History of Computers - The Early Days
advertisement

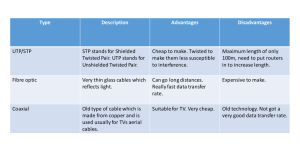
Definition of a Computer Information Processor Input and Output Definition of Modern Computer Inputs, outputs, processes and stores information Physical: Keyboard, monitor, etc. – are these necessary components? History of Computers - Long, Long Ago beads on rods to count and calculate still widely used in Asia History of Computers - Way Back When Slide Rule 1630 based on Napier’s rules for logarithms used until 1970s History of Computers - 19th Century Joseph Marie Jacquard First stored program metal cards Did no computing first computer manufacturing still in use today! Charles Babbage - 1792-1871 Difference Engine c.1822 huge calculator, never finished Analytical Engine 1833 could store numbers calculating “mill” used punched metal cards for instructions powered by steam! accurate to six decimal places Inspiration for Herman Hollerith for 1890 census Discussion Question What was the biggest advance that led to modern computers? Electricity Transistor Microchip Data storage Vacuum Tubes - 1941 - 1956 First Generation Electronic Computers used Vacuum Tubes Vacuum tubes are glass tubes with circuits inside. Vacuum tubes have no air inside of them, which protects the circuitry. UNIVAC – 1950-51 first fully electronic digital computer built in the U.S. Created at the University of Pennsylvania contained 18,000 vacuum tubes Cost $487,000 ENIAC that preceded it (late 1940s) weighed 30 tons Grace Hopper (1906-1992) Programmed UNIVAC Recipient of Computer Science’s first “Man of the Year Award” First compiler for a computer programming language, led to COBOL First Transistor Used Silicon (semiconductor developed in 1948 won a Nobel prize on-off switch 2nd Generation Computers used Transistors, starting in 1956 Second Generation – 19651963 1956 – Computers began to incorporate Transistors Replaced vacuum tubes with Transistors Integrated Circuits Third Generation Computers used Integrated Circuits (chips). Integrated Circuits are transistors, resistors, and capacitors integrated together into a single “chip” First one made by Texas Instruments in 1958 Operating System Software – Instructions for Computer ‘Operating system’ is set of instructions loaded each time a computer is started ‘Program’ is instructions loaded when needed Third Generation – 1964-1971 1964-1971 Integrated Circuit Operating System Getting smaller, cheaper The First Microprocessor – 1971 The 4004 had 2,250 transistors four-bit chunks (four 1’s or 0’s) 108Khz Called “Microchip” What is a Microchip? Very Large Scale Integrated Circuit (VLSIC) Transistors, resistors, and capacitors 4004 had 2,250 transistors Pentium IV had 42 MILLION transistors Each transistor 0.13 microns (10-6 meters) 4th Generation – began 1971 MICROCHIPS! Getting smaller and smaller, but we are still using microchip technology Birth of Personal Computers - 1975 256 byte memory (not Kilobytes or Megabytes) 2 MHz Intel 8080 chips Just a box with flashing lights cost $395 kit, $495 assembled. Generations of Electronic Computers First Generation Technology Vacuum Tubes Second Gen. Transistors Size Filled half a room Filled Whole Buildings Third Gen. Integrated Circuits (multiple transistors) Smaller Fourth Gen. Microchips (millions of transistors) Tiny - Palm Pilot is as power ful as old building sized computer Over the past 50 years, the Electronic Computer has evolved rapidly. Connections: Which evolved from the other, which was an entirely new creation • • • • vacuum tube integrated circuit transistor microchip Evolution of Electronics Integrated Circuit Transistor Vacuum Tube Microchip (VLSIC) Evolution of Electronics Vacuum Tube – a dinosaur without a modern lineage Transistor Integrated Circuit Microchip First Mass Market PC IBM PC - 1981 IBM-Intel-Microsoft joint venture First wide-selling personal computer used in business 8088 Microchip - 29,000 transistors 4.77 Mhz processing speed 256 K RAM (Random Access Memory) standard One or two floppy disk drives Open architecture Apple Computers Founded 1977 Apple II released 1977 widely used in schools Macintosh (left) released in 1984, Motorola 68000 Microchip processor first commercial computer with graphical user interface (GUI) and pointing device (mouse) The first GUI? XEROX PARC Today: 2014 Traditionally Intel divides the Core platform into three segments--Core i3 at the low end, Core i5 for the midrange, and Core i7 at the high end. Following that