File
advertisement

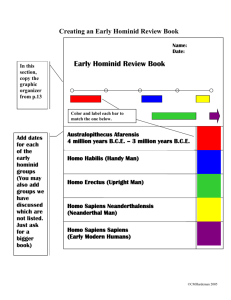
History of Human Evolution By Ariadna and Jessica THE FIRST HUMANS Hominids- earliest members of the human family. First hominid lived in Africa, 6 or 7 million years ago. A VERY ANCIENT RELATIVE Chad’s skull is the oldest hominid fossil in this gallery Sahelanthropus tchadensis lived at least six million years ago FOUR-MILLION-YEAR-OLD FRAGMENTS The first members of Homo, evolved from a member called Australopithecus. Oldest evidence from hominid are from four million years were found in Kenya. FOUR-MILLION-YEAR-OLD FRAGMENTS CONTINUE…. Fossils are called Australopithecus Anamensis. FOCUS ON: THE CHANGING LANDSCAPE 10 million years ago climate in Africa changed, this caused a chain reaction for the human evolution. Our ancestors had to adapt to the new climate. DNA FAMILY TREE The DNA of humans and chimpanzees is 98% the same. Researchers estimated that the last common ancestor lived more or less 7 million years ago. LITTLE FOOT In 1997, scientists in South Africa found a nearly complete skeleton of a hominid who lived more than 3 million years ago. LITTLE FOOT Continue… Surrounded by soli rock, it could be among the most complete early hominid skeletons ever uncovered. LITTLE FOOT Continue… “Little Foot” because its tiny foot bones were the first to be discovered. probably belonged to an early species of Australopithecus. EXAMINE THE EVIDENCE: Primate feet ☀Humans have a big toe that is lined up with the other toes. ☀Modern human feet are also arched ☀Helped distribute weight easily as we walk. EXAMINE THE EVIDENCE: Primate feet •The human foot helps us walk upright. • Modern human feet are also arched, so they distribute weight as we walk. FINDING THE FOSSIL •Ronald Clarke discovered four foot bones that clearly belonged to a hominid. •He searched and eventually found part of a leg bone with an unusually clean break. FINDING THE FOSSIL Continue… Two days later, using only hand-held lamps, Motsumi and Molefe found the matching leg. A WALK THROUGH TIME •Some 3.5 million years ago, two ancient hominids walked across an open plain in eastern Africa •A nearby volcano had recently erupted, Rain had fallen giving the ash the consistency of wet cement •The hominids footprints were captured in fossilized tracks. FOCUS ON: Australopithecus WHEN: 4 to 2 million years ago WHERE: parts of eastern, southern and central Africa BRAIN SIZE: around 300 to 500 cubic centimeters DIET: mainly plants; probably some insects and small animals FOCUS ON: Australopithecus Continue… AVERAGE ADULT HEIGHT: females: 1.1 meters (3 feet, 6 inches) males: 1.4 meters (4 feet, 6 inches) AVERAGE ADULT WEIGHT: females: 30 kg (66 pounds) males: 65 kg (143 pounds) . INTERPRETING THE FOOTPRINTS • Experts interpreted footprints at Tanzania. •One hominid was clearly larger than the other. In the hall a male and a female walk together. •This scene has evidence. Who Walked Here? •The two hominids who made the Laetoli footprints were not the only ones to leave their mark •They also found tracks of carnivores and threetoed horselike mammals known as Hipparion. A STAR SPECIES •Researchers have found hundreds of fossils from dozens of Australopithecus afarensis. •Best understood of the early hominids. EXAMINE THE EVIDENCE: Leg bones • • • Thigh Bone is angled; Knee and foot are near the midline of the body (Human) Thigh Bone is not angled; knee and foot are father from the midline of the body (Chimp) Thigh bone is angled (homid) AN UNFAMILIAR FACE Australopithecus afarensis had a project face and AT HOME IN THE TREES •Altougt Australopitecus afarensis walked upright when on the ground, this homid was still very apelike (like a monkey) •Member of this species probably spent part of their time in trees, finding food and shelter there TELLTALE TRACKS •In 1978, paleanthropologists in eastern Africa discovered a trail of ancient human footprints at the Laetoli site in tanzania. •2 early hominids, probobly member of the genus Australopithecus, walked