Competencies for R&D staff - National Institute for Health Research
advertisement

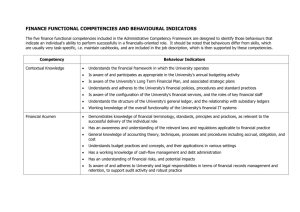
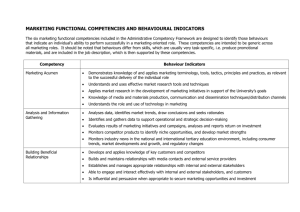
NIHR Research Support Services framework - competencies for Research and Development staff Research Support Services (RSS) framework The NIHR Research Support Services framework helps to make the initiation and delivery of research studies faster and easier. The framework of tools includes an operational capability statement, study planning and risk assessment, guidelines for effective local standard operating procedures (SOPs) and a competency framework to help develop consistent, streamlined and risk-proportionate research management practice across the NHS in England. (www.nihr.ac.uk/systems/Pages/Research_Support_Services.aspx) Competencies This set of practical competencies has been developed by a team of experienced NHS R&D managers who understand what an effective research support team needs to know, understand and be able to do, in order to provide an effective service for health research in an organisation. How to use the competencies These competencies recognise the diversity of roles within organisations and can be used in a “pick and mix” style to suit individual requirements. Each competency has five levels to reflect a range of abilities from a new or inexperienced team member to a proactive leader of activity. The competencies are an aid to identifying and developing skills but it is for managers and team members to decide how they are used and to what level. They are designed to be usable for: Developing job descriptions Assessing current skill levels Working towards new skills and objectives Staff appraisal, performance review and personal development 1 Competencies for R&D staff – November 2013 Level E D C B A A. Supporting (the growth and delivery of) NHS Research within own organisation A1. Strategic context A1.1 National objectives and priorities. Is unaware of national objectives and priorities for research. Is aware of national objectives and priorities for research but is not involved in articulating them. Is able to advise researchers on national objectives and priorities for research. Promotes national objectives and priorities for research. Develops local strategy for research in line with national objectives and priorities. A1.2 Local strategic direction. Is unaware of the local strategy for research. Is aware of the local strategy for research but is not involved in developing or articulating it. Is able to advise researchers on the local strategy for research in their organisation. Promotes the local strategy for research through presentations and training. Sets the local strategy for research in line with national objectives and priorities and ensures its implementation. A1.2 Promotion of research. Is unaware of the need to promote research. Understands the Actively promotes importance of research within own promoting research department. but is not part of their role. Promotes the use of research in evidence based practice and the importance of research to patients and the organisation at an executive level. Engages with external bodies to promote the conduct of research within own and partner organisations. 2 Competencies for R&D staff – November 2013 Level A1.3 Chief executive/Board engagement to support research activity. E Is unaware of the need and benefits of chief executive/Board engagement in research. D C B A Understands the need and benefits of chief executive/Board level engagement in research but is not part of their role. Understands and is proactive in promoting/seeking chief executive/Board engagement to support research in the organisation. Leads on the organisation’s R&D Operational Capability Statement (OCS) for Board consideration and sign off and publication. Understands the importance of keeping the Board aware of key performance indicators (KPIs) for research and keeping the OCS up to date. Identifies and presents opportunities and risks at executive level for consideration and takes proactive action to implement the decisions. Is aware of the organisation’s stakeholders and partnerships but does not understand their role Is aware of the organisation’s immediate stakeholders and partnerships and works effectively with them at a transactional level. Understands how own role and others fit within and complement the range of stakeholders and partnerships and the wider health research agenda (e.g. the NIHR and Health Research Authority). Is able to work strategically with the range of stakeholders and partnerships to deliver the organisation’s objectives. A2. Working with external Partners A2. Stakeholders & Partnerships. Is unaware of the organisation’s immediate stakeholders and partnerships. 3 Competencies for R&D staff – November 2013 Level E D C B A A2.2 Research networks. Is unaware of research networks. Is aware of research networks but unclear of their role. Is aware of and understands the role of research networks and works with them to support researchers and to share information. Works collaboratively with research networks to implement new local initiatives. Takes an active leadership role in driving continuous improvement across research networks to which the organization belongs. A2.3 Industry. Is unaware of the difference between commercial and non-commercial research studies. Is aware of the difference between commercial and noncommercial research studies but is not part of their role. Facilitates the opening of commercial studies at sites. Takes part in feasibility and site selection visits. Facilitates the opening of and extends the oversight