designation is a model number. You may also see a suffix at the end of the model number: K for unlocked processors, S for “performance-optimized” processors, or T for “power-optimized” processors. The S and T variants are generally for OEM use only--expect to see them in desktops and laptops on retail shelves. An unlocked, higher-end Ivy Bridge CPU, for example, could be named the Intel Core i7-3770K. 1990s: Pentiums and Power Macs Early 1990s began penetration of computers into every niche: every desk, most homes, etc. Faster, less expensive computers paved way for this Windows 95 was first decent GUI for “PCs” Macs became more PC compatible - easy file transfers Apple effort at licensing OS (Power Computing) Mac conversion to Intel chip Prices have plummeted $2000 for entry level to $400-$500 $6000 for top of line to $1000-$1500 21st Century Computing Great increases in speed, storage, and memory Increased networking, speed in Internet Broadband growth Netbooks / iPad / tablets Smart Phones Impact of touch technology 3G to 4G (3-5 Mbps / 8-10 Mbps) What’s next for computers? Use your imagination to come up with what the coming years hold for computers. What can we expect in two years? What can we expect in twenty years? Voice interface? Cloud computing growth True ubiquity? Interface to almost all activities? Internet & WWW Internet Overview G Advanced Research Projects Agency G Pentagon / University relationship G LANs and WANs G Single location / wide geographic area G ARPANET combined with LANs and WANs became the Internet in 1983 G TCP/IP protocol (Bob Kahn and Vint Cerf) G Packet switching and IP addresses Domain Name System (DNS) IP address 158.135.172.2 Text-based DNS translates human language into the computer’s ‘phone number’ TLD -- .com , .net, .edu ccTLD -- country code -- .ca , .uk (list) Determined by IANA, Internet Assigned Numbers Authority Organizational identifier – tamuc , google Domain names administered by ICANN -- Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers Buy domains from registrars (Mad Dog, GoDaddy, 1and1 Basics Web server holds web site ‘web server’ software Main page is index.html Html in file interpreted by browser Connectons in page are internal or external Web site creation / hosting Wix, Raptor, Dreamweaver, Cascade CMS Programs on the Internet… WWW -- Tim Berners-Lee devised HTML language which led to Mosaic A browser interprets the HTML Web page creation... XML--extensible markup language SOAP--simple objects access protocol (based on XML XHTML--another form of XML VRML Now HTML5 App creation iOS / xCode Programs on the Internet… E-mail Newsgroups / Usenet (link) Chat / IM (AIM, iChat, Meebo) Telnet (link) FTP (Fetch, etc.) Internet Phone (Skype, Google Voice) Web 2.0 (blogs, Second Life, podcasts…) Video streams (Bittorent, Veoh, Hulu, clicker) What’s going on today… Blogs / moblogs / vlogs Journalism / bloggers RSS feeds Podcasts, etc. / newsreader software New economic models -- Google Legal issues -- RIAA, MPAA, SoundExchange Other issues Malware, Digital Divide, charging fees to Internet sites, net neutrality (Comcast) Web 2.0? Google Docs (YouTube ‘tutorial’) / Drive Apple OS X Leopard / Snow Leopard / Lion / Mountain Lion What is ‘Digital Media’? / New Media -Canada DMS What is ‘Internet 2’? Increase speeds Spread technologies and applications Take advantage of digital libraries, virtual laboratories, tele-immersion What is Web 2.0? Semantic Web Web 2.0 What is… Digg? Stumble Upon? Photobucket? Jumpcut? The WayBack Machine? The Machine is using us? Otherwise going on…………. ? Mobile Computing Devices PDAs (personal digital assistant – ‘Newton’) Functions / changes through the years GPS Vehicle fixed / portable Satellite connection vs. most others Cell Phones iPhone example (smart phone) Portable Video Games GameBoy, Nintendo DS, Sony PSP / music, movies Ultra Mobile PCs -- Origami / Microsoft (site) CES -- Microsoft focus on touch technologies Wearable Computers? Tablets Broadcasting vs. streaming DTV – multicasting DVB-H (digital video broadcasting handheld) standard for broadcasting to handsets DMB (digital multimedia broadcasting) for multimedia broadcasting -- not available in North America Streaming allows VOD -- AT&T Mobile (MediaFlo), Verizon (ending 12/2012) Backseat TV Developing Technologies 3G / 4G cell phones -- packet and circuit switching Wi-Fi 802.11 and 802.11x refers to a family of specifications developed by the IEEE for wireless LAN technology. