005 Outline • Introduction • Cluster-Based Semi-Asynchronous Power-Saving Protocol • Routing Protocol For The Proposed Power-Saving Protocol • Simulation • Conclusion Introduction --background • Existing power saving protocol (PS) for MANET can be categorized into • Synchronous • Asynchronous • For the multi-hop MANET • Clock synchronous • Neighbor discovery • Network partition Introduction --background • Use the asynchronous PS protocol can conquer the clock synchronization problem • To find the asynchronous neighbor, hosts need to keep awake for some extra time • Broadcast cost is high Introduction --motivation and goal • Motivation • Use cluster-based semi-asynchronous PS protocol for multi-hop MANETs • Goal • To Achieve the power efficiency of the synchronous PS protocol, and could be applied to a multi-hop MANET Cluster-Based Semi-Asynchronous Power-Saving Protocols A. Channel Model B. Power Mode Scheduling Environment Cluster A Cluster B • Cluster member and cluster head is one hop distance • Cluster A->Cluster D Cluster C Cluster D Intra-cluster: synchronous Inter-cluster: asynchronous • How to detect the neighbor is an important issue Environment • Watcher • To detect its asynchronous neighbors • The members of each cluster may serve as watchers in turn Channel Model • Beacon interval • Active window • Open the receiver and listen to any packet and take proper actions • Synchronous window • Cluster header informs member to action Channel Model • Beacon window • For other PS hosts to send their beacon • MTIM (Multi-hop window) • For other hosts to send their MTIM frames to the PS host Channel Model Periodically-fully-awake interval Quorum-based protocol Power Mode Scheduling • The designing features of proposed protocol • Adaptive • Sensitive to neighbor change • Energy efficient Power Mode Scheduling • Tightly coupled clusters (location-based) Cluster header knows 1.How many cluster member 2.The location of its cluster member Cluster A Cluster B Power Mode Scheduling Periodically-fully-awake interval Cyclic quorum scheme Power Mode Scheduling • Loosely coupled clusters (SNRprobability-based) Cluster header only knows 1.How many member in the cluster P d r 2k nr d Routing Protocol For The Proposed Power-Saving Protocol Inter-cluster Routing B A C Simulation Simulation • • • • • • • Simulator : C program Hosts : 100 hosts Area size : 1000 x 1000 m Transmission range : 250 m Transmission rate : 2M bits/sec Beacon interval : 100 ms Host power : 100 J Simulation • Survival ratio • Throughput • Lifetime throughput Simulation Simulation Simulation Moving Speed= 0 m/sec Simulation Moving Speed= 20 m/sec Simulation Traffic load= 1 m/sec Simulation Traffic load= 5 m/sec Simulation Simulation Conclusion • Proposed two strategies to conquer the deficiency of asynchronous • Simulation results have shown that the proposed schemes outperform better than the asynchronous schemes