class 23 self affirmation
advertisement
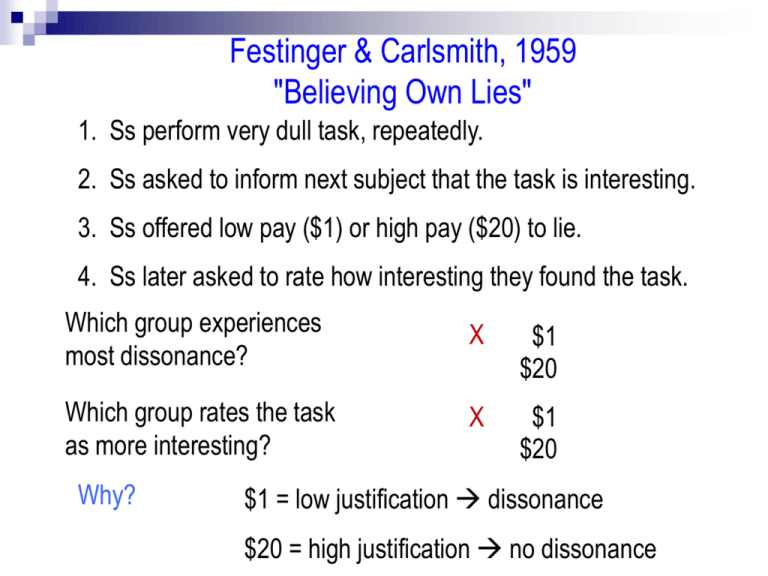
Festinger & Carlsmith, 1959 "Believing Own Lies" 1. Ss perform very dull task, repeatedly. 2. Ss asked to inform next subject that the task is interesting. 3. Ss offered low pay ($1) or high pay ($20) to lie. 4. Ss later asked to rate how interesting they found the task. Which group experiences most dissonance? X $1 $20 Which group rates the task as more interesting? X $1 $20 Why? $1 = low justification dissonance $20 = high justification no dissonance Dissonance and Behavioral Control: Robbie the Robot Study Lepper, 1972 1. Child rates toys, including desirable "Robbie the Robot". 2. E. leaves room, tells child "don't play w' Robbie, and if you do:" a. Low threat: I will be a little annoyed with you. b. High threat: I will be very angry, and will do something. 3. Child returns to study later, new E., can play with any toy including R. the R. 4. Which child plays w' R the R? Low threat or high threat? Why? Low threat X High threat Low threat = under-justification dissonance Why? Dissonance Disrupts Behaviorism Premise of behaviorism: Punishments are negatively reinforcing. Question: What conditions produce more liking of neutral stims? Neutral Stimuli Reinforcement Beh. Predicts CD Shows Dull discussion group Embarrassment Dislike Liking Fill bin with spools Low pay Dislike Liking Mediocre toys Punishment threat Dislike Liking Self Perception Theory Challenges Cog. Dissonance Cog. Dissonance Theory: Discordance btwn. actions and beliefs creates negative arousal. Hence, dissonance is motivational/affective Daryl Bem: No need to posit any underlying arousal. Could be purely self-perception. People evaluate own actions as they would others. NOTE: Harks back to "Symbolic Interactionism" No internal conflict or complex motives, just attributions based on self-observed behavior. Testing Self-Perception Vs. Dissonance Bem & McConnell, 1970 Premise: We infer own attitudes from our most recent behavior. Beh. due to "insufficient justification", infer corresponding attitude. After new attitude adopted, old attitude will be forgotten. No "change in attitude" Instead earlier attitude "overwritten" by self-perceived new attitude. Method: Counter-Attitudinal Essay, low justification vs. high justification DV: Attitude recall Result: Which group better recalls initial attitude, low or high justification? High justification. Why? Saw selves voicing views under powerful external pressure. Views voiced under pressure probably not sincere. Arousal as a Necessary Condition for Cog. Diss. and Attitude Change Cooper, Zanna, & Taves, 1978 Premise: Damn you Bem, it is arousal!!!! If arousal, then if arousal dampened, less CD; if arousal boosted, more CD "Attitudes will change following counter-attitudinal behavior if and only if arousal accompanies behavior." Method: Ss complete counter-attitudinal essay--"Should Richard Nixon be pardoned?" Either high-choice or low choice conditions. Before essay, as part of "separate study" Ss ingest pill. Told it is placebo but in actuality it is either: tranquilizer, placebo, amphetamine Tranquilizer Predict: Attitude change in "high choice" but not if pill is _____________? Arousal as a Necessary Condition for Cog. Diss. and Attitude Change Cooper, Zanna, & Taves, 1978 Tranq'zer Class 21: Self Affirmation Name Calling, Compliance, and an Alternative Means to Dissonance Reduction Steele name-calling study: Most dissonance studies involve S seeing self behaving contrary to self-image. What if outside person did so? Method: Calls housewives in Utah (why Utah?) Housewives in one of four extp'l conditions X 1. 2. 3. 4. Relevant negative name: "you are not cooperative" Relevant positive name: "you are cooperative" Irrelevant negative name: "you are a bad driver" No contact control group. DV: Compliance with food co-op request, to list all foods, 2 days later. According to Dissonance, which group should comply? Name Calling and Compliance Compliance Steele, 1985 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Relevant Negative Relevant Positive Irrelevant Negative What explains this result? Why didn't earlier CD research show similar result? Control Never checked! The Role of the Self in Cognitive Dissonance Dissonance induced by: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Writing essays you don’t believe in. Reading lurid sexual text in front of leering experimenter Lying about interest value of boring task for just $1.00 Breaking a stranger’s camera Eating grasshoppers with minimal incentive Waiting until 4:30 AM for space ship that never arrives Experientially, what do these situations have in common? Make people feel badly about themselves. Principles of Self Affirmation Theory 1. People have a basic need to maintain fundamental sense of self as worthy 2. After self worth has been threatened, people are motivated to restore general integrity, not simply correct the specific threat. 