Teaching with Models
advertisement

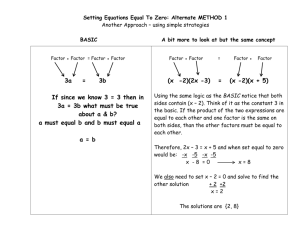
Specialized Instruction Differentiation •Precocity •Complexity •Intensity •Creative •Conceptual •Perfectionistic Joyce Van Tassel-Baska 2009 Learner Char. and Corresponding Emphasis in the Curriculum The Learner The Curriculum Precocity Advanced Content Intensity Process/product depth Complexity Issues/concepts/ themes/ideas Creativity Dimension • Design/construct a model based on principles or criteria • Provide alternatives for tasks, products • Direct oral and written communication to a real-world audience Quest Model for Creative Writing The Hero (Create a character with heroic qualities) Returns home with the solution, answers, and/or wisdom (Define the outcomes of the quest – new understandings, insights, and tangible rewards for the hero) Encounters a problem or challenge (Define the challenge) Has exploits that tests his/her commitment to the quest (Define adventures/people/ situations encountered) Goes on a journey to seek answers to the problem/challenge (Define the journey in respect to type, duration and purpose) Freytags Plot Line Katie Carson’s Classroom 1.Once upon a time… 2.And every day… 3. Until one day… 4. And then… 5. And then… 6. Until finally… 7. And ever since… Tomlinson, Carol Ann and Doubet, Kristina; “Reach Them to Teach Them” Educational Leadership: Summer 05, Vol. 62, # 10. Hamburger Model for Persuasive Writing Definition: A closed plane bound by 3 or more line segments Characteristics: more line segments, multiple angles Polygon Examples: square, triangle, rectangle, quadrangle Non-examples: circle, arc Vocabulary Map Word Definition Use in sentence Part of speech A synonym An antonym Purpose/ Goal Implications/ Consequences Point of View What will the group do this evening? Inferences Evidence/ Data Concepts/Ideas Assumptions 1. Identify your issue or problem 2. Read about your issue and identify points of view or arguments through information sources 3. Form a set of questions that can be answered by a specific set of data 4. Gather evidence through research techniques such as surveys, interviews, or analysis of primary and secondary source documents 5. Manipulate and transform data so that they can be interpreted. 6. Draw conclusions and make inferences 7. Determine implications and consequences 8. Communicate your findings Reasoning about a Situation or Event What is the situation? Who are the stakeholders? What is the point of view for each stakeholder? What are the assumptions of each group? What are the implications of these views? Consists of Different Types sand Rock and gravel including clay silt ? ? B y r y y g Rules from Tom Kelley’s book, The Ten Faces of Innovation: 1. Go for Quantity. Good ideas emerge from lots of ideas. Set a numerical goal – say, a total of one hundred ideas. 2. Encourage Wild Ideas – Extremism is a virtue. The right idea often flows from what initially seems outlandish. 3. Be Visual – Pictures unlock creativity. 4. Defer Judgment – There’s no such thing as a bad idea, so banish the naysayers. Think creatively first and critically later. 5. One Conversation at a Time – Listen, be polite, and build on others’ suggestions. Curriculum Compacting 1) What’s important? 2) What can be skipped or eliminated? 3) What do students already know or are able to do? 4) What will they grasp easily? 5) What can be accomplished quickly? The goal is to modify or “streamline” curriculum to allow students to move at a quicker pace and then have time to pursue an alternate topic or go into greater depth in an area of study. Basic Skills Compacting Content Compacting Spelling, Math Computation, Language Arts Basic Skills Social Studies, Science, Literature, Math Applications, and Problem-Solving Pretesting is easily used to document proficiency. Students may already know some material or may be able to read advanced material or master objectives more quickly. 1. The teacher previews the student task and selects the most difficult examples. 2. The examples are marked (*) and students are given the opportunity to do these items first as a means of demonstrating mastery or understanding. 3. If students are able to demonstrate mastery, then they are provided alternate activities for that period of time. Student’s Name: ________________________________ Content Area Documenting Mastery Alternate Activities Content Area Math ---Decimal Fractions Documenting Mastery Score of 85 percent or higher on the pretest Alternate Activities Will work with class on days they learn concepts she has not mastered Will work on alternate math enrichment activities on other days Content Area Documenting Mastery Social Studies--Colonial Living Unit Students will read chapters 5 & 6 in text at own pace High Interest Strong Readers---- Will read and pick up concepts quickly Do chapter exercises 3, 7, &9 Take unit test when ready Alternate Activities Students will select a topic of interest from a list of alternate activities related to an aspect of colonial living for an independent study 4 3 2 Fluency I can think of many ideas. I can think of some ideas If I get some I have a help, I can hard time think of ideas thinking of ideas Flexibility I notice what is surprising and unusual I notice unusual things around me When someone reminds me, notice I hardly ever notice unusual things Evaluation I know several ways of deciding I can tell which ideas are worth working on With help, I can tell which ideas worthwhile I cannot tell which ideas are worthwhile Risk-taking I like to try new ideas I try new ideas Sometimes I try new ideas I do not try new ideas Seeking Challenges Goal setting (etc.) Goal setting Goal setting (etc.) I do not set goals I can usually add details to make better Sometimes, I can think of way to make better I do not know how to make better Elaboration When I have good idea, I add details to make great 1 Score Criteria Exemplary (45) Good (2-3) Needs Improvement (0-1) Initial Questions Questions are probing and help clarify facts All questions may not be relevant Few or no questions formulated Understanding the problem Clearly defines the problem Statement has some vagueness or missing information Problem defined incorrectly Seeking information Identifies several sources of information Relies on few sources Not clear as to what is needed Risk-taking I try new ideas Sometimes I try new ideas I do not try new ideas Integration of knowledge Effectively applies previous knowledge Applies limited amount of prior knowledge Unable to connect previous knowledge Is this fair? 1. Asking the same as other students; to stretch a bit, learn new skills 2. Promoting success at new level; not failure at new level 3. Acknowledging skills; to not do so would be malpractice 4. Perfect time to do this “Challenging the Gifted Child in the Classroom. The Challenge Magazine of The Center for Gifted Studies. Western Kentucky University. No. 20 Winter 2008 Renzulli, Joseph, Reis, Sally, Swicord, Curriculum Differentiation for Gifted and Talented Students – Webinar – Slideshare Tomlinson, Carol Ann (1995). How to Differentiate Instruction in Mixed-Ability Classrooms. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development. Tomlinson, Carol Ann & Doubet, Kristina (2006). SMART in the Middle Grades – Classroom That Work for Bright Middle Schoolers. Westerville, OH: National Middle School Association. Tomlinson, Carol Ann (1995). How to Differentiate Instruction in Mixed-Ability Classrooms. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development. Tomlinson, Carol Ann & Doubet, Kristina (2006). SMART in the Middle Grades – Classroom That Work for Bright Middle Schoolers. Westerville, OH: National Middle School Association. Van Tassel-Baska, Joyce (2003). Content-Based Curriculum. Waco, TX: Prufrock Press, Inc. p. 16