The Role of Feedback in Instructional Design and Student Assessment
advertisement

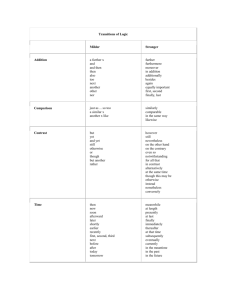
Teaching for Fluency with Information Technology: The Role of Feedback in Instructional Design and Student Assessment Explorations in Instructional Technology Mark Urban-Lurain Don Weinshank October 27, 2000 www.cse.msu.edu/~cse101 Overview Context: Teaching non-CS majors Instructional Design Uses of technology Results Implications Fluency with Information Technology What does it mean to be a literate college graduate in an information age? Information technology is ubiquitous “Computer Literacy” associated with training Being Fluent with Information Technology (FIT) Committee on Information Technology Literacy, 1999 CSE 101 MSU introductory course for non-CS majors Instructional Principles 1. Concepts and principles promote transfer within domain 2. “Assessment drives instruction” (Yelon) 3. Study – test – restudy – retest Performance assessments evaluate mastery of concepts 6. Student-centered Formative evaluation improves student performance 5. “Write the final exam first” Move focus from what is taught to what is learned 4. Necessary for solving new problems High inter-rater reliability critical Mastery-model learning ensures objectives met What students can do, not what they can say Uses of Technology in Instruction Delivery of content Communication Television CBI / CBT Web-based E-mail Discussion groups Real-time chat Feedback and monitoring Formative evaluation Iterative course development and improvement Course Design & Implementation Design Phase Design Inputs Instructional Goals Instructional Design Implementation Phase Instruction Incoming Students ` Assessment Outcomes Discriminant Analysis Multivariate statistical classification procedure Dependent variable: final course grade Independent variables Each student classified in group with highest probability Incoming student data Classroom / instructional data Assessment performance data Evaluate classification accuracy Interpret discriminant functions Independent variable correlations with functions Similar to interpreting loadings in Factor Analysis Skill to Schema Map 4 Update SS Link Web search 7 New SS Charts Path Functions Public folder Computer specs. Footnote Modify style Web format Private folder URL 3 TOC Find rename file Find application Boolean search 2 6 5 SIRS: Course, TA, ATA End of semester student survey about course Three Factors SIRS for Lead TA “Fairness” Student preparation and participation Course resources One Factor SIRS for Assistant TA One Factor Fairness Factor 35.3% of variance on this factor accounted for by: Final grade in course TA SIRS Number of BT attempts ATA SIRS Cumulative GPA ACT Mathematics Computer specifications Incoming computer communication experience Participation Factor 19.8% of variance on this factor accounted for by: TA SIRS Attendance ATA SIRS ACT Social Science Number of BT attempts Create chart Incoming knowledge of computer terms ACT Mathematics Find - rename file Path TOC NO course grade Course Resources Factor 11.3 % of variance on this factor accounted for by: TA SIRS Attendance ATA SIRS Extension task: backgrounds Web pages in Web folder Number of BT attempts NO course grade Lead TA SIRS 27.8 % of variance on Lead TA SIRS accounted for by: Fairness factor Preparation and participation factor TA Experience Course resources factor ATA SIRS Attendance Private folder Extension task: excel function Number of BT attempts NO course grade Assistant TA SIRS 13.4 % of variance on ATA SIRS accounted for by: Fairness factor Preparation and participation factor Student E-mail factor TA SIRS Course resources factor Attendance Path TA Experience NO course grade Technology in Instructional Design and Student Assessment Data-rich instructional system Performance-based assessments Detailed information about each student CQI for all aspects of instructional system Labor intensive Inter-rater reliability Analyzing student conceptual frameworks Intervention strategies Early identification Targeted for schematic structures Implications Instructional design process can be used