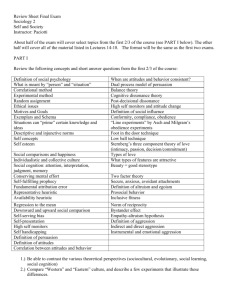
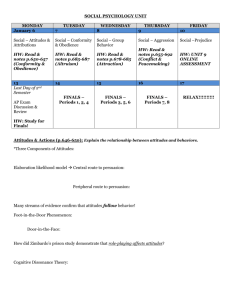
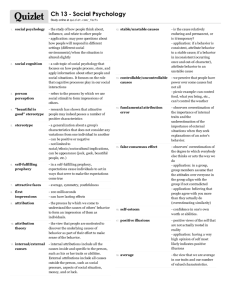
Social Psychology PRESENTATION
advertisement

Social Psychology Chapter 13 AP Psychology Alice F. Short Hilliard Davidson High School Chapter Preview • • • • • • Social Cognition Social Behavior Social Influence Intergroup Relations Close Relationships Social Psychology and Health and Wellness Social Psychology • social psychology - the study of how people think about, influence, and relate to other people • social cognitions • social influences • social relations Social Cognition • How do people select, interpret, remember, and use social information? • Person Perception – physical attractiveness • stereotype – a generalization about a group’s characteristics that does not consider any variations from one individual to another – natural = cognitive processing limitations • “Beautiful is good” stereotype • self-fulfilling prophecy – expectations cause individuals to act in ways that serve to make the expectations come true – teacher expectations of “late bloomers” expectations met • composite faces, symmetry, and youthfulness – first impressions • 100 milliseconds form first impression • attribution – the process by which we come to understand the cause of others’ behavior and form an impression of them as individuals Social Cognition: Attribution Theory • attributions - explanations for why people behave the way they do • attribution theory - attempt to discover underlying causes of behavior as part of their effort to make sense of the behavior – internal/external causes • internal: traits and abilities • external: social pressure, aspects of situation – stable/unstable causes • hostile or bad mood? – controllable/uncontrollable causes • should we hold it against you? Social Cognition: Attribution • attribution errors – actor – person who produces the behavior – observer – person who offers a causal explanation for actor’s behavior – observers often explain actors’ behaviors incorrectly – fundamental attribution error • overestimate the importance of internal traits • underestimate the importance of external causes • Zimbardo on Abu Ghraib prison – TED TALKS – actors often explain own behavior in terms of external causes Fundamental Attribution Error Social Cognition • heuristics - cognitive shortcuts that speed decision making – stereotypes = type of heuristic – false consensus effect • overestimating the degree to which everyone else thinks or acts the way we do • use our outlook to predict that of others A SHORT Time to Ponder • How do politicians use the false consensus effect to their advantage? The Self as a Social Object • self-esteem – the degree to which we have positive or negative feelings about ourselves – positive illusions – views of ourselves that are not necessarily rooted in reality – self-serving bias – tendency to take credit for success and deny responsibility for failure • internal attributions • external attributions – self-objectification – tendency to see oneself primarily as an object in the eyes of others • DOCUMENTARY: MISSRepresentation A SHORT Time to Ponder • What’s so wrong with average? (By definition, 50 percent of people will always be below average.) • In what ways do you objectify yourself? • Would you perform differently depending on the way you were dressed? Social Cognition: The Self as Object • stereotype threat - a self-fulfilling fear about being judged on the basis of a negative stereotype about our group – living “down” to expectations • African American males = work academically by checking box • White males = worse at sports when reminded • Asian women = better at math by checking box “Asian” box, worse by checking “female” box • social comparison - process by which we evaluate our thoughts, feelings, behaviors, and abilities in relation to other people – social comparison theory – when no objective means are available to evaluate our opinions and abilities, we compare ourselves with others A SHORT Time to Ponder • What stereotype should you think about for yourself before starting the AP Psychology test, or any academic test for that matter? Attitudes • attitudes - beliefs about people, places, and ideas • Can attitudes predict behavior? – when attitudes are strong – when attitudes are rehearsed – when person has vested interest • Can behavior predict attitudes? – cognitive dissonance – an individuals psychological discomfort (dissonance) caused by two inconsistent thoughts • uneasy when behavior ≠beliefs • effort justification – type of dissonance reduction, means rationalizing the amount of effort we put into something – low money – hazing – self perception theory – Daryl Bem’s (1967) theory on how behaviors influence attitudes, stating that individuals make inferences about their attitudes by perceiving their behavior • I do something; therefore, I must like it. Cognitive Dissonance Theory • Discomfort caused by two dissonant thoughts – thoughts of ones attitude v. ones behavior • Dissonance reduced by – changing behaviors to match attitude – changing attitudes to match behavior Self-Perception Theory • self-perception theory - individuals make inferences about their own attitudes by perceiving their own behavior, especially if their attitudes are unclear • cognitive dissonance and self-perception theory explain the connection between attitudes and behavior Attitudes and Behavior Persuasion • 2 Essential Questions: – What makes an individual decide to give up an original attitude and adopt a new one? – What makes