Biology 4th MP Quarterly Exam Study Guide
advertisement

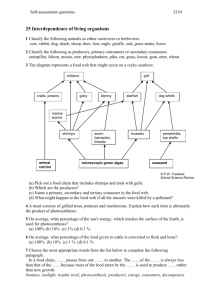
Biology 4th MP Quarterly Exam Study Guide • Genetic drift: change in allele frequency due to chance • Bottleneck Effect: genetic drift after a bottleneck event (when an event drastically reduces population size) – Example: Flood waters move through a forest and wipe out any mice that were not able to climb up a tree • Founder Effect: genetic drift that occurs after the start of a new population (when a few individuals start a new population) – Example: A bird eats two out of five types of fruit in an area and flies to another area and drops the seeds there – the two types of fruit begin a new population in that area • Gene flow: transfer of genetic information from one population to another – Makes nearby populations similar • Natural selection: organisms that have favorable traits that are well-suited to the environment in which they live will be more likely to thrive, reproduce, and pass their traits to future generations than organisms without favorable traits • INCREASES species diversity (different beak types of finches due to different food sources) -Environment can cause an increase in the number of individuals with beneficial phenotypes and a decrease of individuals without beneficial phenotypes. -Black pocket mice increased due to phenotype helping them blend in with new dark environment from black hardened lava rock -Mutations -Combination of gametes formed by meiosis during sexual reproduction • Sexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction produces genetically identical offspring with NO variation. • When two populations of a species can no longer successfully mate • Leads to speciation -Behavioral isolation: differences in courtship or mating behaviors -Geographic isolation: physical barriers that divide a population into two or more groups -Temporal isolation: timing prevents reproduction between populations • Disruptive selection • Directional selection • Stabilizing selection • Compare the amino acid sequences of the proteins – species with more differences are less closely related • Embryology compares similarities in developmental stages of different organisms to provide evidence that they share a common ancestor. Structures that had a function in an ancestor but don’t in modern day organisms. Ex.: Wings on flightless birds show they evolved from ancestors that flew. They’ve since evolved adaptations to travel efficiently in other ways. • Homologous structures are structures in different organisms that share similar structures but perform different functions provides evidence of a common ancestor. Ex.: forelimbs of humans and cats. 1. Organism: Alligator 2. Population: 5 Alligators 3. Community: Alligators, Birds, Grass, Frogs, Trees 4. Ecosystem: Alligators, Birds, Grass, Frogs, Trees, Soil, Water, Sunlight 5. Biome: Temperate Deciduous Forest Decomposers break down dead plants and animals. This process returns nitrogen to the soil so that bacteria can fix it for plants. They are related through photosynthesis and respiration. Carbon is taken in by plants through photosynthesis. Oxygen is given off from photosynthesis and used for respiration. Similarity: A food web contains multiple related food chains. (Both show feeding relationships) Difference: Food chains show one feeding relationship, food webs show multiple feeding relationships. A. Mutualism: Both organisms benefit from the relationship. Ex: bee and flower B. Commensalism: One organism benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed. Ex: clownfish and sea anemone C. Parasitism: One organism benefits from the relationship while the other is harmed. Ex: tick and human • BIOTIC: Living (animals, plants, etc) • ABIOTIC: Non-Living (water, light, soil,) • • • • • • • Grass would increase Lizards would decrease Hawks would decrease Rabbits and mice would increase Snakes would increase Mice would decrease Grass would decrease Competition: 2 male lions fight for a female, or for food. 2 species of plants fight for the same sunlight and soil. Predation: A fox hunts, kills, and eats a rabbit. • Approximately on Day 22 • Snakes would DECREASE because they have nothing to eat. Locusts would INCREASE because nothing is eating them. • Reduce CO2 emissions to cut back on global warming, use renewable energy like solar energy to cut back on burning fossil fuels like oil and gas. Recycle to cut down on waste,etc. • They have no natural predators so they can easily take over a new area. They take space and food away from the native species that lives there.