Methods and Tools
advertisement

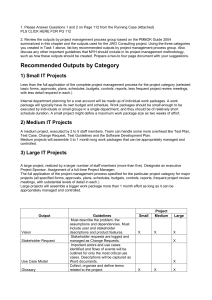
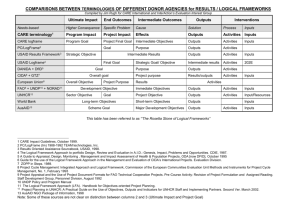
Objective-Oriented Project Planning (ZOPP) Dr Anthony Wemakor Dept of Community Nutrition SMHS UDS Project and Programme • A project can be described as the process of using inputs to carry out activities in order to achieve previously defined objectives. • A programme is a series of projects in a sector, sub-sector or region that are linked together by a clearly defined concept. Project Cycle Management Evaluation (See) Plan (Idea) PDM Implementation (Do) 3 Why Project Planning Objective-oriented – not activity-driven Consistency Logical - Logically sets objectives and actions Participatory Transparency and accountability Monitoring and evaluation Framework for assessing relevance, feasibility and sustainability Describes external factors that influence the project’s success: assumptions and risks 4 Project planning instruments • Methods to facilitate the planning and implementation of projects and programmes • Late 1960s Logical Framework Approach (LFA) (USAID) • Early 1980s Objective-Oriented Project Planning (ZOPP) (GTZ) European countries adapted the ZOPP 5 Objective-oriented project planning (ZOPP) Goal-oriented project planning “Zeroing on People and Processes” ZOPP ZOPP is a systematic structure for identification, planning, and management of projects Applied through iterative workshops with project authorities, beneficiaries and stakeholders Utilizes problem analysis and stakeholder analysis to create a project planning matrix similar to logical project framework Methods and Tools Zopp Workshops Lasts from 1 day to 2 weeks (avg. 1 week) Participants selected to represent all interest groups Basic premise: main interest groups must be represented from all levels Exercise requires a facilitator with a high degree of experience and skill ZOPP ZOPP has 2 phases: A. Analysis Analysis phase comprises 5 sub-types 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Stakeholder analysis Problem analysis Objective analysis Alternative analysis Assumptions B. Project planning A. Analysis Participant analysis: (interests, motives, attitudes and implications for project) Problem analysis: major problems grouped into a problem-tree with cause and effect and identification of the core problem Objectives analysis: a restatement of the problems into realistically achievable goals; Alternatives analysis: assessment of alternative objectives according to resources, feasibility, cost-benefit ratio, social risks, sustainability and other factors as decided by group. Prepared on charts. Assumptions: These conditions are necessary for successful transformation of problems into secured objectives. 1. Participant/stakeholder Any group within or outside a project that has a stake in the project’s activities and/or outcomes. Examples Government Local Authorities Vulnerable groups Employers Workers NGOs 1. Participant/stakeholder Analysis Purpose: To identify those groups who, directly or indirectly, will affect or be affected by a project. To determine, through consultation, the issues, concerns and information needs of different stakeholders To estimate the probable impact which various stakeholders will have on the project To identify measures to enhance stakeholder support for the sustainable development objectives of the project. Methods and Tools Importance of Stakeholder Analysis Stakeholder Analysis promotes the three necessary conditions for the effective implementation of a project. 1. Awareness/Commitment: that stakeholders understand and believe in the objectives and implementation strategy of the project. 2. Capability: that stakeholders believe they can cope with and benefit from the changes which the project is intended to bring 3. Inclusion: that stakeholders feel they are valued, consulted and part of the change process which the project represents Step 3 Identify the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats of the Stakeholders to the Project (SWOT) What are the strengths and weaknesses of the stakeholders? As a consequence, what are the opportunities and threats of the external environment? Step 4 Methods and Tools Identify the main individuals/groups of Stakeholders who need special attention and propose specific measures in a summary table: Stakeholder Stakeholder Interest(s) in the Project Assessment of Impact Potential Strategies for Obtaining Support or Reducing Obstacles 2. Problem Analysis Purpose: To identify major problems and their main causal relationships. Output: ‘Problem tree’: a graphical arrangement of problems differentiated according to ‘causes’ and ‘effects’ Methods and Tools Core Problem Approach 1. Identify a “core” or central problem 2. List all the problems related to or stemming from the core problem 3. Determine which related problems are causes and which are effects of the core problem 4. Arrange the problems in a cause-effect heirarchy around the core problem Example: Problem Tree of Infant Malnutrition, Iquitos, Peru, 2005 Methods and Tools Problem Tree Analysis Relies on: • Group-based interaction e.g. Workshop format • Participation of key stakeholders • Process facilitation • Achieving consensus on problems, causes and effects 3. Objective analysis The Problem Tree provides the basis for the objective analysis: a) the identification of specific project objectives – by converting problems or constraints into specific objectives b) the definition of project activities and outputs – by substituting cause-effect relationships with means-end relationships B. Project Planning Methods and Tools • The output of the Analysis Phase of the ZOPP process feeds into the planning phase. • The output of the project planning phase is the Project Planning Matrix (PPM). • The PPM is a 4 x 4 matrix. • The PPM is a one-page summary of: why the project is