Internal Controls - Financial Management Services
advertisement

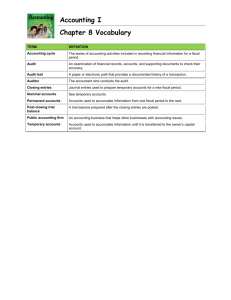
Session Objectives • Understand and apply INTERNAL CONTROL concepts to accomplish your organization’s objectives • RISK Assessment and Management • ETHICAL VALUES and CONDUCT Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Why should you care? Internal Controls minimize the RISKS to your Organization!!! Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 RISKS your Organization faces • Financial Reporting • Compliance • Operational • Loss of Assets Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Financial Institutional Policy I-1 Role of Fiscal Officer, Account Manager, and Account Supervisor. • Account Supervisor has a leadership or executive role. • Account Manager has an operational role. • Fiscal Officer has an oversight role. Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 It’s your Job Financial Institutional Policy I-1 “…trained and hired for the purpose of providing fiscal, policy, and internal control management of all funds...” “…responsible for ensuring that processes and related controls have been established to achieve the mission and objectives of their organization(s). “ Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 What is Internal Control Internal control is a PROCESS of specific policies and procedures designed to provide reasonable assurance that organization’s objectives will be met •Provide reliable financial reporting •Promote efficient and effective operations •Helps ensure compliance with policy •Protect University Assets Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Internal Control Components Information Monitor Performance Establish Control Environment Perform Risk Assessment Implement Control Activities Communication Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 and and Goals & Objectives Control Environment TONE AT THE TOP – Integrity, ethical values, and behavior of management – Management’s control consciousness – Management’s commitment to competence It’s the way you do Business – Organization structure – Assignment of authority and responsibility – Policies and practices Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 What do we mean by “Tone at the Top” ? • Promote ethical • • • • • values & conduct Walk the walk Lead by example Be approachable Compliance w/Policy Don’t circumvent rules • Full disclosure • Fix problems • Equal treatment for • • equal offenses Reward things that are done right Hug your Auditor Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Questions • Which attributes of a Super Fiscal Officer can be useful in exhibiting a strong “Tone at the top”? • When should you be demonstrating a strong “Tone at the top”? Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Defining Ethics? eth·ic Pronunciation: 'e-thik Function: noun from Greek Éthos, Date: 14th century 1 the discipline dealing with what is good and bad and with moral duty and obligation 2 a: a set of moral principles or values b : the principles of conduct governing an individual or a group <professional ethics> Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Defining Ethics? ”Doing the right thing” Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 What’s the Right Thing? “What are the Rules” Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Ethical Rules? • Is it legal and in compliance with • • IU policy? Is it fair? – Honest, truthful, responsible, trustworthy, respect individual Would it pass the newspaper test (or the Mom test)? Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Why Ethics are important to your Organization? Responsibility Regulatory requirements Return on integrity (the other ROI) Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Responsibility/Regulatory requirements • Expected to be good stewards of $ given to us by – State/Feds – Students – Parents – Donors Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Return on integrity (the other ROI) Good Ethics = Good Business – Better employee decision making – Greater employee commitment to the organization – Reduced unethical or illegal behavior – Better work environment – Better reputation and image for IU Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 ETHICS Closing Thoughts Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Silence is NOT Golden • Speak out! • Be outraged! • Silence implies your consent!! Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Important to talk • Transparency • Get other perspectives/input • Hopefully Consensus Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Who you going to call? • Supervisor • Human Resources • Purchasing • Accounting/FMS • University Legal Counsel • Internal Audit • Police Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Causes of Ethical Failures 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. NO “Tone at the Top” NO Consistency Train Wrecks Fear of Retaliation No Reporting Mechanisms No Education, Communication or Tools Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Factors of an Ethical Environment • Integrity of senior management – Are they leading by example? Walking the talk? • Clear ethical expectations – Stake in the ground (Code of Ethical Conduct, discussions) – Understand why • Consistency – Doesn’t count unless price is paid • What else? Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 QUESTION What specifically are you going to do to promote a strong ethical environment in your organization? Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Written goals and objectives? • Internal control is pointless without goals and objectives. • Written goals and objectives focus efforts toward desired outcomes. • Written goals and objectives provide a rationale for resource allocation. • Written goals and objectives are evidence of thoughtful management. Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 What objectives do we need? • Mission statement. • Operations objectives. • Financial reporting objectives. • Compliance objectives. • Objectives for all significant activities. Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 What are risks? • A risk is anything that could jeopardize the achievement of your organization’s objective. – Operate effectively and efficiently and achieve our goals – Provide reliable financial data – Comply with applicable laws, policies, and procedures – Protect the university’s assets from loss Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Risk Assessment is a process to • Identify significant risks • Assess risks • – What is the likelihood of occurrence? – What is the potential impact? Manage these risks through • Avoidance • Acceptance and Sharing (Insurance) • Mitigate with Controls Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 How do we identify risks? • You know your risks. • For each objective, ask yourself: – What could go wrong? – What assets do we need to protect? – How could someone steal from us? – What is our greatest legal exposure? – What else? Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Assess Risks • Likelihood – probability of occurrence • Impact – effect on IU/your organization – Loss of resources – Loss of public trust – Violation of policies, laws, regulations – Bad publicity – Decreased enrollment – What else? Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 QUESTION What are the three major RISKS facing your school or department? Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Internal Control Components Information Monitor Performance Establish Control Environment Perform Risk Assessment Implement Control Activities Communication Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 and and Goals & Objectives Control Activities • The policies and procedures that help ensure that actions identified as necessary to manage risks are carried out properly and in a timely manner – must be implemented thoughtfully, conscientiously, and consistently – unusual conditions identified must be investigated and appropriate corrective action taken – Should be proactive, value added, and cost effective Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Control Activities • Approvals, Authorizations, and Verifications – Having written policies and procedures and limits to authority • Reconciliations – Explanations of the differences between two different sets of data Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Control Activities • Reviews of Performance – For programs, departments, and individual employees • Security of Assets – Limiting access, keeping records, and making periodic counts to compare to our records Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Control Activities • Segregation of Functions – The approval, recording/reconciling, and custody functions should be segregated • Controls over Information Systems – Application and development, controls within applications, security of data and machines Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 What control activities do I need? • Enough to help ensure that you are managing • • your significant risks. Actions should be taken and control activities should be performed to mitigate significant risks to acceptable levels. An action to manage a risk can be anything. Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 What needs to be approved? • Per policy, all financial transactions must be approved by the dept Fiscal Officer. – FO can delegate signature authority • What to approve and what to delegate? • Generally, the higher the risk activities the higher level of approval/authorization. Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 What needs to be reconciled? • Information about high risk activities should be • • • reconciled to ensure its accuracy and completeness. Monthly operating reports must be reconciled to departmental records. Payroll voucher reports should be reviewed and compared to departmental records. What else? Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 What activities should be reviewed? • Information about high risk activities must be • reviewed by management. Generally, the Chair/Director/PI should review reports which compare budget to actual – To measure performance. – To detect problems. • Performance reviews of staff • Management’s review should be documented. Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 What assets need to be secured? • Liquid assets, assets with alternative uses, • • dangerous assets, vital documents, critical systems, and confidential information need to be secured. Access to these assets should be restricted. Perpetual records should be maintained; periodic physical counts should be performed-differences should be checked. Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 What duties need to be segregated? • It depends on the risk assessment • The approval, accounting/reconciling, and asset custody functions should be segregated. • Generally, duties related to cash receipts, payroll and purchases are high risk and should be segregated. Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 How do we control our computers? • It depends on the risk assessment • If critical or confidential information then both • the information and the computer need to be controlled. Basic controls are – Password protecting information. – Backing-up information. – Virus Scanning – Practicing safe computing – What else? Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Internal Control Components Information Monitor Performance Establish Control Environment Perform Risk Assessment Implement Control Activities Communication Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 and and Goals & Objectives Information and Communication • Communicate policies and procedures – Supervisors and employees understand objectives and job responsibilities • Get the information you (and staff) need • Do performance evaluations • Measure customer satisfaction • Open door policy – Hear the good and the bad news Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Monitor Performance • Evaluating your Internal Controls to determine – Adequately designed – Properly executed, and – Effective • How can we KNOW? Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 How can we KNOW? – Ongoing supervisory activities – Look at your processes – Periodic evaluations • Self-assessment • Peer review • Internal audit • External audits Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Monitor Performance • Internal Controls are effective if you know: – The extent to which your organization’s goals and objectives are being achieved – In compliance with relevant policies, etc. – Financial records are reliable – Assets are safeguarded – Resources are use to advance organization’s mission Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Who is Responsible for Control? •EVERYONE • Management is responsible for establishing a controlled environment. • Faculty and staff are responsible for carrying out internal controls by following policies and procedures. • Internal Audit, in an advisory/consultant role, is responsible for evaluating whether appropriate controls have been implemented and if they are functioning as intended . Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Internal Control • Is a Process • Designed to provide reasonable assurance that organization’s objectives will be met – Provides reliable financial reporting – Promotes efficient and effective operations – Helps ensure compliance with policy – Protects university Assets Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Why Internal Controls fail? • Human Errors - Bad Judgment • Management Override • Collusion • Cost versus Benefit Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Internal Control components Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Organizational Objectives Identify & Assess Risks Identify Current Controls Identify & Assess Residual Risks Action Define Organization’s Goals and Objectives? l Define goals and objectives in relation to l Mission, l Activities and processes, l Financial reporting requirements, and l Compliance issues Acceptable No Yes Document Risk Acceptance Decision Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Organizational Objectives Identify & Assess Risks Identify and assess potential RISKs by asking What Could Go WRONG ? What must go RIGHT? Identify Current Controls Identify & Assess Residual Risks Action How likely is it that the risk will happen? What will be the impact) if it happens? Acceptable No Yes Document Risk Acceptance Decision Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Organizational Objectives Identify & Assess Risks What controls are in place to achieve your objectives ? l Identify Current Control s Identify & Assess Residual Risks Action l Acceptable No Yes l Control Environment l Tone at Top l Competence l Roles & Responsibilities Information & Communication Control Activities Document Risk Acceptance Decision Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Organizational Objectives Identify & Assess Risks What could still go wrong given existing controls ? l Look at your risks, and your existing controls to identify any gaps. Identify Current Controls Identify & Assess Residual Risks Action Acceptable No Yes Document Risk Acceptance Decision Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Organizational Objectives Identify & Assess Risks Identify Current Controls Can you live with the Residual Risk ? l l Do your existing controls, provide reasonable assurance that you will get achieve your objectives? Something's you can’t control (changes in government regulations, weather) Identify & Assess Residual Risks Action l Acceptable Risk acceptance decision will depend on the culture of the organization No Yes Document Risk Acceptance Decision Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Organizational Objectives Identify & Assess Risks Identify Current Controls Action Planning l If the level of uncontrolled risk is too high/unacceptable then action plans are developed to reduce the residual risk to an acceptable level. Identify & Assess Residual Risks Action Acceptable No Yes Document Risk Acceptance Decision Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Group Exercise • Case Study • Planning a SURPRISE 50th Birthday Party for your spouse • Objectives • identify • Risks • identify and assess Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 SURPRISE 50th Birthday Party • OBJECTIVES • Risks Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Assess Risk Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 SURPRISE 50th Birthday Party • Controls – Control Environment - Competent team – Budget with authorizations and approvals – Segregation of Functions – Reconcilations – Controls over Information Systems • Residual Risks –? Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Identify Controls Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 QUIZ - Internal control is a • PROCESS of specific policies and procedures • Designed to provide reasonable assurance that organization’s objectives will be met – – – – Provide reliable financial reporting Promote efficient and effective operations Helps ensure compliance with policy Protect university Assets Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Who is Responsible for Control ? • In a word, everyone • Management is responsible for establishing a controlled environment. • Faculty and staff are responsible for carrying out internal controls by following policies and procedures. • Internal Audit, in an advisory/consultant role, is responsible for evaluating whether appropriate controls have been implemented and if they are functioning as intended. Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 QUIZ • Name four Control Activities: 1. 2. 3. 4. Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 QUIZ The most important Internal Control component is: 1. Risk assessment/management process 2. Hug your auditor 3. Positive “Tone at the Top” 4. Strong ethical climate 5. Control environment with answers 3 & 4 Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Quiz Risk Assessment/Management is: 1. Planning a surprise birthday party 2. A department at IU 3. A process to assess risks and controls as they impact on the achievement of a business objective Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 QUIZ Effective Internal Control Systems will: 1. Provide reasonable assurance that your 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. organizations objectives will be met Promote reliable financial reporting Provide efficient and effective operations Help ensure compliance with policy Protect university assets All of the above Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Quiz? • Short Definition of Ethics? • What are the Rules? Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Quiz • Short Definition of Ethics? – “Doing the Right Thing” • What Are the Rules? – Moral Values (Is it fair?)? – Is it legal and in compliance with IU policy? – Would it pass the newspaper test (or the Mom test)? Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008 Case Study • Identify 1- 3 SMART OBJECTIVES • Identify the 1- 3 possible RISKs that would prevent you from achieving your objectives • List the CONTROLS you would implement to mitigate these risks Fiscal Officer Development Series September 11, 2008