of commercial studies to ensure projects are recruiting to time and target. Applies proactive commercial insight to the delivery of R&D in the organisation and takes a strategic view on the importance of working with industry. Understands the wider role of individuals in the team in working effectively and takes care to understand the roles and workloads of others. Actively manages team working and delegates responsibilities where appropriate. Ensures roles and responsibilities for research are clear within the team working environment and facilitates wider collaborative team working between R&D and other departments within own organization and bridging A3. Working as a team to deliver successful research projects A3.1 Team working. Does not understand the role of team working. Understands the role of team working and is supportive of the team helping others where necessary. 4 Competencies for R&D staff – November 2013 Level E D C B A organizational boundaries. A3.2 Good customer Service. Is unaware of the need for good customer service in the department. Understands the need for good customer service and applies it within their role. Promotes and delivers a culture of good customer service across the team. Promotes good customer service and takes action where expectations fall. Is able to create, establish and monitor a good customer service culture in the department and wider stakeholder and partnerships. A3.3 Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs). Is unaware of SOPs in the office. Is aware of the SOPs that are relevant to their role but does not understand the wider implications. Uses SOPs that are relevant to their post, can train others in their use and is proactive in identifying any changes required. Has a full understanding of all SOPs in the department and any updating required and can train others in their use. Reviews and challenges SOPs on local and national merit. A3.4 Role of service support departments. Is unaware of the role of service support departments. Is aware of the role of service support departments in the delivery of research. Is aware of and ensures investigators and other users are aware of the role of service support departments in their research. Uses early assessment tools (e.g. the Research Support Service Framework planning tool). Works with investigators and service support departments from an early point to ensure research gets undertaken and delivered effectively. Engages with support departments to ensure research is appropriately supported and delivered at a strategic level. Takes remedial actions when necessary. 5 Competencies for R&D staff – November 2013 Level E D C B A B. Supporting research projects throughout their lifecycle and managing research delivery B1 Supporting development of new studies – early stages B1.1 Protocol advice. Is unaware of the purpose of a protocol. Is aware of the purpose of a protocol but unable to advise on content. Understands the importance of a robust protocol. Can signpost researchers to research design and other support services. Liaises with the NIHR Research Design Service or other sources of advice and researcher to help ensure a robust protocol is developed. Provides advice to researchers on research methodology and protocol design. B1.2 Sponsorship decisions. Is unaware that decisions are made around sponsorship. Is aware of the information required in deciding to sponsor but is not part of their role. Is able to advise and explain to researchers the information required for the decision to sponsor. Is able to make the sponsorship decision for defined studies. Undertakes the final decision on whether to sponsor a study and ensures that a mechanism for oversight of project is in place. B1.3 Intellectual Property (IP). Is unaware of the meaning of IP. Is aware of IP but does not understand its implications. Has a good understanding of IP. Is able to advise researchers on the organisation’s IP policy. Manages and negotiates research IP on behalf of the organisation. B1.4 Scientific Peer Review. Is unaware of the scientific requirements of a research project. Is aware that research needs to be safe and scientifically sound. Understands the role of peer review. Able to advise others on how to obtain peer review. Has a good working relationship with academic partners and actively promotes scientific review. 6 Competencies for R&D staff – November 2013 Level E D C B A B2 Supporting good financial and contractual management B2.2 Funding for research. Is unaware of the need for research to be financed. Is aware that research needs to be financially supported but unsure of the mechanisms for this. Aware of the different funding avenues for commercial and noncommercial studies. Understands the role of funding bodies, their requirements and the importance of appropriate research funding being available. Actively sources funding solutions locally and nationally for research. B2.3 Funding for research support. Is unaware of the various methods of financially supporting researchrelated services. Is aware that research-related services can be supported from different sources but unsure which is appropriate. Is able to signpost researchers to relevant information on financial support for researchrelated services. Is able to advise researchers on local and NIHR support funding streams. Is able to explain and apply AcoRD and the NIHR funding streams including e.g. Research Capability Funding (RCF). B2.4 Costing a project. Is unaware of the importance of costing a research project. Is aware of relevant costing templates (e.g. NIHR) but does not use them every time. Has a good understanding of research costs, NHS support costs and treatment costs. Can signpost people to the relevant member of staff/source of information. Is able to advise researchers and staff on costing a project. Can complete a simple costing template and negotiate realistic costs. Has a relationship with the service support departments. Ensures that there are agreed processes in place for calculating and accepting project costs. Can negotiate on realistic costs with external partners/ commissioners. 