Environment
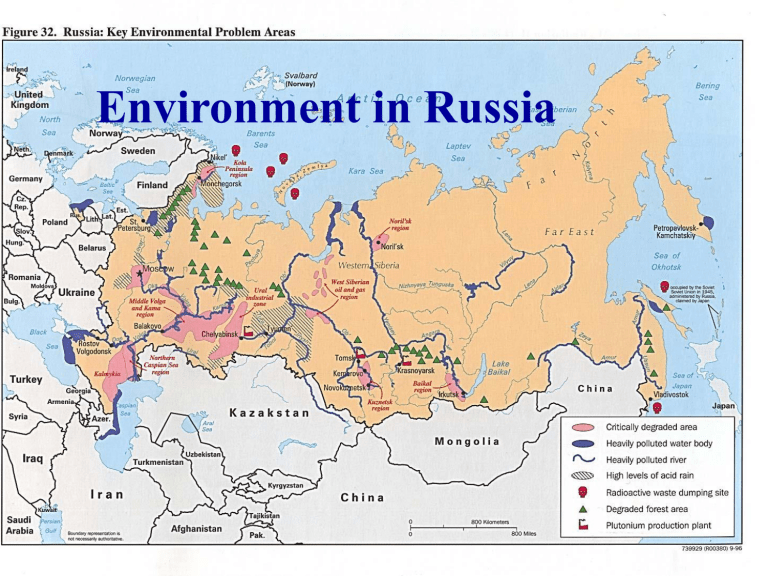
Environment in Russia
Environment in Central Asia
USSR was worse than West
• 2.5 X air pollution of
U.S. (per GNP)
• 20% water unsafe
• 1/3 of arable land affected by acid rain
• Etc., etc.
Why USSR was worse
• Heavy industry
• Expand agriculture
• “Inexhaustible” resources
• Legitimacy, self-sufficiency through technology
• Sacrifice for defense
Why USSR was worse
• Leadership technicians; questioning prevented
• Little free opposition
• Secrecy; lack of enforcement
• Central planning insensitive
• Only capitalism harms nature
WATER
Aral Sea
• Once the 4th largest inland body of water in the world. A series of dams was built to irrigate cotton.
• Aral Sea reduced to about 25% of its 1960 volume, 4x salinity wiped out the fishery.
• Pollutants became airborne as dust, causing significant local health problems.
Aral Sea Interbasin water transfers
(river diversions)
Kara
Kum
Canal
Amu Darya Size of
Aral Sea
Environmental damage estimated at $1.25 -$2.5 billion a year.
Caspian Sea
Western,
Russian oil and gas
Companies in Caspian
Basin
Caspian Sea
Caspian
Seal in
Kazakstan
Caspian sturgeon and its caviar
Oil spill off
Baku, Azerbaijan
Dnieper R.
Dniester R.
Moldova
Ukraine
Sea of
Crimea
Azov
Danube R.
Romania
BLACK SEA
Bulg.
Bosporus
Turkey
Don R.
Russia
Georgia
Metals plant on
Dnieper River
Sea of Azov
Eutrophication (Algae growth)
Lake
Baikal
Environmental objections to paper mills as early as 1960s
80% of fish in Tisza River / wetlands died, spill to Danube
Cyanide disaster
Australian-owned gold mine in Romania, 2000
Gabcikovo Dams,
Slovakia
Conflict, protests between
Slovakia and Hungary over diversion of
Danube River
AIR & LAND
Kola Peninsula, NW Russia
Black
Triangle
Devastation from acid rain, SO2, toxics
GDR POLAND
CZECHOSLOVAKIA
Donbass coal fields, E. Ukraine
Donbass & Kuzbass
Kuzbass coal fields, W. Siberia
Kalmykia
European
Buddhist
Mongols
Desertification
Chemicals/
Salinization
Oil development
Sakha
(Yakutia)
• Siberian indigenous
• Coal, metals mining
• Logging
Clear-cutting in Siberia
Japanese and South Korean companies take advantage of “fire sale”
International campaign to protect Amur Tiger along Chinese border
Noril’sk nickel smelter
Arctic Haze and Acid Rain
WAR
Kola Peninsula
Acid rain,
Mining,
Nuclear subs scuttled
Toxic military bases
Abandoned Soviet military bases in Eastern
Europe have toxic wastes (like U.S.
bases elsewhere.)
Sverdlovsk anthrax, 1979
Bioweapons disaster,
79 cases (66 dead) in Yeltsin’s district
Toxic cloud after NATO bombing of
Pancevo plant in Yugoslavia, 1999
Bombing civilian chemical plants
Uranium mining
Roma (Gypsy) kids playing on radioactive mill tailings from
Soviet uranium mine in Pécs, Hungary
Soviet nuclear tests in Kazakstan
Genetic defects near Semey
(Semipalatinsk)
Kazaks protest
Kyshtym waste disaster, 1957
Orphans
– Explosion at Soviet weapons factory forces evacuation of over 10,000 people in Ural Mts.
– Area size of Rhode Island still uninhabited; thousands of cancers reported
Novaya
Zemlya
NUCLEAR
POWER
Chernobyl disaster,
April 1986
400 million people exposed in 20 countries
“It Can’t Happen Here”
• U.S. reaction to Chernobyl, 1986
– Blamed on Communism, graphite reactor
• Also Soviet reaction to Three-Mile Island, 1979
– Blamed on Capitalism, pressurized-water reactor
• No technology 100% safe
– Three-Mile Island bubble almost burst
8,000 deaths in 14 years
3.5 million sick, one/third of them children
My grandmother, by Luda
Death of my life, by Marina
Chernobyl is war, by Irena
Beauty and the beast, by Helena
Nothing escapes radiation, by Irena
Chernobyl, our hell, by Eugenia
Self-portrait, by Natasha
Chernobyl’s political fallout
• Secrecy stimulated glasnost , environmental opposition
• Stimulated nationalism in Ukraine, Belarus, other republics that lost clean-up workers.
• Questioning of the heart of technocratic power
• USSR collapsed within 5 years.
Positives since end of USSR
• Democratization: NGOs, data
• Decentralization: local sensitivity
• Deindustrialization of old areas
• Expanded national parks
• Protection laws stronger by 1993
Negatives since end of USSR
• Financial difficulties; jobs stressed
• Reduced monitoring, enforcement
• Increased affluence, cars, waste
• Profit motive; foreign firms
• Putin dismantled agency, 2002
Other positives in Eastern Europe
• Ecological dissidents in transition
• Increased spending
• Pollution control technology
• Loss of markets
• Entry into E.U. standards









