Medical Terminology
advertisement

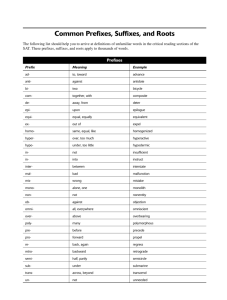
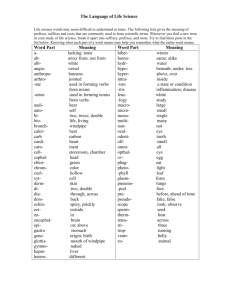
Where did medical terminology come from? Most come from Greek or Latin As medicine advanced, more modern terms have come from German, French and English Generally medical terms for determining illness or describing surgery have Greek origins. Terms for parts of the body generally have Latin roots. Sample Medical Record Mrs Gravelle is an 80 year old female with deteriorating general health. She suffers with the following chronic conditions: blepharitis, which occludes her vision at time; angiocele of coronary vessels causing a tachycardia between 120-130. frequent episodes of epistaxis. Current complaints include SOB and congestion of the sinus and chest area. Bilateral rales are present, nares are inflamed with profuse rhinorrhea. Rx is BR, antibiotics QiD, 240 cc of cl liq Q1hr. Decongestant Q4h and PRN. Pronounciation of medical terms ch is sometimes pronounced like a k Examples: chemoreceptor, chronic ps is pronounced like s Examples: psychiatry, psychology pn is pronounced with only the n sound Examples: pneumonia, pneumogastric c and g are given the soft sound of s and j respectively Examples: cell, cilia, genetics, Giardia ae and oe are pronounced ee Examples: fasciae, coelom i at the end of a word is pronounced eye (to form a plural) Examples: alveoli, glomeruli es when forming the final letters of a word, is often pronounced as a separate syllable Example: nares (nah’reez) Medical Word Parts Prefix:Beginning part of a word preceding the word root. Example: peri Root: Central part and determines the meaning of a word. Example: cardi- Suffix:Last part of the word that changes its meaning. Example: -itis Combining A root with an added vowel for easier pronunciation. Form Example: rhin/o Common Abbreviations Cath. B/P hs Spec. CPR Pc q Q2h qod, QOD NPO bid IV HyperROM po qhs Pt, pt I&O post am, AM fx lab w/c qid, QID amt. dc CA Abbreviations (continued) ss pm, PM BR, br ax c/o ht liq. OOB, oob c postop O2 stat wt cc BRP noct, noc. OPD bm, BM CBC s dx amb H2O Examples Please write the following situation out in whole words/no abbreviations: 58 y/o male c/o SOB and fever. Upon arrival to ED his VS are as follows: T 102.3 P 115 R 30 BP 102/60 and and O2 at 85%. Pt. w/hx of COPD, URI, Lung CA, CHF and DM. Orders are as follows: stat CXR, stat CBC, adm O2 at 2l/min and start IV of D5NS @ 125ml/h. Admit to med unit, DM diet, VS Q4h, BR w/BRP Examples Write the following sentences in abbreviated format: 20 milliequivalent of potassium chloride by mouth four times a day before meals. Temperature, pulse and respirations every 6hours Eight ounces of magnesium citrate every four hours until BM Complete bedrest until blood pressure less than 145 three times Admit to Coronary Care Unit, electrocardiogram immedately, blood work to be done: complete blood count, blood/urea/nitrogen; vital signs every four hours Prefixes Syllable or word placed at the beginning tells the how, why, where, when, how much, how many, direction, time. Examples: Pre means before Tachy means fast Prefixes Continued Brady means slow Hemi means half These are just a few examples. These prefixes combined with root words and suffixes make up terms that describe human anatomy, organ systems, clinical and diagnostic imaging, lab testing, together with clinical procedures, surgeries and diagnoses. Word Roots Definition: Main words or parts to which prefixes and suffixes can be added. By learning basic prefixes, suffixes, and word roots, you will frequently be able to interpret the meaning of a word even when you have never before seen the word In the example appendicitis, the word root is appendix. By adding the prefix pseudo, which means “false,” and the suffix itis, which means “inflammation,” the word becomes pseudoappendicitis. This is interpreted as a “false inflammation of the appendix.” Word Roots Continued When prefixes, suffixes, and/or word roots are joined together, vowels are frequently added. Common examples include a, e, i, ia, io, o and u. The vowels are not used if the word root or suffix begins with a vowel. Example: encephal (o) means brain. When it is combined with itis, meaning inflammation of, the vowel is not used for