Analisis Data 1
advertisement

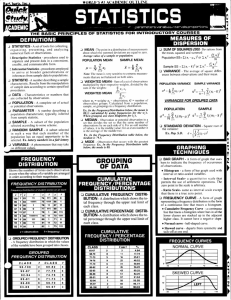
ANALISIS DATA SMT 310 retnosubekti@uny.ac.id Motivasi Memahami analisis eksplorasi dan konfirmasi Landasan statistika deskriptif dan inferensi Bersinergi dengan komputasi statistik untuk mengupgrade kemampuan analisis data Deskripsi Penyusunan dan rangkuman data numerik Penyajian data univariat Transformasi data Sampel acak Statistika konfirmasi Analisis variansi Hubungan antara dua variabel Analisis data kategorik Referensi Erickson, Bonnie H & Nosanchuk. 1987. Memahami Data : Statistika untuk Ilmu Sosial. (terjemahan RK. Sembiring & Manase Malo). Jakarta: LP3ES Griffiths D., Stirling W.D, Weldon K.L . 1998. Understanding Data : Principles and Practice of Statistics. Brisbane : John Willey & Sons Kontrak Penilaian Bobot : Tugas Kuis Usip Uas : 20% : 15% : 25% : 40% REVIEW STATISTIKA ? STATISTIK ? STATISTIKA DESKRIPTIF ? Statistika inferensi Populasi Sampel Parameter Statistik Data Nilai ujian metode stastistik 20 orang mahasiswa adalah : 91 50 73 74 55 86 70 43 47 80 40 85 64 61 58 95 52 67 83 92 Misalkan diketahui nilai ujian komputasi statistika 50 mahasiswa 44,7 59,8 67,1 57,1 58,2 69,5 60,6 44,2 76 51,2 48,4 63,9 67,8 56,2 60 68,2 48,5 46 72,6 52 42,5 57,2 70,2 57 62,2 70,3 50 76,8 74 65,1 49,1 64,7 74,6 63,6 63 72,2 75,3 75 55,4 67,7 43,1 76,5 68,7 59,9 63,5 72,6 77 73,5 56,3 77,3 Banyaknya penjualan HP di suatu toko : Merek HP Penjualan Nokia 56 SE 45 Samsung 32 LG 22 Lain 45 Skala pengukuran Nominal : Ordinal : Interval : Rasio : Contoh: Nominal: jenis pekerjaan, warna Ordinal: kepangkatan, tingkat pendidikan Interval: tahun kalender (Masehi, Hijriyah), temperatur (Celcius, Fahrenheit) Rasio: berat, panjang, isi Statistika deskriptif Metode atau cara-cara yang digunakan untuk meringkas dan menyajikan data dalam bentuk tabel, grafik atau ringkasan numerik data. Grafik Stem-and-leaf Untuk menunjukkan bentuk distribusi data Data berupa angka dengan minimal dua digit Contoh (Data penghasilan buruh): 439 511555689 602334445556777889 7122344558 8349 92 Stem= 10, Leaf = 1 Intro… Why study statistics? Make decision without complete informations Understanding population, sample Parameter, statistic Descriptive and inferential statistics glossary A population is the collection of all items of interest or under investigation N represents the population size A sample is an observed subset of the population n represents the sample size A parameter is a specific characteristic of a population Mean, Variance, Standard Deviation, Proportion, etc. A statistic is a specific characteristic of a sample Mean, Variance, Standard Deviation, Proportion, etc. Population vs. Sample Population a b Sample cd b ef gh i jk l m n gi o p q rs t u v w x y z c o n r u y Values calculated using population data are called parameters Values computed from sample data are called statistics Examples of Populations Incomes of all families living in yogyakarta All women with pregnancy problem. Grade point averages of all the students in your university … Random sampling Simple random sampling is a procedure in which each member of the population is chosen strictly by chance, each member of the population is equally likely to be chosen, and every possible sample of n objects is equally likely to be chosen The resulting sample is called a random sample Descriptive and Inferential Statistics Two branches of statistics: Descriptive statistics Collecting, summarizing, and processing data to transform data into information Inferential statistics Provide the bases for predictions, forecasts, and estimates that are used to transform information into knowledge and decision Descriptive Statistics Collect data e.g., Survey Present data e.g., Tables and graphs Summarize data e.g., Sample mean = X n i Inferential Statistics Estimation e.g., Estimate the population mean weight using the sample mean weight Hypothesis testing e.g., Test the claim that the population mean weight is 120 pounds Inference is the process of drawing conclusions or making decisions about a population based on sample results The Decision Making Process Decision Knowledge Experience, Theory, Literature, Inferential Statistics, Computers Information Descriptive Statistics, Probability, Computers Begin Here: Identify the Problem Data