7 Competencies for R&D staff – November 2013 Level E D C B A B2.5 Contracts for research. Is unaware of the need for contracts for research activities. Is aware that contracts can be required but has limited understanding of how contracts affect the study management or the process for creating them. Has a good understanding of contracting with commercial companies and non-commercial organisations. Aware how contracts affect the management of a study and can signpost people to the relevant member of staff/source of information. Works with commercial companies and noncommercial organisations and is aware of when a contract is needed. Can administer noncommercial agreements. Forms a good working relationship with the company and can negotiate a commercial contract and advise researchers on noncommercial contracts. B2.6 Invoicing requirements. Is unaware of the need to invoice for services related to research. Is aware that invoicing is important but is not part of their role. Understands the importance of appropriate invoicing to the organisation and their role in the invoicing process. Proactively manages the invoicing process with colleagues. Oversees systems for invoicing for commercial/other income generating studies. Applies the study planning tools to highlight potential problems/risks. Escalates issues and delegates work to others. Promotes the use of the study planning tools to identify and mitigate risks to research initiation and delivery and reports on their impact. Deals with escalated problems B3. Supporting Feasibility and risk assessments of proposed research B3.1 Research Support Is unaware of study Services (RSS) (includes planning tools other similar in-house variations) planning tools. Is aware of study planning tools but is not part of their role. Understands study planning tools and takes delegated actions from others. 8 Competencies for R&D staff – November 2013 Level E D C B A B3.2 Feasibility process. Is unaware of the need for project feasibility. Is aware that studies should be delivered well but not of the process for deciding the number of participants or resources. Understands the importance of feasibility and is able to deliver a robust method for deciding appropriate numbers of participants and resources. Is able to develop and deliver a robust feasibility review system. Engages with researchers on the importance of feasibility. Manages the feasibility process and ensures researchers are fully aware of their responsibilities around project delivery. B3.3 Proportionate Risk management. Is unaware that projects may have risks and that they need to be treated differently (proportionately). Is aware that projects may have risks that need to be treated differently (proportionately) but does not understand why. Understands what a proportionate risk management assessment is and their own role in making an assessment. Is able to lead a risk management assessment taking pragmatic actions and escalating concerns based upon the results. Is able to advise on legislation and risk and is able to manage study risks proportionately. B3.4 Project recruitment strategy. Is unaware of the need to develop recruitment strategies. Is aware that there is a different recruitment strategy and recruitment process for every study. Understands what can prevent or improve recruitment and can advise on avoiding pitfalls. Is able to explore options with research team and collectively decide on best recruitment strategy. Promotes the development of recruitment strategies. 9 Competencies for R&D staff – November 2013 Level E D C B A B4. Supporting Research Study Management and Delivery B4.1. Research study set-up. Is unaware of what needs to be in place before a research study can start recruiting. Is aware of what needs to be in place before recruitment can start. Is able to advise researchers on what needs to be in place before recruitment can start. Is able to work with researchers to ensure that set up processes are completed in a timely way and allow a prompt start to recruitment. Establishes a system which ensures prompt study set up (post approval) and research team readiness to start recruitment. B4.2 First patient first visit metric. Is unaware of the time within which the first patient should be recruited. Is aware of the first patient metric but is not part of their role. Is able to remind and advise researchers on how to ensure patients are available to a study through robust feasibility. Is able to engage with the research team to ensure patients are available and meet the study criteria. Reports on first patient metric results. Establishes a system for recording and reporting the first patient into a study. Delegates the delivery of the system. B4.3 Meeting the NIHR metrics and contract benchmarks. Is unaware of the NIHR metrics and contract benchmarks. Is aware of the NIHR metrics and contract benchmark requirements at team level but not of any wider implications. Is aware of the NIHR metrics and contract benchmark requirements and their wider importance and impact and is able to advise others. Is able to implement processes and solutions that allow the organisation and investigators to meet