Nature of God In Buddhism, Hinduism, Christianity and Islam
advertisement

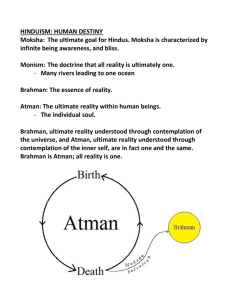
Nature of God In Buddhism, Hinduism, Christianity and Islam Hinduism Brahman – the Ultimate Reality Beyond human experience and comprehension Aspects of this Ultimate Reality can however be understood through deities and avatars (manifestation of a deity on earth) The Vedas Ancient Indian texts that provide the basis of Hinduism for many schools of thought. The Upanishads are the texts at the end of the Vedas They are the basis for more Orthodox Hinduism. In the Vedas we find teachings on the Ultimate Reality and the deities of Hinduism, that Brahman is impersonal and that the deities play important roles in lives of Hindus. The Trimurti Brahman Nirguna Brahman Impersonal, transcendent The negation of all attributes Outside time and space Saguna Brahman The Personal God The Creator (aspects expressed as Brahma, Vishnu and Shiva) These are not separate but both Brahman Buddhism There is no concept of a personal God in Buddhism The world exists as a cause result of cause and effect, not creation In some schools of thought, deities are respected and leant from, but not worshipped. They were humans that attained Nirvana through the same processes as any human Tara Female Bodhisattva in Tibetan Buddhism. Represents success in work and achievements. What does this passage mean? There is grief but none suffering, There is no doer though there is action. There is quietude but none tranquil. There is the path but none walks upon the path. (Buddhaghosa; Visuddhi Magga 16) Task Read and highlight the text Compare and contrast Hindu and Buddhist teachings on the existence of an Ultimate Reality and gods and goddesses. Prep Research Islamic and Christian understandings of the Ultimate Reality. Compare and contrast two concepts of Ultimate Reality (one must be monotheistic) Christianity God is immanent and transcendent God is personal God is experienced in different ways, shown by the Trinity Father Why father? What are the characteristics of an ideal father? Biblical passages – God as father God is a righteous judge, a God who expresses his wrath every day. (Psalm 7:11) Behold, God is my helper; the Lord is the upholder of my life. (Psalm 54:4) It is the LORD your God you must follow, and him you must revere. Keep his commands and obey him; serve him and hold fast to him. (Deuteronomy 13:4) And I will pray the Father, and he shall give you another Comforter, that he may abide with you for ever (John 14.16) Son and Spirit Comforter Sacrifice Saviour Immanent Personal Task Read the Nicene Creed Outline key Christian beliefs on the nature of God Islam Tahwid (Tawhid, Tawheed etc) – concept of uncompromising monotheism in Islam. Allah is one and Allah is unique. This is a teaching at the heart of Islam No one and nothing else is to be prayed to or worshipped. Say 'He is Allah the One' 112:1 Surely Allah alone is the creator of all things and he is the One, the Most Supreme 13:17 Read the first Surah of the Qur’an What does this tell us about Islamic beliefs on the Nature of God? Prep Research characteristics of Allah and compare and contrast them with characteristics of the Christian God. Read and highlight the short essay on Tawhid