Protein Synthesis Worksheet - Molecular-Biology-Resource
advertisement

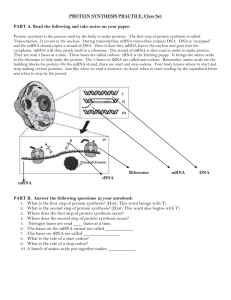
SAY IT WITH DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS WORKSHEET Category Resource type Basic Concepts of Science Dry lab Scientific Investigation Skills and Career Exploration A1.11 communicate ideas, plans, procedures, results, and conclusions orally, in writing, and/or in electronic presentations, using appropriate language and a variety of formats Prior Knowledge Students have an understanding of: The Central Dogma Basepairing in DNA vs. RNA Splicing Redundancy in the genetic code Overall Expectations Specific Expectations D2 Investigate, through laboratory activities the structures of cell components and their roles in processes that occur within the cell D2.1 use appropriate terminology related to molecular genetics D2.2 analyse a simulated strand of DNA to determine the genetic code and base pairing of DNA D3.3 explain the steps involved in the process of protein synthesis and how genetic expression is controlled in prokaryotes and eukaryotes Student Learning Goals By the end of the activity students will be to: Identify the amino acid that is coded by a given DNA sequence Identify the DNA sequence from a strand of amino acids in a polypeptide Teacher’s Notes Directions Suggestions Limitations Modifications for special need students Resource(s) This activity is to be completed after the students have learned about the central dogma, which is a fundamental and basic concept in molecular genetics. It is intended to review and solidify the concept that the genetic code provides the instructions for protein synthesis. This is an AfL activity to ensure that students understand the central dogma. Review base pairing in DNA (A with T and G with C) vs. RNA (A with U and G with C) Ask the students to create their own secret message (PART B #4). The students can trade This activity can also be done backwards (from translation to transcription); students will learn how to determine the DNA sequences for a polypeptide/protein This activity drastically simplifies how protein synthesis occurs. o it does not accurately represent how DNA transcription occurs in eukaryotes since it leaves out mRNA processing (e.g. splicing out of introns); o It does not include other cell components (e.g. RNA polymerase, ribosomes) that are involved in DNA transcription and translation; Students should notice that methionine is found in the middle of certain DNA sequences or not at all in the questions. Students should be reminded that methionine signals for ribosomal translation. Make sure to go over the instructions as well as repeating the instructions several times Allow more time for students to complete the activity. For example, if the teacher chooses to ask the students to create their own messages, the message swop can be completed next class. This also gives students more time to ask the teacher questions one-on-one if need be. This activity was adopted and modified from: http://www.indiana.edu/~ensiweb/connections/genetics/dna.les.html SAY IT WITH DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS WORKSHEET DNA RNA transcription Protein translation The Central Dogma states that DNA directs the synthesis of proteins by producing RNA via transcription followed by ribosomal translation of RNA into polypeptides. In this activity, you will decode sequences of DNA into "secret" messages. PART A Determine the “secret” message by transcribing and then translating the bases from the given strands of DNA below (#1-3). Use the dictionary to determine the letter that corresponds to each tRNA codon. You must record ALL your steps from transcription to translation, including the amino acids that correspond to each tRNA codon. For example: Given DNA CTT mRNA GAA tRNA CUU Letter E Amino Acid Glu If you have done this correctly, the letters should spell out a message in English. DICTIONARY tRNA AAA AAC AAG AAU ACA ACC ACG ACU AGA AGC AGG AGU AUA AUC AUG AUU AA Letter Phe F Leu L Phe F Leu L Cys C Trp W Cys C Thr O Ser S Ser S Ser S Ser S Tyr Y spc Tyr Y spc - Note: AA = Amino Acid Spc = “space” tRNA CAA CAC CAG CAU CCA CCC CCG CCU CGA CGC CGG CGU CUA CUC CUG CUU AA Letter Val V Val V Val V Val V Gly G Gly G Gly G Gly G Ala A Ala A Ala A Ala A Asp D Glu E Asp D Glu E tRNA GAA GAC GAG GAU GCA GCC GCG GCU GGA GGC GGG GGU GUA GUC GUG GUU AA Leu Leu Leu Leu Arg Arg Arg Arg Pro Pro Pro Pro His Glu His Glu Letter L L L L R R R R P P P P H Q H Q tRNA UAA UAC UAG UAU UCA UCC UCG UCU UGA UGC UGG UGU UUA UUC UUG UUU AA Letter Iso I Met M Iso I Iso I Ser S Arg R Ser S Arg R Thr T Thr T Thr T Thr T Asn N Lys K Asn N Lys K 1) DNA : CTA TTA CGA ATC TAG AGC ATT GAA TAG AAA CTT mRNA: tRNA: AA: letter: 2) DNA : TAC ATA ATC TAC TAG TTA CTA ATC TAT AGA ATT TAC CGA CCC TTG TAT mRNA: tRNA : AA: letter: DNA : AAA TAG ACG CTT TTA TGC mRNA: tRNA : AA: letter: 3) DNA: TGA GTG CTT ATT ACG CTC TTA TGC TCC CGC GAG ATC CTA ACT CCC TAC mRNA: tRNA : AA: letter: DNA:CGT ATT TAA TCA ATC ACT TTG ATC TGG GTG CTC ATT TGC CTT AGGTGA mRNA: tRNA : AA: letter: PART B Answer the questions below. 1) Several codons code for “spc”. Explain why this is an advantage or disadvantage for the organism. 2) Are the given strands of DNA from a eukaryotic or prokaryotic organism? Explain your answer. 3) Explain where translation would begin for: a. DNA sequence #1: CTA TTA CGA ATC TAG AGC ATT GAA TAG AAA CTT b. DNA sequence #3: TGA GTG CTT ATT ACG CTC TTA TGC TCC CGC GAG ATC CTA ACT CCC TAC CGT ATT TAA TCA ATC ACT TTG ATC TGG GTG CTC ATT TGC CTT AGGTGA 4) Construct your own secret DNA message by working backwards in the space provided below (from English AA tRNA mRNA DNA). This message will be handed in on a separate piece of paper with ONLY the DNA sequence on it and then it will be randomly given out to one of your classmates to decode. Keep in mind that the letters B, J, U, X, and Z cannot be used in your message. (CAUTION: obscene or derogatory messages are not acceptable). ANSWERS 1) DNA : CTA TTA CGA ATC TAG AGC ATT GAA TAG AAA CTT mRNA: GAU AAU GCU UAG AUC TCG UAA CUU AUC UUU GAA tRNA: CUA UUA CGA AUC UAG AGC AUUGAA UAG AAA CUU AA: Asp Asn Ala spc Iso Ser spc Leu Iso Phe Glu