the NIHR metrics and contract benchmark requirements. Works with senior staff to develop the strategy to meet the NIHR metrics and contract benchmark requirements and communicates the impact of metrics on the organisation. B4.4 Using internal key performance indicators (KPIs) to Is unaware of the purpose and usage Is aware of KPIs but is not involved in their Is aware of KPIs and uses them at team level to Develops KPIs to report to senior managers on Develops and oversees KPIs and local strategy to ensure performance is 10 Competencies for R&D staff – November 2013 Level E D C B A monitor performance. of KPIs. usage. monitor performance. performance. monitored and reported to the chief executive/Board. B4.5 Supporting research delivery. Is unaware that researchers need to be supported in order to deliver the objectives of the research. Is aware of the need to support researchers to meet the objectives and metrics but not the mechanism for doing so. Understands the importance of supporting research, study recruitment and delivery. Monitors recruitment and escalates concerns. Acts on escalated concerns about delivery and performance and is able to support research teams in developing remedial action plans. Takes an overview of successful and unsuccessful studies and leads on determining the future of those research projects. B4.6 Research management advice for all types of research in which the organisation[s] participate. Is unaware of the requirements of a researcher facing role. Is able to give signposting advice to senior R&D colleagues or to service departments providing support. Is able to provide advice to research teams on good research practice and responsibilities, referring to study protocols and contractual agreements when necessary. Manages the overall delivery of research advice for the organisation. Promotes a holistic view of research and ensures the team has the skills and abilities to support research management. B4.7 Internal and external auditing/monitoring requirements. Is unaware of the need for and learning from robust auditing and monitoring of work undertaken by and of the office. Is aware that regular auditing and monitoring checks need to be carried out but does not understand why. Understands the reasons and information required for audit and monitoring and their role. Is able to implement and advise others on audit and monitoring systems. Establishes an auditing and monitoring system and report on the system outputs to assure key stakeholders of robust governance. 11 Competencies for R&D staff – November 2013 Level E D C B A B4.8 Research Misconduct. Is unaware of the concept of research misconduct. Is aware of the concept of research misconduct but not of the policies and guidance. Is aware of and able to follow policies and guidance on research misconduct and can seek guidance on potential research misconduct issues. Is able to advise staff on the types of situation which may lead to research misconduct. Instigates the appropriate actions in cases of research misconduct. B4.9 Research study closure. Is unaware of the need to close a research study internally. Is aware that research studies need to be closed on internal systems but does not understand how. Is able to monitor the closure of research studies on internal systems. Ensures that appropriate final reporting and close out measures are taken on a study. Ensures research studies are closed and accurate activity reports are made available to the Trust Board and NIHR Networks (B4.3, B4.4). B4.10 Publication and communication of research findings. Is unaware that research findings should be published. Is aware that research findings should be published and can signpost staff to relevant articles. Is able to discuss and advise researchers on the publication of research findings for the Trust and lay audience. Ensures that research findings are published and evidence is acknowledged throughout the life of the project. Through local and national channels actively supports the publication and adoption of research findings into practice. 12 Competencies for R&D staff – November 2013 Level E D C B A C. Understanding Governance and Good Practice for NHS Research (national) C1. Understanding and assessing the regulatory and legislative compliance of a study C1.1 Complying with the Research Governance Framework. Is unaware of the Research Governance Framework (RGF). Is aware of the RGF but cannot describe its purpose. Understands the sections of the RGF that are appropriate to their role. Understands how the framework applies to what they do and can relate it to the role of others in the team. Advises others on the content and application of the RGF. C1.2 NHS local decision process. Is unaware of the local decision process required before a research project can proceed in the organisation. Is aware of their role in the local decision process but cannot describe what others do. Deals with queries relating to their role only but knows who in the department deals with other aspects of a study and can signpost people effectively. Can identify and handle queries relating to their role, understand wider queries and issues and effectively resolve issues in the decision process where required. Manages the decision process as a whole, ensuring it is proportionate to risk and seeks continuous improvement and simplification. C1.3 Regulatory submissions. Is unable to advise or assist with regulatory submissions. Is aware of the process for regulatory submission. Is unable to provide assistance but can signpost people to help. Is able to advise and assist researchers with the completion of regulatory submissions. Is able to develop training and support for researchers on the regulatory submission process. Ensures the team supports researchers in all aspects of the regulatory submission process. 