Dominance - DrMillsLMU

A Mind of Her Own
Anne Campbell
Chapter 4:
Who does she think she is?
Women and status
Jessica Lyon
Danielle Worrill
Vanessa Koman
Dominance as a Male Goal
Factors affecting status:
Animals:
Physical size and strength
Humans:
Material Wealth
Positions of power
Knowledge and competence of a culturally valued trade
High Status and Reproductive Success through history
In aristocratic societies: Polygamy
Men with wealth and power had many reproductive opportunities
•Resources
•Power
In egalitarian societies: Monogamy
Men with better hunting skills affairs and illegitimate children
•Indispensable to tribe was more likely to have
• Others pledged loyalty for food provided
Recent Trends
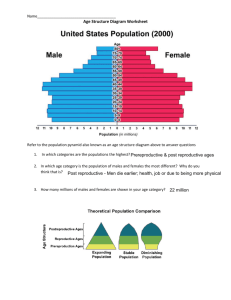
Is there a diminishing relationship between status and reproductive success?
H igh and low status families have comparable numbers of children
Factors contributing to this trend:
Monogamy
Contraception
*
BUT, male competition for dominance is for reproductive access, not number of offspring.
Why Female Dominance Buys
Female reproductive success is defined by the survival of offspring in whom females are already invested
Quantified by:
• Number of offspring born
• Number of young surviving to reproductive maturity
• Age and point in breeding season when first conception occurs
Advantages of Female Dominance
Regular and ample food supply accelerates growth, sustains gestation and lactation, mother’s survival through times of famine
Not subject to harassment less likely to have stress-induced reproductive suppression infants less likely to be harmed by other adults
If rank is heritable, the offspring will also share the same benefits
Who is the Prettiest of them all?
Criteria for high status females:
– Physical attractiveness
– Belonging but not excelling
– To blend in rather than stand out
* To be attractive to boys without alienating other girls
Growing up Competitive behavioral sex differences come about at a very early age cross culturally
Boys
More aggressive
Girls
More cooperative
Prefer playing in large Form “dyads”, “triads” or groups close friends
Resolve problems using Give up on a game when rules arguments arise
65% of free time playing 35% of free time playing games games
Social Dominance
Much more important to boys
Five ways boys use speech to dominate
– Giving orders
– Calling people names
– Threatening/ boasting
– Refusing to obey orders
– Winning arguments
Girls don’t need to do those things
Self Esteem
Boys may use this to hide their actual insecurity
Look for friends with worse performance and worse status to increase their own self-esteem
Men do not discuss deep topics with other men for fear of it leaking out and ruining their reputation
Men and Friendships
Not too many close male friendships
See male-female relationships as more meaningful and intimate
Don’t think much if a friendship fades or is lost
Women and Status
Humans prefer patrilocal residence
Girls are less competitive than boys and solve disagreements verbally
more concerned with intimacy and equality
Women as leaders
• Women downplay their abilities and intelligence
• more likely to rule democratically as opposed to ruling like a dictator
• female co-workers conversations
• Women trade high status for femalefemale friendships
Why winning is Dangerous
• Benefits
-Females get resources necessary for offspring survival
-males get a “ticket in the copulatory lottery of possible fatherhood”
• Costs
Competition can be deadly
“failed revolution” for female bonded primates
death of offspring
human females fear for their reputation & fears being excluded from their clique
• winning for females, leads to rejection
Agency vs. Communion
Agency
-individual
Communion
-merge
Circumplex Model of Personality
Dominance
Hostility
Submission
Nurturance
•
Bems Sex-Role Inventory
•
Instrumentality and
Expressiveness - Spence
Female bonds
Chimps; non Bonded females
The socialization of
Bonobos
Lemurs, Baboons, vervets, macaques
The role of Food in
Dominance
Dominance Hierarchy in Primates
Lemurs, Baboons, vervets, macaques
The role of Food in
Dominance
Dominance
• Matril Line dominance
• A F……Z
Mother
2 nd daughter first daughter
new females enter at the bottom
Beneficial for females to become high ranking
Gender Knowledge vs. Gender
Differences
Stereotypes
Can children I.D. gender differences
Gender Differences
What happens when one identically twin boy is raised as a girl?
Lesions in the
Female and Male brain
Characteristics of socially accepted males and females picture compliments of twins realm.com