matlab iv
advertisement

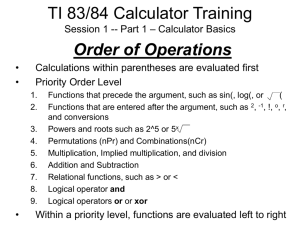
Mathematics
Roots, Differentiation and Integration
Prof. Muhammad Saeed
1. r = roots(p)
2. r = fzero(func,x0),
3. r = fzero(func,[x1 x2])
a) r = fzero('3*x^3+2*x^2-5*x+7',5)
b) r = fzero(@myfun,x0)
c) r = fzero(@(x) exp(x)*sin(x),x0)
d) Hfnc = @(x) x^2*cos(2*x)*sin(x*x)
r = fzero(Hfnc, [x0 x1])
4. a= 1.5; r = fzero(@(x) myfun(x,a),0.1)
5. options = optimset('Display','iter','TolFun',1e-8)
opts=optimset(options,'TolX',1e-4)
r = fzero(fun,x0,opts)
Mathematical modeling & Simulations
2
6. [r,fval] = fzero(...)
7. [r,fval,exitflag] = fzero(...)
8. [r,fval,exitflag,output] = fzero(...)
output.algorithm :
output.funcCount
output.intervaliterations:
output.iterations:
output.message:
Algorithm used
Number of function evaluations
Number of iterations taken to find an
interval
Number of zero-finding iterations
Exit message
ExitFlags
1
-1
-3
-4
-5
9.
Function converged to a solution x.
Algorithm was terminated by the output function.
NaN or Inf function value was encountered during search for
an interval containing a sign change.
Complex function value was encountered during search for an
interval containing a sign change.
Algorithm might have converged to a singular point.
[….. ] =fminbnd(…)
Mathematical modeling & Simulations
3
[r,p,k] = residue(b,a)
[b,a] = residue(r,p,k)
b( s ) 7 S 3 4 S 2 8 S 1
3
a(s) 2S 3S 2 7S 9
1. Symbolic
a.
syms x t z alpha;
# int(-2*x/(1+x^2)^2)
# int(x/(1+z^2),z)
# int(x*log(1+x),0,1)
# int(2*x, sin(t), 1)
Mathematical modeling & Simulations
4
2. Numerical
#
#
Z = trapz(Y)
Z = trapz(X,Y)
Example: IntegralTrapz.m
Z = quad(hfun,a,b)
Z = quad(hfun,a,b,tol)
[Z,fcnt] = quad(...)
Z= quad(@fun,a,b)
[Z, fcnt]=quad(……)
Z=quad(fun,a,b,tol,trace)
Z=quadl(……..)
#
#
#
#
#
#
#
“The quad function may be most efficient for low accuracies with
nonsmooth integrands. The quadl function may be more efficient
than quad at higher accuracies with smooth integrands.”
Mathematical modeling & Simulations
5
q = quadgk(fun,a,b)
[q,errbnd] = quadgk(fun,a,b,tol)
[q,errbnd] = quadgk(fun,a,b,param1,val1,param2,val2,...)
[q,errbnd] = quadgk(@(x)x.^5.*exp(-x).*sin(x),0,inf,
'RelTol',1e-8,'AbsTol',1e-12)
“The ‘quadgk’ function may be most efficient for high accuracies and oscillatory
integrands. It supports infinite intervals and can handle moderate singularities at
the endpoints. It also supports contour integration along piecewise linear paths.”
q = dblquad(fun,xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax)
q = dblquad(fun,xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax,tol)
q = dblquad(fun,xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax,tol,method)
q = dblquad(@(x,y)sqrt(max(1-(x.^2+y.^2),0)), -1, 1, -1, 1)
triplequad(fun,xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax,zmin,zmax)
triplequad(fun,xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax,zmin,zmax,tol)
triplequad(fun,xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax,zmin,zmax,tol,method)
F = @(x,y,z)y*sin(x)+z*cos(x); Q = triplequad(F,0,pi,0,1,-1,1);
1.
Symbolic
•
syms x
•
2.
f = sin(5*x)
g = exp(x)*cos(x); diff(g); diff(g,2)
syms s t
f = sin(s*t) ;
diff(f,t) ;
diff(f,s);
diff(f,t,2);
Numerical
•
diff(x) ; diff(y)
z=diff(y)./diff(x)
z=diff(y,2)./diff(x,2)
•
polyder(p)
•
polyder(a,b)
Mathematical modeling & Simulations
7
Mathematical modeling & Simulations
8
END
Mathematical modeling & Simulations
9