upright across the African plan. EXAMINE THE EVIDENCE: Footprints •big toe is in line with other toes •foot is arched •impression is deep at the heel, indicating the heel struck the ground first •impression is deep at the big toe, indicating the hominid pushed off from the big toe at the end of each step LUCY •Most familiar is Lucy •Lived in Eastern Africa more than 3 million years ago •Lucy walked upright, like modern humans Examine the Evidence: Primate skeletons •long fingers and toes are good for climbing treesshort •legs are helpful for moving around in trees •wide and short pelvis suggests upright posture •thigh bones angle in toward knees, making upright walking easier ONE OF THE FAMILY •1974, Lucy was named after the Beatles' song "Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds," •Researchers listened to as they celebrated on the night of their remarkable find. BRANCHES ON THE FAMILY TREE •Only one species of hominid on the planet today: modern humans or homo sapiens •Between about 3.4 and 1.5 million years ago, at least 11 hominid species lived in Africa. •Many of them were members of the genus Australopithecus •Australopith went extinct about 1.4 million years ago FEATURED FOSSIL: Taung Child The 1924 discovery of this ancient African fossil helped disagree that notion known as the Taung Child Kenyanthropus platyops: hominid lived much earlier than many of the others but it has surprisingly advanced features Like flat face. MALE VS. FEMALE The Paranthropus boisei skulls both have wide, flat faces. only the larger skull has a crest on top. In modern gorillas, males have a similar crest while the smaller females do not EVOLUTIONARY DEAD END? Human evolution is often thought of successive species looks more like modern humans. Paranthropus robustus- seems to have died out leaving no descendants. EARLY TOOLS Around 2.5 million tears ago something new appears in the record Stone tools, sharp edges flakes of rock. DAILY LIFE, 1.8 MILLION YEARS AGO Early members Paranthropus robustus may have used the interiors, or cores, of antelope horns as tools. EARLY STONE TOOLMAKERS Ancestors developed mental capacities beyond those of modern apes. first toolmakers had small brains and archaically proportioned bodies. "HANDY MAN" •Paleoanthropologists Louis and Mary Leakey discovered a lower jaw at Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania. •Had a slightly larger brain than other early African hominids known at the time. "HANDY MAN" Continue… •This larger-brained species was capable of making the stone tools previously found at the sit •They named it Homo habilis, or "handy man." Turkana Boy 1.6 million year old skeleton almost complete found in Kenya, an eight-year-old boy. Named "Turkana Boy," more than five feet tall and much more fully developed than a eightyear-old. Turkana Boy Continue… the boy was still growing and probably would have been six feet as an adult. Turkana Boy is a member of the Homo ergaster, TALL AND LANKY When this fossil was found in 1984, the only other ancient hominid was Lucy. But Turkana Boy is much more complete. HOMINIDS OF LAKE TURKANA •Researchers found a lot of hominid remains in Africa's Rift Valley •the surrounding areas were once home to early hominids. • A wide variety of hominids have been found there some early members of our own genus, Homo, from almost two million years ago. TWO'S COMPANY The 1975 discovery of the nearly complete Homo ergaster skull changed the idea that only one species of hominid could exist at a given time. . LAKE TURKANA TOOLS •the hominids from around two million years ago had a resembled to modern humans •the stone tools they made were still very simple. FOCUS ON: Homo ergaster WHEN: 1.9 to 1.4 million years ago WHERE: Africa DIET: probably mostly plants with some meat AVERAGE ADULT WEIGHT: females: 56 kg (123 pounds) males: 68 kg (150 pounds) WHAT DID EARLY HOMINIDS EAT? •Meat, probably ate it raw. •They know because they found skeletons from animals that had cut marks from stone