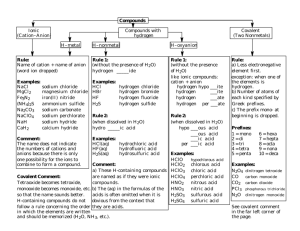
Chemical nomenclature
advertisement

Inorganic chemical nomenclature (textbook: 12 - 25) Noble gases Alkaline earth Alkalimetals metals Chalcogens Halogens METALS Electronegativity Oxidation state (oxidation number) Valence Ionic charge - "real electric charge" cations: Na+ Ca2+ Al3+ anions: Cl- SO42- Chemical formulas We have several types of formulas: (according to the information they contain) 1) Empirical formula 2) Molecular formula 3) "Condensed formula" 4) Structural formula 5) Structural formula showing unshared electrons 1) EMPIRICAL - relative number of each type of atom (ratio of the elements) - e.g. H2SO4 Al2O3 CH2O 2) MOLECULAR - real number of atoms in the molecule - e.g. H2SO4 3) "CONDENSED" Al2O3 C6H12O6 (functional groups) - characteristic groups of atoms (=functional groups) - e.g. Mg(OH)2 (NH4)2SO4 K4[Fe(CN)6] 4) STRUCTURAL - types and arrangement of bonds between atoms 5) STRUCTURAL with unshared electrons - shows also unshared (non-bonding) electron pairs Latin nomenclature (INN) INN = International Nonproprietary Names - intended to be used worldwide for the identification of a given pharmaceutical substance - free of any protection of rights of ownership - recommendations come from World Health Organization (WHO) "Drug names" TRADE NAME - registered to pharmaceutical company - protection of rights of ownership CHEMICAL NAME - long, difficult GENERIC NAME (INN) – "free" e.g. simvastatinum - trade names in the Czech republic: Zocor, Simgal, Simvor, Vasilip, Simvastatin AL, APO-Simva, ... ... - statinum drug for lowering cholesterol Symbols of chemical elements - derived from LATIN name K Kalium N Nitrogenium Na Natrium B Borum Br Bromum Ag Argentum Ar Argonum English name - - - > symbol lead L Le As ? Plumbum Pb Arsenum Trip to linguistics (morphology) PREFIX STEM of the word SUFFIX (ending) hypo - chlor - ate Latin is a highly inflected language. nouns - six cases - many declensions 1. nominative 2. genitive 3. dative 4. accusative 5. vocative 6. ablative Natrium Natrii Natrio Natrium Natrium Natrio Genitive forms element names - usual ending: - UM Lithium, Ferrum, Cuprum, Calcium genitive form -I Lithii, Ferri, Cupri, Calcii Plumbum --> Plumbi Natrium --> Natrii Elements with different names in English and in Latin !!! Sb Cu Au Fe Pb Hg Ni K Si Ag Na Sn W antimony copper gold iron lead mercury nickel potassium silicon silver sodium tin tungsten Stibium Cuprum Aurum Ferrum Plumbum Hydrargyrum Niccolum Kalium Silicium Argentum Natrium Stannum Wolframium Numerical prefixes 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 mono di tri tetra penta hexa hepta octa nona deca 11 12 13 undeca dodeca trideca 20 100 eicosa hecta 1/2 3/2 hemi sesqui Names of oxides 1) Oxides of NONMETALS CO CO2 carbon monoxide carbon dioxide SO2 SO3 sulfur dioxide sulfur trioxide As2O3 As2O5 diarsenic trioxide diarsenic pentoxide - numerical prefixes Names of oxides 1) Oxides of METALS Only one oxid. state: CaO Al2O3 calcium oxide aluminum oxide More oxid. states: FeO Fe2O3 iron (II) oxide iron (III) oxide Names of oxides (INN) Genitive form of the name for the element + OXIDUM (numerical prefixes are employed) K2O CaO Al2O3 SnO2 Sb2O5 SO3 Dikalii oxidum Calcii oxidum Dialuminii trioxidum Stanni dioxidum Distibii pentaoxidum Sulfuris trioxidum ! ( sulfur, -is ) 3rd decl. Names of peroxides element + PEROXIDE H2O2 Na2O2 BaO2 hydrogen peroxide sodium peroxide barium