letter: D N A I S L I F E 2) DNA : TAC ATA ATC TAC TAG TTA CTA ATC TAT AGA ATT TAC CGA CCC TTG TAT mRNA: AUG UAU UAG AUGAUC AAU GAU UAG AUAUCU UAA AUG GCU GGG AAC AUA tRNA : UAC AUA AUC UACUAG UUA CUA AUC UAUAGA AUU UAC CGA CCC UUG UAU AA: Met Tyr spc Met Iso Asn Asp spc Iso Ser spc Met Ala Gly Asn Iso letter: M Y M I N D I S M A G N I DNA : AAA TAG ACG CTT TTA TGC mRNA: UUU AUC UGC GAA AAU ACG tRNA : AAA UAGACG CUU UUA UGC AA: Phe Iso Cys Glu Asn Thr letter: F I C E N T 3) DNA:TGA GTG CTT ATT ACG CTC TTA TGC TCC CGC GAG ATC CTA ACT CCC TAC mRNA: ACUCAC GAA UAA UGC GAGAAU ACG AGG GCG CUC UAGGAU UGA GGG AUG tRNA : UGA GUGCUU AUU ACG CUC UUAUGC UCC CGC GAG AUC CUA ACU CCC UAC AA: Thr His Glu spc Cys Glu Asn Thr Arg Ala Leu spc Asp Thr Gly Met letter: T H E C E N T R A L D O G M DNA:CGT ATT TAA TCA ATC ACT TTG ATC TGG GTG mRNA: GCA UAAAUU AGU UAG UGA AACUAG ACC CAC tRNA : CGU AUU UAA UCA AUC ACU UUGAUC UGG GUG AA: Ala spc Iso Ser spc Thr Asn spc Thr His letter: A I S O N T H CTC ATT TGC CTT AGGTGA GAGUAA ACG GAA UCC ACU CUC AUU UGC CUUAGGUGA Glu spc Thr Glu Ser Thr E T E S T PART B Answer the questions below. 5) Several codons code for “spc”. Explain why this is an advantage or disadvantage for the organism. A change in a single base may not necessarily result in a change in amino acid. Therefore, it would be an advantage for the organism to have multiple codons for “spc”. This is an example of redundancy. 6) Are the given strands of DNA from a eukaryotic or prokaryotic organism? Explain your answer. The strands of DNA are from a prokaryotic organism because splicing was not required. 7) Explain where translation would begin for: a. DNA sequence #1: CTA TTA CGA ATC TAG AGC ATT GAA TAG AAA CTT This sequence would not be translated since it lacks methionine (Met)to signal the initiation of translation for the ribosome. b. DNA sequence #3: TGA GTG CTT ATT ACG CTC TTA TGC TCC CGC GAG ATC CTA ACT CCC TAC CGT ATT TAA TCA ATC ACT TTG ATC TGG GTG CTC ATT TGC CTT AGGTGA Translation would begin at TAC, which is underlined above. Translation begins here because TAC codes for methionine, which signals the initiation of translation for the ribosome. 8) Construct your own secret DNA message by working backwards below (from English AA tRNA mRNA DNA). This message will be handed in on a separate piece of paper with ONLY the DNA sequence on it and then it will be randomly given out to one of your classmates to decode. Keep in mind that the letters B, J, U, X, and Z cannot be used in your message. (CAUTION: obscene or derogatory messages are not acceptable). All students will have a different message. ADDITIONAL DNA MESSAGES with ANSWERS KEY 1. CCT CTT TGC ACT CGG ATC GTA CGC TAT TCT ATG ATT ACA CGG TTG CGA TCC ATA ATC Get a hairy canary (A. Mulder) 2. AGA TAC TAG GAC CTT ACT CGA TTG CTG ATT GCG CGA CTA TAA CGG TGC CTC ACT CGG ATT AAC TAG TGC TGA AAT CTT ATT ACG GTA CTT CTC GCC ATC Smile and radiate a little cheer (A. Mulder) 3. TCC CTT GGG GAA TAT ACA CGC TGG CTT ACT CGA ATT TGA CTC CGT ACG GTA CTC GCC ATC Replicate a teacher (J. Shepherd) 4. AGA ACA TAA CTC TTA ACA CTC TAA AGA CCA GCA CTC