3. Motive to correct a specific threat is lessened after restoring general sense of worthiness. Logic of Self Affirmation vs. Dissonance Fred is a smoker. Fred sees self as smart and sane. Smart, sane people don’t smoke. How can Fred reduce psychological threat? Cog. Diss Self-Affirm Change behavior "OK, I'm quitting" Y Y Rationalize "I watch diet, so I'll be OK" Y Y Boost self-worth "I just published an article on cognitive dissonance!" N Y Countering Dissonance by Affirming Values: Steele & Lui, 1981 Complete Poli/Econ Values Survey Hold Poli/ Econ Values Don’t Hold Poli/Econ Values Low Justification (High Choice) High Justification (Low Choice) No Attitude Change Attitude Change No Attitude Change No Attitude Change Dissonance and Values Affirmation Steele & Lui, 1981 12 Compliance 10 8 6 4 2 0 Low Choice High Choice/No Aff. High Choic/Val. Irrel. What explains this result? Why didn't earlier CD research show similar result? High Choice/Val Rel. Never checked! Dissonance and the Lab Coat Steele & Lui, 1983 Ss pre-identified: science oriented or not science oriented Ss rate record albums: can choose 5th or 6th favorite (choice cond) are given either 5th or 6th favorite (no-choice cond) While "ratings are reviewed", Ss go to "second study" Second study: wear lab coat / don't wear lab coat Ss return to Study 1, reveal "true attitudes" re. albums DV: Degree of attitude change regarding albums No Lab Coat Lab Coat Not Sci. oriented Attitude change Attitude change Sci. oriented Attitude change No Attitude change Dissonance and the Lab Coat Steele & Lui, 1983 Degree of Attitude Change 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 No Lab Coat Lab Coat 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 Not Science Oriented Science Oriented Self Affirmation and the Need to Judge Others Lui & Steele, 1986 Judging others is pleasurable. More likely to judge others when we feel less in control. Why? Would affirmation affect tendency to judge others? Why? Helplessness Only Helplessness + Affirmation Not Econ/Political Values Oriented High Judging High Judging Econ/Political Values Oriented High Judging Low Judging Self Affirmation and the Need to Judge Others Lui & Steele, 1986 7 Judging Others 6 5 Helplessness Only Helplessness +Affirmation 4 3 2 1 0 Not ValueOriented ValueOriented Reducing Biased Evaluation by Affirming the Self Cohen, Aronson, & Steele, 2000 Premise: People hold firmly to opinions, esp. those connected to core values. Would flexibility re. opinions relax if self-worth affirmed. (Why?) Method: Ss pre-selected on favoring/not favoring capital punishment. Ss also rank personal values "Sources of Validation" scale Ss told study concerns memory, Complete "Personal Memory Exercise": Affirmation Cond: Describe 3-4 instances where they upheld top source of validation (from S of V) scale Control Cond: List everything they ate last 48 hrs. Ss read & recall capital punish. essay opposed to their views DV: How favorably is anti-attitude essay evaluated? Reducing Biased Evaluation by Affirming the Self Favorability Rating Cohen, Aronson, & Steele, 2000 0.25 0.2 0.15 0.1 0.05 0 -0.05 -0.1 -0.15 -0.2 -0.25 -0.3 Affirmed Not Affirmed Self Affirmation Questions 1. If one kind of self-insult (i.e., dissonant behavior, lack of control) can be redeemed by a very different kind of self-relevant behavior (i.e., recalling personal values, wearing a lab coat, cooperating with crazy survey) what does this say about the nature of the self? Is the self a unified whole or a conglomeration of parts? 2. How would self affirmation affect the tendency to self-blame following a tragedy over which one has objectively little control (like earthquake)? Why?








