Creating Static Electricity
advertisement

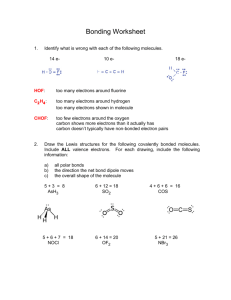
Creating Static Electricity Electrical Insulators • Conductivity is the ability of materials to allow electrons to move freely in them • Materials that hold onto their electrons and do not allow them to move easily are called electrical insulators • ex) Dry wood, glass, and plastic are all examples of electrical insulators • An insulator can hold a static charge because static charges remain nearly fixed in place. Electrical Conductors • An electrical conductor is a solid, liquid, or gas that allows the movement of electrons • ex) silver, aluminum, iron, moist skin, salt water, water vapor • A conductor can’t hold a static charge because it allows the charges to flow through it • • Conductors and Insulators Since electrons cannot move through an insulator they can be very useful to us to protect us from shocks A simple electric kettle would be very hazardous if the two wires that supplied electricity to it did not have a rubber coating over them Why do we get more shocks in the winter than in summer? • This is because in winter the air is far dryer than in the summer and dry air is an insulator and therefore does not take any of the charges our body might pick up during the day. So when we go and touch another conductor (a door handle) ZAP we receive a shock • • Charging by Friction When two objects made of different materials rub together, electrons can be transferred from one object to the other This is because different atoms (which make up the objects) have a different ability to attract electrons and a different ability to hold onto their own electrons. Electrostatic Series acetate glass wool fur, hair calcium, magnesium, lead silk aluminum, zinc cotton paraffin wax ebonite polyethelene (plastic) carbon, copper, nickel rubber sulphur platinum, gold Weak hold on electrons More likely to gain electrons Strong hold on electrons Electrostatic Series • To determine what charges will form, compare the location on the table of the two objects. The object that is higher on the table will lose electrons and become positive • ex) when cotton and human hair rub what charge will form on each object? Cotton is lower on the list than hair • Cotton will hold its electrons better. Hair will lose its electrons to the cotton and become positive. Cotton will become negative. Electrostatic Series • Consider the following pairs are rubbed together. Give charge on each: • Plastic ________ Silk _______ • Fur __________ Rubber • glass ____ silk ______ • Vinyl ______ Plastic ______ • Ebonite _________ wool _____________ • • • Charging by Induction Charging by induction means charging without direct contact When a negative charge approaches a neutral object, the electrons inside the neutral object are repelled. This causes an induced positive charge on the side closest to the negative object and an induced negative charge on the opposite side. When a positive charge approaches a neutral object, the electrons inside the neutral object are attracted. This causes an induced negative charge on the side closest to the positive object and induced positive charge on the opposite side. Charging by Induction Induction is used in photocopiers, lightning, dust filters and electrostatic painting. Charging by Contact • Negative charges (or electrons) will always move from where there are the greatest number to where there are the fewest • If there is a big enough difference and the two objects are close enough together, this jumping may cause a spark • When do we see the greatest spark - when the air is dry or when there is high humidity ? When the air is dry because dry air is an insulator Charging by Contact • • When transferring by contact, negative charges move from one object to the object being touched Remember! Only the negative charges move! Charging by Contact Sparks produced by a charge transferred by contact can be dangerous Transferring a charge by friction is difficult to avoid; when charging by contact occurs, one object is already electrically charged The other object may or may not be charged, the important factor is that there is a DIFFERENCE in the charge on the two objects Grounding • The earth is large and absorbs large numbers of electrons, ground wire is connected to earth to "dilute" the charge by carrying it to the earth Static Electricity can be Dangerous • With any phenomena, one of the first things people think of is whether or not it is dangerous to them. Static electricity can be dangerous in certain situations. Lightning • Lightning during a thunderstorm is very high voltage, high power static electricity. Getting struck by lightning is extremely dangerous and kills several people each year. Therefore, you should be careful about standing in an open field and near metal poles or trees during a thunderstorm, in order to avoid getting zapped. • The record for being struck by lightning and not being killed is held by a U.S. Forest Ranger. He has been struck by lightning 9 different times! Dangerous Static Electricity Sparks and computers • • When you walk across a rug and then touch someone, you can often cause a spark to fly. This can be irritating, especially if you touch someone on the nose, but it is not necessarily dangerous On the other hand, if you happen to touch a computer circuit board, the spark — even a very small one — can severely damage the circuitry. The sudden surge of electrons can easily fry microchips in the computer. That is why technicians who work on computers are very careful to avoid build-up of static electricity Dangerous Static Electricity Explosions • • When a gasoline truck fills the underground tanks at a filling station, they are very careful about any buildup of static electricity caused by the flowing liquid into the tank. A static electrical spark could cause an explosion of the gasoline. Special precautions are made through the use of grounding cables to prevent any sparks Another area of concern about static electricity is in grain elevators and storage bins. When they pour the wheat or grain into the bin, the air gets filled with a lot of very fine dust. Any spark caused by static electricity can cause the dust to ignite and explode.