in any discipline Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology CQI Distance Education Demonstrates instruction at needed scale On-line assessments How to provide active, constructivist learning on line? Questions? CSE 101 Web site www.cse.msu.edu/~cse101 Instructional design detail slides Design Inputs Design Inputs • • • Literature • CS0 • Learning • Assessment Client department needs Design team experience Instructional Goals Instructional Goals • • • • • FITness Problem solving Transfer Retention No programming Deductive Instruction Skill 1 Skill 2 Concept Skill 3 Inductive Instruction Schema 1 Schema 2 Skill 1 Skill 2 Concept Skill 3 Schema 3 Instructional Design Instructional Design • • • • • 1950 students / semester Multiple “tracks” • Common first half • Diverge for focal problems All lab-based classes • 65 sections • No lectures Problem-based, collaborative learning Performance-based assessments Incoming Students Incoming Students • Undergraduates in non-technical majors • GPA • ACT scores • Class standing • Major • Gender • Ethnicity • Computing experience Instruction Instruction • • • • • Classroom staff • Lead Teaching Assistant • Assistant Teaching Assistant Lesson plans Problem-based learning • Series of exercises Homework Instructional resources • Web, Textbook Assessment Assessment • • • • Performance-based Modified mastery model Bridge Tasks • Determine grade through 3.0 • Formative • Summative Final project • May increase 3.0 to 3.5 or 4.0 Bridge Task Competencies in CSE 101 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 Advanced Web site creation; Java Applets; Object embedding 3.0 Track C E-mail; Web; Distributed network file systems; Help Bibliographic databases; Creating Web pages Advanced Word-processing Spreadsheets (functions, charts); Hardware; Software Track A Advanced spreadsheets; Importing; Data analysis; Add-on tools 3.0 Track D Advanced spreadsheets; Fiscal analysis; Add-on tools Bridge Task Detail Drilldown 1 Creating Assessments Bridge Task (BT) Database • Each Bridge Task (BT) has dimensions (M) that define the skills and concepts being evaluated. • Within each dimension are some number of instances (n) of text describing tasks for that dimension. • A bridge task consists of one randomly selected instance from each dimension for that bridge task Dim 1 Dim 2 Instance i Instance i+1 Instance i+2 Instance i+n Instance i Instance i+1 Instance i+2 Instance i+n Dim M Instance i Instance i+1 Instance i+2 Instance i+n Evaluation Criteria Student Evaluation PASS or FAIL Bridge Task (BT) Database Dim 1 Dim 2 Instance i Instance i+1 Instance i+2 Instance i+n Instance i Instance i+1 Instance i+2 Instance i+n Dim M Instance i Instance i+1 Instance i+2 Instance i+n Dim 1 Instance 1 Dim 2 Instance i+2 Dim M Instance i+n Criteria i Criteria i+1 Criteria i+2 Criteria i+n Criteria i Criteria i+1 Criteria i+2 Criteria i+n Criteria i Criteria i+1 Criteria i+2 Criteria i+n Bridge Task Detail Drilldown 2 Delivering Assessments Student Enters: Pilot ID PID PW Submits to Web Server Create Query Student Records Database Request New BT Individual Student BT Web Page Assemble Text Returns Web Server Dim 1 (i+1) Dim 2 (i+n) Dim M (i) Bridge Task (BT) Database Randomly select one instance from each of M dimensions for desired BT Dim 1 Dim 2 Instance i Instance i+1 Instance i+2 Instance i+n Instance i Instance i+1 Instance i+2 Instance i+n Dim M Instance i Instance i+1 Instance i+2 Instance i+n Evaluating Assessments Grader Queuing Create Query Dim M Criteria Dim 2 Criteria Dim 1 Criteria Student Bridge Task Grader evaluates each criteria PASS or FAIL Student Records Database Request Criteria Individual Student BT Checklist Returns Bridge Task (BT) Database Record PASS / FAIL for each criteria Provide criteria for instances used to construct student’s BT Student Records Database Dim 1 Dim 2 Criteria i Criteria i+1 Criteria i+2 Criteria i+n Criteria i Criteria i+1 Criteria i+2 Criteria i+n Dim M Criteria i Criteria i+1 Criteria i+2 Criteria i+n Outcomes Outcomes • • • • • Student final grades SIRS TA feedback Oversight Committee: Associate Deans Client department feedback