Trophic level - Willimon-PHS
advertisement

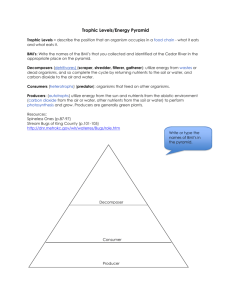
Energy Flow Through Trophic Levels Biology 12(C) Energy Flow Through Trophic Levels Learning Objectives • Analyze the flow of matter and energy through trophic levels using various models, including food chains, food webs, and ecological pyramids Energy Flow Through Trophic Levels Individual organisms within a community survive by: • Producing food • Feeding on other organisms Flow of matter and energy – energy in food is transferred from one organism to another • Organized system of energy flow through ecosystem Trophic Levels Trophic level – distinct level of feeding within ecosystem • Species at each level vary in different communities Trophic levels: • Producer • Consumer – Primary – Secondary – Tertiary (or top) • Decomposer Trophic Levels Producer – produce own food, first or lowest trophic level • Example: plants Primary consumer – firstorder consumer, eats a producer • Example: grasshopper Trophic Levels Primary consumer – first-order consumer, eats a producer • Example: grasshopper Secondary consumer – second-order consumer, eats primary consumer • Example: lizard Trophic Levels Secondary consumer – second-order consumer, eats primary consumer • Example: lizard Tertiary consumer – thirdorder consumer, eats secondary consumer • Example: snake Trophic Levels Decomposer (saprobe) – breaks down dead plant and animal matter and returns nutrients to soil – Examples: bacteria and fungi Trophic Levels Sometimes consumers are referred to by type of food they eat rather than trophic level: • Herbivore – eats only plants – Examples: deer, rabbit • Carnivore – eats only animals – Examples: lion, shark • Omnivore – eats plants and animals – Examples: bear, human • Scavenger – feed only on dead organisms – Examples: vulture, hyena Food Chains Food chain – sequence of organisms feeding on one another at a lower trophic level Producer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Food Webs Food web – network of interacting food chains • Most organisms eat more than one food type • Ecosystems usually contain more than one food chain • Complex relationships between trophic levels Food Webs Highest Trophic Level Lowest Trophic Level Food Webs • Which organisms are the producers? – Pond weed and algae • Which organisms are the secondary consumers? – Perch, minnow, and dragonfly • Which organisms do frogs eat? – Minnow and dragonfly Complex Food Web Food Webs • Which consumers feed on bivalves? – Sea ducks, tundra swans, and herbivorous ducks • Which consumers feed on zooplankton? – Small fish, bivalves Ecological Pyramids Ecological pyramid – used to visualize food chains • Pyramid of energy – amount of energy in bodies of organisms at each trophic level • Pyramid of numbers – number of organisms feeding at each trophic level • Pyramid of biomass – total mass of dry, organic matter at each trophic level Pyramid of Energy Energy decreases up the pyramid: • Grass captures sun’s energy • Rabbit obtains 10% of stored energy in grass • Snake obtains 10% of stored energy in rabbit • Eagle receives 10% of stored energy snake Pyramid of Energy 1 kcal 10 kcal 100 kcal 1000 kcal Pyramid of Numbers Numbers decrease up the pyramid: • More individual organisms at lower trophic levels • Fewer individuals at higher trophic levels Pyramid of Numbers Pyramid of Biomass Biomass decreases up the pyramid: • Greatest biomass at producer level • Least biomass at tertiary consumer level Pyramid of Biomass Tertiary Consumer (1.5 grams/square meter) Secondary Consumer (11 grams/square meter) Decomposer 5 grams/square meter Primary Consumer (37 grams/square meter) Producers 807 grams/square meter Pyramid of Biomass Planktonic ecosystem dominated by small, floating organisms • Zooplankton consume phytoplankton rapidly • Producers population can never become large • Phytoplankton reproduce rapidly Inverted Pyramid of Biomass of Aquatic Ecosystem Zooplankton 21 grams/square meter Phytoplankton 4 grams/square meter Energy Flow Through Trophic Levels • Matter of one organism passed to another when eaten – Cycles through ecosystem • Energy stored in organism passed to another when eaten – Enters from sun – Flows through trophic levels – Lost as work and energy Energy Flow Through Trophic Levels Learning Objectives • Analyze the flow of matter and energy through trophic levels using various models, including food chains, food webs, and ecological pyramids