13 Competencies for R&D staff – November 2013 Level E D C B A C1.4 Regulation and Legislation. Is unaware of the regulations and legislation that apply to research. Is aware that there are regulations and legislation that apply to research but cannot describe the requirements in general terms. Is aware of the need for legal and regulatory compliance (in particular CTIMPs, HTA, DPA, role of Caldicott guardian, MCA, IRMER and ARSAC) and is able to describe in broad terms what is required. Is able to apply the appropriate regulations and legislation pragmatically and proportionately to their work. Advises others on appropriate legislation and regulations applicable to their research and is confident in challenging inappropriate or unnecessary application. C1.5 Awareness of Regulatory Bodies in research. Is unaware of the existence of regulatory bodies. Is aware of regulatory bodies but not what they do and/or why. Is aware of regulatory bodies and their role. Understands the role of regulatory bodies, how applications are made and the requirements for approval. Works effectively with regulatory bodies including ethics and MHRA, is confident in understanding their requirements and roles and is able to advise staff appropriately. C1.6 Research Management and Governance systems (IRAS, CSP, NIHR Portal, local research management system). Is unaware of the research management and governance systems and databases used by R&D. Uses research management and governance systems within their role. Uses research management and governance systems pragmatically and proportionately within their role and can run reports from the systems. Understands research management and governance systems and can explain their use to others. Fully understands and actively promotes the use of research management and governance systems and explores their strategic use in supporting the management of research activity and reporting metrics. 14 Competencies for R&D staff – November 2013 Level C1.7 Research in the NHS – HR Good Practice Resource Pack (Research Passport System). E Is unaware of the HR Good Practice Resource Pack. D C B Is aware of the HR Good Practice but is not part of their role. Is able to operate the HR Good Practice Resource Pack system effectively and is able to escalate issues where necessary. Is able to advise and guide others on all aspects of the HR Good Practice Resource Pack. A Deals with escalated problems associated with wider HR contractual processes. C2. Understanding the principles of Good Clinical Practice and Good Research Practice within R&D C2.1 Good Clinical Practice (GCP) and good research practice. Is unaware of the principles and requirements of GCP and good research practice.. Is aware of the principles and requirements of GCP and good research practice but does not understand their application. Understands the principles and requirements of GCP and good research practice and how they apply to different studies i.e. GCP is a legal requirement for regulated clinical trials. Understands all the principles and requirements of GCP and good research practice and promotes training and adherence as applicable. Challenges poor practice according to GCP and good research practice principles and requirements and recommends and secures the necessary improvement. C2.2 Adverse Event Reporting. Is unaware of adverse event reporting. Is aware of adverse event reporting but unsure of the process. Is aware of adverse event reporting and able to handle basic queries about the reporting of adverse events. Is able to handle queries about the reporting of adverse events and can administer the process for reporting adverse events. Acts and advises on the process and requirements for adverse event reporting. C2.3 Breaches of Good Clinical Practice (GCP). Is unaware of GCP. Is aware of GCP but unsure of the process Is aware of GCP and able to handle queries about the reporting of GCP Is able to handle queries about the reporting of GCP breaches and can Is able to act and advise on the requirements of reporting GCP breaches 15 Competencies for R&D staff – November 2013 Level C2.4 Training for researchers. E Is unaware of the different training requirements for different types of research studies. D C B A relating to breaches. breaches. administer the process for reporting GCP breaches. and can secure the necessary improvement. Is aware that different types of training requirements may be needed but is unsure about the detail. Is able to identify different training requirements for different types of research studies and can recommend options. Is able to promote appropriate training and ensure its delivery for appropriate staff. Is able to provide advice on, source and/or deliver training on good research practice. Understands the roles and responsibilities of their organisation as a sponsor and/or host and is able to apply them to their role. Is able to advise others on the roles and responsibilities of sponsor and hosts. Is confident in challenging inappropriate delegation of roles and responsibilities and any breaches of sponsor and host roles and responsibilities. C3 Understanding Research Responsibilities and Roles C3.1 Roles & Responsibilities of Sponsors and Hosts. Is unaware of the roles and responsibilities of sponsors and hosts. Is aware of the roles and responsibilities of sponsor and hosts and that they are different but does not apply them in their role. 16 Competencies for R&D staff – November 2013