encephalitis. When it is combined with gram, meaning tracing or record, the vowel “o” is added for encephalogram. Word Roots Continued Example: hepat (o) means liver. When it is combined with itis, the vowel is not used for hepatitis. When it is combined with megaly, meaning enlarged, the vowel “o” is added for hepatomegaly. Other examples: Peri + Cardi/o + Ectomy = Pericardiectomy which is the surgical removal of a portion of the membrane surrounding the heart. Word Roots Continued Crani + otomy = craniotomy crani means pertaining to the skull, otomy means cutting into. Craniotomy is surgical opening into the skull Leuko + cyte = leukocyte leuko means whit, cyte means cell. Leukocyte is a white cell Para + plegia = paraplegia para means lower half of body, plegia means paralysis. Paraplegia is paralysis of the legs and lower body. Suffixes Defined as a syllable or word placed at the end of a word. The ending part of a word that modifies the meaning of the word. Examples: ology-study of, science of; Biology lysis-destruction, dissolving of; Autolysis osis-condition, state, process; Osteoporosis Pulling it All Together It is impossible to memorize all of the words of a medical dictionary that are used in health occupations. By breaking these words into parts, however, it is sometimes possible to figure out their meanings. In order to communicate effectively, health care workers must be familiar with common abbreviations and terminology. Bringing Root Words and Suffixes Together Examples: neuralgia hysterectomy mammogram anemia carditis thrombolysis colostomy cardiomalacia hepatomegaly biologist carcinoma rhinorrhea necrosis cardiomyopathy Bringing Root Words and Suffixes together Examples continued: osteopenia myospasm thrombolysis BellWork for Monday 1/27 When you see the statement “What word elements are used to form common health care terms and abbreviations?” What do you think the term elements means? How would you explain it in terms of medical use? Bell Ringer for Thursday A patient has just had a thoracotomy. Where would you find a surgical wound on this patient? Back Lower leg Neck Chest Bell Ringer for Thursday Which of the following would be a normal complaint of a marathon runner? Nephrosis Myalgia Hematuria Hydrocephalus Bell Ringer for Friday What is the most likely reason to perform a mastectomy? Breast Cancer Fracture Hepatitis Ligament Strain Bell Ringer for Tuesday-Root Word If a patient has had a cerebrovascular accident, what part of their body has been affected? Bell Ringer for Friday-Prefixes What do you think a patient with hypoglycemia is suffering from? Bell Ringer for Tuesday-Root Word If a patient has had a cerebrovascular accident, what part of their body has been affected? Bell Ringer for Thursday-Abbrev. Write following orders as abbreviations: Immediate electrocardiogram, vital signs every 2 hours, 30 cubic centimeters of cough syrup by mouth as needed or whenever necessary Questions Joe has kidney stones, he should see a: gastroenterologist, pathologist, nephrologist or neurologist What prefix means before: pre, semi, sub, tachy If a patient is turned q2h, how many times will the patient be turned during an 8hour shift? 2,4,8,16 What instrument would a doctor use to examine the urinary bladder? Gastroscope, proctoscope, otoscope or cystoscope What prefix means slow: brady, anti, bi, dys Questions Continued: What health professional would use an opthalmascope? Dentist, xray technician, a foot doctor, an eye doctor What prefix means half? Hemi, contra, tachy, contra Maria has osteoporosis. She needs to see a doctor who specializes in the study of the : skin, bones, eyes or lungs. Kate complained of upper abdominal pain immediately after eating spicy food. She most likely has: arteriosclerosis, spelnomegaly, gastritis or nephrosis Questions Continued Physicians believe that Fatima may have septicemia. What would be tested to confirm the diagnosis: sputum, blood, urine, spinal fluid Chris was hit by a baseball and needs a rhinoplasty. He was hit in the: stomach, chest, face, pelvis What root word means ear: chem, erythro, neuro, oto What suffix means removal of: algia, ectomy, ology, stasis Which of the following is symptom of pericarditis: bloody urine, chest pain, difficulty swallowing or headache