carried out, what the project is expected to achieve, how the project is going to achieve these results, factors crucial for the success of the project, how the success of the project can be measured, which data are needed to assess project success, what the project will cost. The Project Planning Matrix Summary of objectives/ activities Objectively Verifiable Indicators Means/Sources of Verification Important Assumptions Overall Goal (OG) Indicators that the OG has been achieved Document/database available to prove that the OG has been achieved For sustaining objectives in the long term Project Purpose (PP) Indicators proving that the PP has been achieved Document/database available to prove that the PP has been achieved For achieving the overall goal Results/Outputs Indicators proving that the results/outputs have been achieved Document/database available to prove that the results/outputs have been achieved For achieving the project purpose Activities Specification of inputs/costs of each activity Records of cost involved e.g. voucher, personnel emolument For achieving the results/outputs Summary of objectives/activities • Overall Goal to which the contributes • Project Purpose: which project purpose needs to be achieved for a significant contribution to be made to the project goal? • Results/Outputs: which results/outputs will have to be obtained in order to achieve anticipated impact? • Activities: which activities will the project have to carry out in order for the results/outputs to be obtained? Important Assumptions • For sustaining objectives in the long term: Which external factors will have to occur in order to assure sustained continuity of the achieved contribution to the OG in the longer term? • For achieving the overall goal: Which external factors will have to occur for the anticipated contribution to the overall goal to actually take place? • For achieving the project purpose? Which important assumptions in relation to the results/outputs 1-..., that cannot be influenced by the project or has been consciously defined as external factors, that must occur for the project purpose to be achieved? • For achieving the results/outputs? Which important assumptions in relation to the activities 1-..., that cannot be influenced by the project or have been consciously defined as external factors, that must occur in order for the results/outputs to be obtained? Methods and Tools Stages in the ZOPP Process Pre-ZOPP: in-house exercise by agencies in preparation for a project. Appraisal ZOPP: in-house appraisal for preparing Project TORs Partner ZOPP: in-country; presentation and discussion of previous phase conclusions and recommendations with staff of project country Take-off ZOPP: in-country; preparation of the plan of operations with personnel responsible for project execution and counterpart authorities. Re-planning ZOPP: prepared in-country; adjustments during project implementation. Methods and Tools • • • • ZOPP’s Iterative Workshops ZOPP’s Iterative Process ZOPP is not a oneshot exercise; Each plannng phase has a specific goal Each goal is the subject of a workshop Each workshop comprised of different stakeholders • Participants analyse key issues throughout the project cycle. • No set formula for successful workshop. • All need to create common language and understand one another divergent views Methods and Tools Conclusion Conclusion Collaboration is not "automatically" part of the ZOPP process. The project team, borrower/donor, and stakeholders must commit to adopting a participatory stance for the overall project; otherwise, the ZOPP process is merely an organizing tool. Logical Framework Analysis Methods and Tools 3. Logical Framework Analysis Q:What is Logical Framework Analysis? A: An analytical tool to assist project specialists and stakeholders in conceptualising: the objectives of a project; the means whereby these objectives will be achieved how progress towards achieving objectives will be measured and, the underlying assumptions and risks which will be faced Contents of the LogFrame Matrix Objectives (Narrative Summary) Goal: (Development Objective) Purpose: (Immediate Objectives) Outputs: Indicate each of the outputs that are to be produced by the project in order to achieve project purpose Activities: Indicate each of the activities that must be undertaken in order to accomplish the outputs. Verifiable Indicators Means of Verification Important Assumptions What are the quantitative ways of measuring, or qualitative ways of judging, whether these broad objectives are being achieved? (estimated time) What sources of information exists, or can be provided cost-effectively? What external factors are necessary for sustaining objectives in the long run? What are the quantitative measures or qualitative evidence by which achievement and distribution of impacts and benefits can be judged (estimated time) What sources of information exists or can be provided cost-effectively? Does provision for collection need to be made under inputsoutputs? (Purpose to Goal): What conditions external to the project are necessary if achievements of the project’s purpose is to contribute to reaching the project goal? What sources of information? (Output of Purpose): What are the factors not within the control of the project which, if not present, are liable to restrict progress from outputs to achievements of project purpose? What are sources of information? (Activity to Output): 1) What external factors must be realised to obtain planned outputs on schedule? 2) What kind of decisions or actions outside the control of the project are necessary for inception of the project? What kind and quantity of outputs, and by when will they be produced? (quantity, quality, time) VI’s should be included against all activities. This is essential for projects reporting and monitoring against the Logical Framework.