CGA TGA Science is Great (H. Bazan) 5. TAA ACT CGG TAC ATT CTA GCT TAG CAC TAA TTA CCC ATC I am driving (T. Nguyen) 6. TAC CGT TTC CTT ATT GAT CGC GCC CCA CTC ATT CTT CGG TCT AGG ATC Make large ears (J.G. Oliva) 7. CTA GCC CTC CGT TAC TAG TTA CCT ACT TAT TCA ATT TTG TAA ACG CTC ATC CGA ACC CGC TTT TAA TTG CCC ACT TAG TCG ATT ACC CGT TTA TGT TAA TTA CCT ATC Dreaming is nice. Awaking is wanting (K. Vo) 8. ACC GTG ATA ACT CGT GCT CTT ATT ACC CTC ACT AAT CTC CGG TCC TTA TAT TTG CCT ATT TGC GTA TAG TCG ATC Why are we learning this (J. Mi1i) 9. TAC CGA TTT CTT ACT AGT GGC TCC TAT TTA CCT ATA ATT ACA GTG TAA ACG TTC CTC TTA TCA ATC Make springy chickens(D. D. Ho) 10. CTA TTA CGA ACT TAG AGC ATT GAA TAG AAA CTT ATC DNA is life (P. Labrador) 11. CTC CAC GTG AGA ATT CAC CGA GCA TCA TAG TGG ATG ATT AGA ACC TAT TAC TAC TAT TTG CCT ATC EVHS Varsity Swimming (A. Valdez-Lanam) 12. ACC GTG ATA ACT CGA GCA CTC ATT GGC AAC CGC TTA TGT AGC ATT CCT TCT CTC CTT TTG ATC Why are plants green (A. Valdez-Lanam) 13. ACG GCT CTC CGT TGT CTC ACT CGA TTG ATT CTC ATG CTT ATC Create an eye (C. Smith) 14. CTG CTT AGT TAT CCA TTG ACT CGA ATT GTG CGC TTG CTG ATC Design a hand (D. Smith) 15. ACA GCC CTT CGC TGC CTC ACT CGA ATT AAA TAT TTG CCA CTC GCT ATC Create a finger (C. Smith) 16. AAA TAT TTA CTA ACT TGG GTA CTT ATT AGC CTC ACG GCG CTT TGT ATT TAC CTC AGA AGC CGA CCA CTC ATC Find the secret message (J. Thailer) 17. CTT CGA TGA ATT CCA GCC CTC CTT TTG ATC CTT CCA CCT AGC ATC CGA TTG CTA ACT GTA CGC TAM Eat green eggs and ham (H. Thompson) 18. AGT TAC TAA GAA CTT ACT TAG TGT TCA ATC GTA CTT CGA GAG TGG GTA ATG Smile it's healthy (H. Thompson) 19. ACC CGA TGG CTC TCT ATC TAT AGC ATT ACA AAC CTC CGA GCG Water is clear (J Blaskey) 20. ACG CTT GAA AAT AGG ACT CGA TCT CTC ATC CCG TCC CTG CGC TGC ATT TGT GTA TAG TTA CCC AGG Cells are great things (A. Skinner) 21. GAA CTC CGA TCT TTG TAT CCG ACT CTA TTA CGG ATC TAA AGC ATT CCT TCC CTT CGT TGT Learning DNA is great (A. Skinner) 22. TAC ATA ACT TAC TAG TTA CTA ATC TAT AGA ATT TAC CGA CCC TTG TAT AAA TAG ACG CTT TTA TGC ATC My mind is magnificent 23. TAA ACT GTG CGA CAC CTC ATT CGT ATC CTA GCG CTT CGT TAC ATC I have a dream 24. AGA CGG CAA CTC ATT TGG GTG CTT ACT TGT TCT CTT CTC AGT ATC Save the trees 25. CCG GCA CTC CTT CTA ATT GCT CTT TAG CCA TTA AGT ACT TAA TTG ATC ACC CGA AAT GAG ATT AGG TGT TCC CTC CTT TGC ATC Greed reigns in Wall Street 26. GAT TAA AAA CTC ACT TAG AGC ATT AGT GGG CTT ACA TAA CGG GAA ATC Life is special 27. ACC GTA ATG ATT TAG AGG ATC CTG TTA CGA ACT TTG CTC ACA CTT AGC AGT CGG TCC ATA ATC Why is DNA necessary 28. GTA CGA GGA GGA ATG ATC CAA CGA AAC CTC TTA TGA TAA TTA CTC AGG ATC CTA CGA ATA ATC Happy Valentines Day 29. AAT CTC CGA GCT TTG TAG TTA CCC ATT TAG AGT ATC TAG TTG TGT CTC GCT CTC AGG TGC TAT TTG CCT ACT Learning is interesting 30. CGA ACT AGA TAA CCC TTA TAG AAA TAT ACA CGC TTG TGA AAC ATA ATC CGG CTG CAA CGT TTA ACA CTC CTA ATT AGG ACA TAA CTC TTG ACA CTT ACT TAG AGA ACT CTC CGC TCA TAG GAG ATA ATT TAC TAA AGA TGA CGG TTT CTT TTG ACT CGA AGC ATT TAC CGC CCC TAG ATC A significantly advanced science is easily mistaken as magic