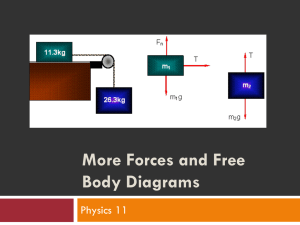
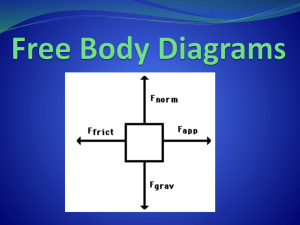
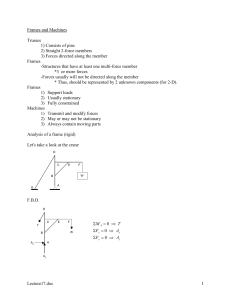
Force/Free Body Diagrams
advertisement

FRICTIONAL FORCES FRICTIO Free body diagram: A book lying on a level table Free body diagram: A person floating in still water Free body diagram: A wrecking ball hanging vertically from a cable Free body diagram: A helicopter hovering in place 3 Free Body Diagrams: Move R, accel R Move R, no accel Move R, accel L Free Body Diagrams Notes Key Terms newton, - N, unit of force in the metric system - force needed to push a 1kg object at a speed of 1m/s for a second. mass, in physics, the quantity of matter in a body regardless of its volume or of any forces acting on it. weight, measure of the force of gravity on a body What does gravity have to do with the weight of an object? Weight (W) varies depending upon the location of the body in the earth's gravitational field (or the gravitational field of some other astronomical body). The acceleration of gravity on earth is approximately: 9.8 m/s² in SI units and 32 ft/s² in US Customary units. To calculate the weight of an object you have to multiply it’s mass times the acceleration of gravity. W = m * g The Statue of Liberty has a mass of 225,000 kg. How much does she weigh? To calculate the weight of an object you have to multiply it’s mass times the acceleration of gravity. Write the formula: W = m * g Substitute known values: W = (225,000 kg) * 9.8 m/s² Present solution with units: W = 2,200,000 N What the heck is 2,200,000 N? The Statue of Liberty weighs 2,207,250 Newtons, which is 495,000 lbs pounds! A free-body diagram illustrates the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object. The object must be isolated and “free” of its surroundings. This is a free-body diagram of the Statue of Liberty. She is represented by a simple box. The forces acting on her are labeled with a magnitude and the arrow shows direction. Notice the surrounding objects are stripped away and the forces acting on the object are shown. 496210 lb 496210 lb “FW” here represents the force of the weight of the statue. “FN” is the normal force, which represents the force Liberty FW = 495,000 lb Island is pushing back up on the statue. Normal: means perpendicular to, (ex. The walls to the floor) The force of the pedestal to the statue is normal to the surface of the ground. The island has a great resistance to compression. The ground is exerting a force upward on the statue perpendicular, or normal, to the surface. FN = 495,000 lb Think of the diagram on an XY plane. If “up” is assumed to be the positive direction, then N is positive and W is negative. •When forces acting on the object cancel each other out it is in a state of static equilibrium. (Positive y-direction) +y FW = -495,000 lb FN = 495,000 lb +x (Positive x-direction) Create a free body diagram (FBD) of the gorilla: FN Gorilla FW Free Body Diagram of the Sitting Gorilla (The box represents the gorilla, W = weight of the gorilla, N = Normal force) Sitting Gorilla Draw a FBD of the wooden swing: Where are the forces on the swing? FT1 FT2 Swing FW Free Body Diagram of the wooden swing (The box represents the wooden swing, W = weight of the swing and the parrot, T represents the ropes that are in tension supporting the weight) Parrot on wooden swing hung by ropes Draw a FBD of bucket the bungee jumper leaped from: Where are the forces on the bucket? FT bucket FW Free Body Diagram of the bucket (T represents the tensile force of the cable the bucket is suspended from, and W is the weight of the diver and the bucket) Bungee jumping from crane Draw a FBD of the ring at point C: Where are the forces on the ring? A B FTCA FTCB C D FTCD Traffic Light supported by cables Free Body Diagram of the ring at point C (T represents the force of the cables that are in tension acting on the ring) Draw a FBD of the traffic light: A B C Where are the forces on the light? FTCD Light D FW Traffic Light supported by cables Free Body Diagram of the traffic light (FTCD represents the force of the cables acting on the light and FW is the weight acting on the light) Draw a FBD of the pin at point A: Where are the forces on point A? FTAB FTAC B A FTAD FTAE Free Body Diagram of pin A C E D Pin-Connected Pratt Through Truss Bridge (If you consider the third dimension, then there is an additional force acting on point A into the paper: The force of the beam that connects the front of the bridge to the back of the bridge.) Sitting Gorilla Draw a FBD of the wooden swing: Where are the forces on the swing? Parrot on wooden swing hung by ropes Draw a FBD of bucket the bungee jumper leaped from: Where are the forces on the bucket? Bungee jumping from crane Draw a FBD of the ring at point C: Where are the forces on the ring? A B C D Traffic Light supported by cables Draw a FBD of the traffic light: Where are the forces on the light? A B C D Traffic Light supported by cables Draw a FBD of the pin at point A: Where are the forces on point A? B A C E D Pin-Connected Pratt Through Truss Bridge