peroxide Names of peroxides (INN) Genitive form of the name for the element + PEROXIDUM H2O2 Na2O2 BaO2 Hydrogenii peroxidum Natrii peroxidum Barii peroxidum Names of hydroxides element + HYDROXIDE ( if element forms more hydroxides – specify it ! ) NaOH Ca(OH)2 Mg(OH)2 sodium hydroxide calcium hydroxide magnesium hydroxide Fe(OH)2 Fe(OH)3 iron (II) hydroxide iron (III) hydroxide Names of hydroxides (INN) Genitive form of the name for element + HYDROXIDUM ( numerical prefix: if element forms more hydroxides ) NaOH Ca(OH)2 Mg(OH)2 Natrii hydroxidum Calcii hydroxidum Magnesii hydroxidum Fe(OH)2 Fe(OH)3 Ferri dihydroxidum Ferri trihydroxidum Names of acids 1. Acids not containing oxygen ("binary acids") HYDRO.... -IC ACID HF HCl HBr HI H2S HCN or hydrofluoric acid hydrochloric acid hydrobromic acid hydroiodic acid hydrogen sulfide hydrogen cyanide HYDROGEN .... -IDE 2. Oxyacids How many oxyacids can the element form ? a) only one H2CO3 H3BO3 H2SiO3 H2MoO4 .... -IC ACID carbonic acid boric acid silicic acid molybdic acid !!! a) two Lower oxidation n. Higher oxidation n. .... -OUS ACID .... -IC ACID H2SO3 H2SO4 sulfurous acid sulfuric acid HNO2 HNO3 nitrous acid nitric acid H3PO3 H3PO4 phosphorous acid phosphoric acid a) more than two HClO HClO2 HClO3 HClO4 The same way: H2MnO4 HMnO4 the halogens Cl, Br, I hypochlorous acid chlorous acid chloric acid perchloric acid "traditional" manganic acid permanganic acid Names of acids (INN) 1. Acids not containing oxygen ("binary acids") ACIDUM HYDRO …… -ICUM HF HCl HBr HI H2S HCN Acidum hydrofluoricum Acidum hydrochloricum Acidum hydrobromicum Acidum hydroiodicum Acidum hydrosulfuricum Acidum hydrocyanicum 2. Oxyacids How many oxyacids can the element form ? a) only one H2CO3 H3BO3 H2SiO3 H2MoO4 ACIDUM ……-ICUM Acidum carbonicum Acidum boricum Acidum silicicum Acidum molybdaenicum a) two Lower oxidation n. Higher oxidation n. ACIDUM ……-OSUM ACIDUM ……-ICUM H2SO3 H2SO4 Acidum sulfurosum Acidum sulfuricum HNO2 HNO3 Acidum nitrosum Acidum nitricum H3PO3 H3PO4 Acidum phosphorosum Acidum phosphoricum a) more than two HClO HClO2 HClO3 HClO4 The same way: H2MnO4 HMnO4 the halogens Cl, Br, I Acidum hypochlorosum Acidum chlorosum Acidum chloricum Acidum hyperchloricum ( perchloricum ) "traditional" Acidum manganicum Acidum hypermanganicum Names of salts 1. Salts of binary acids (acids not containing oxygen) cation + ……- IDE more oxidation states of cation: specify it ! e.g. iron (II) NaCl AgI KCN ZnS sodium chloride silver iodide potassium cyanide zinc sulfide Common elements with two oxidation states in cations FeII iron (II) ferrous FeIII iron (III) ferric CuI copper (I) cuprous CuII copper (II) cupric HgI mercury (I) mercurous HgII mercury (II) mercuric AuI gold (I) AuIII gold (III) SnII tin (II) SnIV tin (IV) TlI thallium (I) TlIII thallium (III) PbII lead (II) PbIV lead (IV) stannous plumbous stannic plumbic Salts of elements with more oxidation states FeCl2 FeCl3 iron (II) chloride iron (III) chloride CuI CuI2 copper (I) iodide copper (II) iodide Hg2Cl2 HgCl2 mercury (I) chloride mercury (II) chloride 2. Salts of oxyacids cation according to acid also: Na2CO3 K2SO3 NaClO FeSO4 NH4BrO2 + … -ATE ( if acid -ic ) … - ITE ( if acid -ous ) HYPO- sodium carbonate potassium sulfite sodium hypochlorite iron (II) sulfate Ammonium bromite PER- Names of salts (INN) 1. Salts of binary acids (acids not containing oxygen) genitive form of the cation + ……- IDUM more oxidation states of cation: NaCl AgI KCN ZnS Natrii chloridum Argenti iodidum Kalii cyanidum Zinci sulfuridum !!! lower: higher -osi -i Common elements with two oxidation states in cations FeII Ferrosi FeIII Ferri CuI Cuprosi CuII Cupri HgI Hydrargyrosi HgII Hydrargyri AuI Aurosi AuIII Auri SnII Stannosi SnIV Stanni TlI Thallosi TlIII Thallii Salts of elements with more oxidation states FeCl2 FeCl3 Ferrosi chloridum Ferri chloridum CuI CuI2 Cuprosi iodidum Cupri iodidum Hg2Cl2 HgCl2 Hydrargyrosi chloridum Hydrargyri chloridum 2. Salts of oxyacids cation in genitive + … -AS ( -osi, -i ) … - IS according to acid also: Na2CO3 K2SO3 NaClO FeSO4 NH4BrO2 HYPO- Natrii carbonas Kalii sulfis Natrii hypochloris Ferrosi sulfas Ammonii bromis ( if acid -icum ) ( if acid -osum ) HYPER- Names of hydrogensalts HYDROGEN (numerical prefix if needed) NaHS NaHCO3 KHSO3 sodium hydrogen sulfide sodium hydrogen carbonate potassium hydrogen sulfite Na3PO4 Na2HPO4 NaH2PO4 sodium phosphate sodium hydrogen phosphate sodium dihydrogen phosphate Names of hydrogensalts (INN) prefix: HYDROGENO(numerical prefix if needed) NaHS NaHCO3 KHSO3 Natrii hydrogenosulfuridum Natrii hydrogenocarbonas Kalii hydrogenosulfis Na3PO4 Na2HPO4 NaH2PO4 Natrii phosphas Natrii hydrogenophosphas Natrii dihydrogenophosphas Names of basic salts Mg(OH)Cl Cd(OH)I Al(OH)CO3 Magnesium chloride hydroxide Cadmium iodide hydroxide Aluminum carbonate hydroxide Names of basic salts (INN) prefix: Mg(OH)Cl Cd(OH)I Al(OH)CO3 SUB- Magnesii subchloridum Cadmii subiodidum Aluminii subcarbonas Names of hydrates ….. HYDRATE numerical prefix CuSO4 . 5 H2O copper (II) sulfate pentahydrate MgCl2 . 6 H2O magnesium chloride hexahydrate CaSO4 . 1/2 H2O calcium sulfate hemihydrate anhydrous: Na2CO3 (Only if you want to point out this.) sodium carbonate anhydrous Names of hydrates (INN) ….. HYDRICUS ( -UM) numerical prefix CuSO4 . 5 H2O Cupri sulfas pentahydricus MgCl2 . 6 H2O Magnesii chloridum hexahydricum CaSO4 . 1/2 H2O Calcii sulfas hemihydricus anhydrous: Na2CO3 (Only if you want to point out this.) Natrii carbonas anhydricus Names of polyacids and their salts (Number of central atoms is expressed by numerical prefix) H2B4O7 Na2B4O7 tetraboric acid sodium tetraborate H2Cr2O7 K2Cr2O7 dichromic acid potassium dichromate Names of polyacids and their salts (INN) (Number of central atoms is expressed by numerical prefix) H2B4O7 Na2B4O7 Acidum tetraboricum Natrii tetraboras H2Cr2O7 K2Cr2O7 Acidum dichromicum Kalii dichromas "Functional replacement" derivatives of oxyacids Peroxyacids -O-H group replaced by -O-O-H (HOO)NO2 (HOO)2CO peroxynitric acid diperoxycarbonic acid Thioacids oxygen is replaced by sulfur H2S2O3 H2CS3 ( -O-H replaced by -S-H ) =O replaced by =S thiosulfuric acid trithiocarbonic acid "Functional replacement" derivatives of oxyacids (INN) Peroxyacids -O-H group replaced by -O-O-H (HOO)NO2 (HOO)2CO Acidum peroxonitricum Acidum diperoxocarbonicum Thioacids oxygen is replaced by sulfur H2S2O3 H2CS3 ( -O-H replaced by -S-H ) =O replaced by =S Acidum thiosulfuricum Acidum trithiocarbonicum Double salts (salts containing more than one cation or anion) AlK(SO4)2 CaMg(CO3)2 Aluminum potassium sulfate ZnBrF Cu3(CO3)2F2 Zinc bromide fluoride Calcium magnesium carbonate Copper (II) carbonate fluoride Double salts (INN) (salts containing more than one cation or anion) AlK(SO4)2 CaMg(CO3)2 Aluminii kalii sulfas ZnBrF Cu3(CO3)2F2 Zinci bromidum fluoridum Calcii magnesii carbonas Cupri carbonas fluoridum