a person decide to act on an attitude that he or she has not acted on before Persuasion 1. The Communicator (credibility) – trustworthiness, expertise, attractiveness, likeability, similarity 2. Medium (television versus print) – but should it? 3. The Target (age, attitude, strength) 4. Message (rational versus emotional strategy) – elaboration likelihood model: • central route – sound, logical argument – effective: ability and motivation to pay attention to the facts • peripheral route – non-message factors (credibility, attractiveness, emotional appeals) – effective: people are not paying attention; don’t want to expend mental effort Persuasion • Successful Persuasion – foot-in-the-door technique • small request big demand – door-in-the-face technique • biggest demand smaller “concessionary demand” – reciprocity and obligation – SHORT DISCUSSION: How do you use either of these techniques on your parents? • Resisting Persuasion – inoculation – William McGuire • introducing a weak version of a persuasive message and allowing them time to argue against it (like a vaccine) • inoculation: Credit card companies prey on college students! Social Behavior • we behave in social ways toward the people around us • two extremes of human social activity… – altruism (prosocial behavior) – aggression Prosocial Behavior • altruism (prosocial behavior) - an unselfish interest in helping someone else • • • • random acts of kindness debate: is it possible to be completely altruistic? Ayn Rand: opposed to altruism… why? egoism – giving to another person to ensure reciprocity; to gain self-esteem; to present one-self as powerful, competent, or caring; or to avoid censure from ones self and others for failing to live up to society’s expectations • reciprocity Prosocial Behavior • explanations of altruism – evolutionary – promoting survival of family’s genes • research: humans not necessarily self-centered • animals: demonstrate altruism – psychological factors • mood – happy people = more helpful – feelings of elevation (video: photo shoot) • empathy – a person’s feelings of oneness with the emotional state of another – sociocultural factors • market economies – more prosocial behavior (trust = requirement) • investment in established religion – emphasis on golden rule • gender – women: more helpful in nurturing situations – men: more helpful in dangerous situations and when feel competent to help Prosocial Behavior • The Bystander Effect – Darley and Latané (1968) – individuals are less likely to help in an emergency when others are present then when the observer is alone – diffusion of responsibility • Media Influence – listening to music with prosocial lyrics increases kindness – TV shows with positive content increase prosocial behavior – Lemmings video game prosocial behavior A SHORT Time to Ponder • Do you believe that human nature is more selfish or altruistic? • “Happy people just don’t kill their husbands, they just don’t.” – Elle Woods, Legally Blonde • Do your favorite TV shows promote prosocial behavior? • Should TV be required to promote prosocial behavior? • Can you think of a time when altruism is linked to aggression? Aggression • aggression – social behavior whose objective is to harm someone, either physically or verbally • biological influences – evolutionary views – more likely to survive – genetic basis • breeding docile animals and vicious animals • physical aggression – more linked to genes • social aggression – more linked to environmental – neurobiological factors • • • • • • limbic system - active frontal lobes of brain – smaller / less functioning low levels of serotonin high levels of testosterone results = less consistent with humans than animals operational definitions of aggression external validity criticism Aggression • psychological influences – aversive circumstances triggers aggression • frustration – the blocking of an individual’s attempts to reach a goal triggers aggression • frustration-aggression hypothesis – frustration always leads to aggression • weather, physical pain, crowding triggers aggression – cognitive determinants • priming (seeing a weapon prime hostile thoughts) • perception of unfairness triggers aggression – observational learning • Bobo doll study, Bandura, Ch. 6 • violence on TV • violence at home Aggression • sociocultural influences – cultural variations • inequality (gap b/w the rich and poor) – U.S. higher homicide rate compared to other developed countries… greater inequality (YouTube clip) • culture of honor – honor killings – the South Aggression – media violence • television – increases aggression – changes attitudes towards violence – violence in home = more significant • violent pornography – small effect on male sexual aggression – increases acceptance of violence toward women – rape myth – the false belief that women desire coercive sex • violent video games – “rational though is suspended and highly arousing aggressive scripts are increasingly likely to be learned” – CORRELATIONAL RESEARCH: » more aggressive » less sensitive to real-life violence » more likely to engage in delinquent acts » lower grades Critical Controversy: A SHORT Time to Ponder • Do you or people you know play violent video games? If so, what impact, if any, do you think this activity has on your or their thoughts and feelings? • Would you allow your child to play violent video games? Why or why not? • What do you think policymakers should do with regard to the controversy over the effects of playing video games? Aggression • reducing aggression – decrease rewards – lessen exposure – encourage empathy – monitor adolescents’ activity Social Influence: Conformity • conformity – a change in a person’s behavior to coincide more closely with a group standard – can lead to enhanced cooperation among group members • Asch’s Experiment (1951) – factors that contribute to conformity • informational social influence – the influence other people have on us because we want to be right • normative social influence – the influence others have on us because we want them to like us – volunteer participant conformed to incorrect answers 35% of time – VIDEO Clip: – demonstrates power of conformity (breaking social norms) • cognitive neuroscience – fMRI images - when women found others disagreed, they responded as mistakes Social Influence: Conformity • Which line is the same length? • CHALLENGE: As a group, try to convince someone of something obviously incorrect… Social Influence: Obedience • obedience – behavior the complies with the explicit demands of the individual in authority – obedient: authority figure demands we do • Stanley Milgram’s Experiments (1965, 1974) – factors that contribute to disobedience • disobedient models • authority figure not legitimate or not close by • victim made to seem more human – ethical concerns regarding Milgram – deception – VIDEO: TED Talks (may leave the room – very graphic) Social Influence: Obedience • How far do you think you would go? Group Influence • Deindividuation – erosion of personal identity and responsibility – anonymity – example: KKK • group, darkness, wearing white • Social Contagion – imitative behavior – spread of behavior, emotions, and ideas – examples: social fads, the popularity of dog breeds, the spread of unhealthy behaviors (smoking and drinking in adolescents), symptoms of eating disorders among young women – experiment: go someplace quiet and start coughing – observations: misbehaviors in school (talking, packing up early, etc.) • Group Performance – social facilitation: arousal with well-learned tasks – social loafing: reduced accountability Group Decision Making • Risky Shift – group decisions are riskier than average individual decisions • Group Polarization – discussion strengthens the individual’s position Group Decision Making: Groupthink • groupthink – group harmony valued over “right” or “correct” – impaired decision making and avoidance of realistic appraisal – symptoms of groupthink • • • • • overestimating the power and morality of one’s group close-mindedness lack of willingness to hear all sides of an argument pressure for uniformity “get with the program” dissent meets with very strong disapproval – avoiding groupthink • • • • • avoid isolation allow the airing of all sides of an argument have an impartial leader include outside experts in the debate encourage group members who are strongly identified with the group to speak out in defense Group Decision Making: Majority-Minority Influence • Majority-Minority Influence – majority: normative and informational pressure • informational – greater opportunity to share • normative – set group norms those who do not go along may be ignored or given the boot – minority: informational pressure • • • • cannot win with normative pressure must use informational pressure consistency and confidence = key must win over majority members A SHORT Challenge • Can you think of a minority position that you support? – Create a cogent argument in support. – Then consistently and confidently defend it. Intergroup Relations • Group Identity – us versus them • Social Identity – define ourselves in terms of group membership – assumes commonalities Intergroup Relations • Henry Tajfel’s Social Identity Theory – our social identities are a crucial part of our self-image and a valuable source of positive feelings about ourselves – in-groups versus out-groups • in-group – a group that has special value in comparison with other groups • out-group • focus more on the differences between the groups than on their similarities • Tajfel’s Reseach (1978) – dot estimation (over or under) to create arbitrary groups – asked to award money to other participants • awarded money to members of their “own group” more – conclusion: we favor the members of in-groups based on trivial differences... • Ethnocentrism – favoring one’s own group over other groups – out-groups not just different, but worse/inferior/less than A SHORT Time to Ponder: Tajfel’s Reseach (1978) • How has this concept been used around the world and through history to oppress people? – Rwanda – Slavery in the United States Social Identity Prejudice • an unjustified negative attitude toward a group and its members • explicit versus implicit racism – explicit racism – a persons conscious and openly shared attitude, which might be measured using a questionaire – implicit racism – attitudes that exist on a deeper, hidden level… must be measure with a method that does not require awareness • Implicit Associations Test (IAT) – a computerized survey that assesses the ease with which a person can associate a Black or White person with good things • THE DOLL TEST: VIDEO!! If you find it—the original vide, I will drop the lowest grade from every person in your class period for the fourth quarter AND I will buy your class donuts and coffee from the place of your choice • explanations for prejudice – competition between groups – cultural learning • Dream Deferred, post cards, and kids learning racism… – motivation to enhance self-esteem – limitations in cognitive processes Prejudice • “ethnic cleansing” • U.S. racial