tools. GROUP LIVING? •Scientists are not sure exactly how large early hominid groups were. •no question that ancient primates were social animals African plains New hominid species continued to emerge and thrive on the African plains. ANCIENT COUSINS different species of the genus Homo lived in Africa around two million years ago Homo ergaster is the most plausible ancestor of modern humans FEATURED FOSSIL: Skull from Olduvai Gorge the genus Homo is notable for its large brain, estimated at nearly 80 percent the size of an average modern human brain. this skull is very different from other known Homo skulls found in Africa from the same period. NEW TOOLS around 1.5 million years ago, a more complex type of tool appeared. first time in human history hominids visualized the tools in their heads before starting to make them. OUT OF AFRICA We were not the first hominids to exit Africa. Some of our relatives began leaving that continent at least 1.8 million years ago, long before Homo sapiens evolved. Best fossil evidence for early hominid migrations comes from the Caucasus. DEEP UNDER DMANISI Scientists discovered remains of ancient rhinoceroses about 1.8 million years old the oldest sample of human fossils found outside of Africa. THE FIRST EMIGRANTS? First hominids to leave Africaare Homo ergaster. The tall body form of Homo ergaster allowed for walking over long distances in the open sun. SIMPLE TOOLS Artifacts found at Dmanisi a core a chopper a cutting flake EXAMINE THE EVIDENCE: Dmanisi skull Scientists thought the tall and relatively slender Homo ergaster was the first hominid to leave Africa The skulls from Dmanisi are puzzlingly varied in their size and anatomical details, so more than one species may have lived in this region 1.8 million years ago. ANIMAL EMIGRANTS Researchers digging at Dmanisi found hundreds of animal fossils. Some time before 1.8 million years ago, these adaptable creatures migrated north into the Caucasus. Zhoukoudian, China Before excavations began in the 1920s, people dug up fossilized bones from ancient cave Later researchers digging there found fossil remains of an ancient hominid they named "Peking Man." THE FIRST EUROPEANS Humans began spreading out from Africa almost two million years ago. The first early humans to penetrate the harsh climates of western Europe arrived quite early over one million years ago. HOW DID HOMINIDS REACH EUROPE? •the Mediterranean Sea •the Strait of Gibraltar •By land FEATURED FOSSIL: Gran Dolina Boy Researchers working in the Sierra de Atapuerca of Spain have found remains of early hominids. Most complete fossils is the "Gran Dolina Boy," who was around age 11. FEATURED FOSSIL: Gran Dolina Boy Continue… The Gran Dolina hominids were among the first Europeans, having reached northern Spain by around 800,000 years ago. Bodo skull The skull of Homo heidelbergensis was found in Africa; others of the same species have been found in Europe and Asia. Kabwe skull The Kabwe skull, the first ancient hominid fossil ever found in Africa, was discovered by miners. NEANDERTHAL First Homo neanderthalensis fossil was found in 1856 hundreds more have been found. EXAMINE THE EVIDENCE: Neanderthal skeleton Neanderthal: low braincase and doublearched brow ridge flaring, funnel-shaped chest flaring pelvis robust fingers and toes Modern human: tall, rounded braincase and small, divided brow ridge cylindrical, barrel-shaped chest narrow pelvis slender fingers and toes SKELETON STAFF First complete Neanderthal skeleton project took two years to complete. THE NEANDERTHALS Neanderthals: remarkable group. First appearing about 200,000 years ago Brains large as ours, outstanding toolmakers. they dominated Europe and parts of western Asia until they died out less than 30,000 years ago. NEANDER VALLEY, GERMANY In 1856, workers digging for lime found bones in the Neander Valley, thought they discovered an ancient cave bear. Bones were classified unknown species of human, Homo neanderthalensis. NURTURING NEANDERTHALS? 