prejudice – “black names” video – Freakonomics video clip • white names – 50% more likely to get an interview • Are you racist? – 88% of Americans say no Stereotyping and Prejudice • stereotype - a generalization about a group • discrimination - unjustified negative or harmful action – Civil Rights Act of 1964 (revised 1991) • unlawful to deny someone employment on the basis of gender or ethnicity – video: actresses / typecasting Stereotyping and Prejudice • How can relationships between ethnic groups be improved? – contact does not lead to tolerance / warm relations • Gordon Allport (1954) – think that they are equal status – feel that an authority figure sanctions the positive relationships – believe that friendship might emerge from the interaction – engage in cooperative tasks in which everyone hast to contribute Stereotyping and Prejudice • Improving Interethnic Relations – Contact Only is Not Effect – Works best if groups: • • • • think they are of equal status feel an authority figure approves positive relations anticipate emergent friendship engage in cooperative tasks – task-oriented cooperation: • Sherif’s robbers cave study • Aronson’s jigsaw classroom Stereotyping and Prejudice • task-oriented cooperation: – Muzafer Sherif’s robbers cave study • organized groups of 11-year-old boys into “Rattlers” and the “Eagles” in a summer camp called Robbers Cave • competed in baseball, touch football, tug-of-war • relations became ugly • brought together to complete tasks – repairing camp’s only water supply system, pooling money to rent movie • shows how competitive and cooperative activities changes perceptions of the out-group – Eliot Aronson’s jigsaw classroom • real-world application: violence and ethnic tensions in desegregated schools between African Americans, Mexican Americans and Whites • jigsaw classroom – all students have to pull together to get the “big picture” – each group contains similar ethnic and ability level • associated with increased self-esteem, better academic performance, friendships among classmates, and improved interethnic perceptions Sherif’s Robbers Cave Study Close Relationships • TED Talks: Reverse-Engineering on-line dating • Attraction – proximity (physical closeness) – strong predictor of attraction • mere exposure effect – the phenomenon that the more we encounter someone or something (a person, a word, and image), the more probable it is that we will start liking the person or thing even if we do not realize we have seen it before • promise of acquaintanceship – we like those who like us • similar attitudes, behavior patterns, taste in clothes, intelligence, personality other friends, values, lifestyle, physical attractiveness – similarity • consensual validation – our own attitudes and behavior are supported when someone else’s attitudes and behavior our similar to our s—their attitudes and behavior validate ours • tend to shy away from the unknown Close Relationships: Love • Romantic Love – passionate love (romantic love) – love with strong components of sexuality and infatuation, often dominant in the early part of a love relationship – “in-love” – sexuality and infatuation • Affectionate Love – companionate love (affectionate love) – love that occurs when individuals desire to have another person near and have a deep, caring affection for the person – deep caring affection – passion gives way to affection Close Relationships: Love • Social Exchange Theory – fair exchange of “goods” – minimize costs, maximize benefits – equity – a feeling on the part of the individuals in the relationship that each is doing his or her fair share • most important predictor of relationship success • fades over time in a relationship (becomes distasteful) • Investment Model – factors in stability of relationship – predicts satisfaction and stability • commitment to partner – predicts willingness to sacrifice • investment in relationship – brings out the best in eachother • lack of attractive alternatives Social Psychology and Health and Wellness • Social Ties and Health – isolation and mortality • loneliness linked with impaired physical health – social support and coping • Fighting Loneliness – join activities with others • diverse social network live longer • narrow social network live shorter – act pleasant – get help Chapter Summary • Describe the influences on people’s perceptions and attributions of others. • Identify how people are influenced in social settings. • Discuss inter-group relations. • Explain the nature of close relationships. • Describe social processes affecting health and wellness. Chapter Summary • Social Psychology – study of how we think about, influence, and relate to other people • Social Cognition – person perception – attribution and the fundamental attribution error – heuristics – self-esteem – attitudes – cognitive dissonance/self perception Chapter Summary • Persuasion • Prosocial Behavior – altruism – bystander effect – media influence • Aggression – biological influences – psychological influences – sociocultural influences Chapter Summary • Social Influence – conformity – Asch’s study – obedience – Milgram’s study – group influence • deindividuation, social contagion, group performance • group decision making • Intergroup Relations – social identity – prejudice and stereotyping Chapter Summary • Close Relationships – attraction – proximity and similarity – romantic (passionate) love – affectionate (companionate) love – social exchange theory and investment model • Social Psychology and Health and Wellness – social ties and health