1950s, scientists found remains of 9 Neanderthals in Iraq. One adult male had arm bones that were severely deformed indicating he had suffered from a major disability FINAL DAYS Neanderthals died out less than 30,000 years ago FOCUS ON: Homo neanderthalensis WHEN: 200,000 to 30,000 years ago WHERE: Europe and western CHANGING VIEWS Scientists think Neanderthals lived in complex social groups Controlled fire Fairly proficient hunters They did bury their dead TELLTALE TEETH Front teeth of many Neanderthals have been worn down dramatically Maybe they used their teeth as tools. 40,000-YEAR-OLD DNA DNA is a delicate molecule Neanderthals and modern humans are two separate species. handling ancient DNA takes great care EARLY CHILDHOOD Fossils of children are rare, found the remains of a number of young Neanderthals, from newborn to several years old. Young Neanderthals and modern humans resemble each other more closely than the adults do Roc de Marsal, France In 1961, a skeleton of a Neanderthal child was found beneath the floor of the Roc de Marsal cave HOW LONG DID CHILDHOOD LAST? Female chimpanzees, are considered fully adult at 13. Studies on fossils of hominid children suggest that early humans grew up quickly and that the long childhood and teenage years of our species may be unique. FEATURED FOSSIL: Roc de Marsal child Some of the characteristic Neanderthal traits are visible even at an early age ( 3-4 years old). Making Better Tools 300,000 years ago, hominids began making more advanced stone tools using a new technique. Neanderthals were masters and used it to make a wide variety of handsomely shaped, sharp tools. THE EXPANSION OF HOMO SAPIENS Our species evolved 150,000 years ago, short time we have existed have populated the entire globe. Today Homo sapiens is the only living species of hominid around the world. HOW DID MODERN HUMANS SPREAD AROUND THE GLOBE? Migrated on foot certainly took thousands of years and many generations People probably settled in one location for a while MODERN HUMAN Homo sapiens first appearing in Africa around 150,000 years ago now populates the entire world. Our closest relatives have died out EXAMINE THE EVIDENCE: The modern human •high, vertical forehead •small nasal aperture •Chin •cylindrical rib cage •narrow pelvis THE SYMBOLIC WORLD One of the very first symbolic objects may be a 75,000-year-old engraved ochre plaque from South Africa. Scientists are confident that we emerged in Africa. Fossils from the period between 200,000 and 100,000 years ago are rare. Hominid fossils allow scholars to trace the evolution of the modern human body. Until recently, the earliest evidence of modern behavior could be seen in the cave art of Europe, which dates back some 35,000 years. DNA studies suggest that Homo sapiens had appeared by about 150,000 years ago. In 2003, announced the discovery of Homo sapiens. At the time of their discovery, these skulls were the oldest fossils ever identified as modern humans. The skull known as Omo 1 has many features in common with modern human skulls. After about 200,000 years ago, nearly modern humans lived across Africa. Two partial skulls were found on opposite ends of the continent: one in Morocco, and the other in South Africa. Paleoanthropologists don't know exactly where in Africa Homo sapiens first evolved. A partial skull, which had certain modern features, was discovered in Sudan in 1924. Then in 1996, researchers determined a likely age of about 133,000 years. • First moved into Asia • Before 1920, people dug up bones from ancient caves • Zhoukoudian, China found remains of hominid named Peking man • Evolved in eastern Asia and lived there for 1.5 million years • Skull found in Island of Flores, Indonesia, from a hominid nicknamed "The Hobbit.” • Flores Hominid: lived 18,000 years ago • Same time as modern humans • It had a tiny brain • Hominids left Africa • Deep below Spain’s Altapuerca Hill’s, there is a pit of bones • Found the best and most preserved fossil hominid skulls in the Pit of Bones