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, pronounced I-triple-E WiMax Also known as IEEE 802.16--intended for wireless "metropolitan area networks". Provides broadband wireless access (BWA) up to 30 miles (50 km) for fixed stations, and 3 - 10 miles (5 - 15 km) for mobile stations. WiFi/802.11 wireless local area network standard is limited in most cases to only 100 - 300 feet (30 - 100m). Why 802? The 802 group is the section of the IEEE involved in network operations and technologies, including mid-sized networks and local networks. Group 15 deals specifically with wireless networking technologies, and includes the now ubiquitous 802.15.1 working group, which is also known as Bluetooth. Developing Technologies Bluetooth Name comes from Harald Bluetooth, king of Denmark in the late 900s There are lots of different ways that electronic devices can connect to one another--Component cables, Electrical wires, Ethernet cables, WiFi, Infrared signals… Bluetooth is essentially a networking standard that works at two levels: It provides agreement at the physical level -- Bluetooth is a radio-frequency standard; AND, it provides agreement at the protocol level, where products have to agree on when bits are sent, how many will be sent at a time, and how the parties in a conversation can be sure that the message received is the same as the message sent. (cell phone, GPS, PDA-Starfield example) Developing Technologies ZigBee The set of specs built around the IEEE 802.15.4 wireless protocol. Name "ZigBee" derived from the erratic zigging patterns many bees make between flowers when collecting pollen. The standard is regulated by a group known as the ZigBee Alliance, with over 150 members worldwide. Bluetooth focuses on connectivity between large packet user devices--laptops, phones, major peripherals…. ZigBee is designed to provide highly efficient connectivity between small packet devices. Developing Technologies WPAN Wireless personal area network Bluetooth and Zigbee Personal hotspots RFID “IBM Uses RFID to Track Conference Attendees” “New chip promises to track kids from miles away” Tracks things and people DTV? / HD Radio Multicasting channels -- data transmission? Two way interactivity FCC approval Technical changes Copper wires to fiber optic cable Circuit Switching to packet switching Landline to wireless Convergence of technologies and companies Technical examples Fiber Optic Technicians (jobs promotion) Early telephones (women as operators) Early telephones (dialing a rotary phone) (push button phone) Making ‘free’ phone calls (discussion VoIP) Skype Netzero Voice / Messenger / iChat Jajah.com Google Voice Cell Phones Early -- 2-way radio type service Phone / ‘cells’ / towers Ugly towers? Connects to Mobile Telephone Switching Office (MTSO) Going to another cell phone in same area on same service, routed to another tower To another service or a landline, routed to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) Generations ‘two-way radio’ style ‘cellular’ process developed by (‘old’) AT&T IG -- analog -- 1983 -- AMPS -- ‘advanced mobile phone service 2G -- digital introduction -- early 1990s CDMA, TDMA initially in the U.S. (CDMA: Sprint, Verizon) GSM type adopted first in Europe (AT&T / TMobile) Generations 3G -- higher data transmission speeds -switch to packet switching (Interim -- ‘2.5G’ ‘Edge’) Verizon, AT&T, Sprint & T-Mobile all offer high speed 3G wireless networks. All moving to 4G...but, interim technologies 3G -- about 3 mbps throughput; 4G about 10 mbps (about 10x faster) Based on phone AND network infrastructure 3G vs. 4G Explanation Direct link Cell phone as hybrid medium Delivery of video to cellular phones is becoming more widespread… voice / data … and Verizon’s V-Cast service (3G EV-DO) MobiTV service. Both use the cellular network to deliver the content. New service and technology, MediaFlo, developed by Qualcomm, uses part of the television broadcasting spectrum (channel 55) to send multimedia content to mobile phones (as noted before). Allows wireless carriers to offer video content without taking up much needed bandwidth in their cellular network. What is broadband? ITU -- minimum speed of 256 kilobits/second FCC -- 1996 Telecommunications Act: 200 Kb/s bidirectionally Wired Wireless Satellite Alternate: DTV multicast channels (etc.) Broadband delivery -- wired DSL DSLAM / extenders (digital subscriber line access multiplexer) IPTV (AT&T: U-verse, Verizon: FiOS) Dedicated line (no slowdown) Cable modem (DOCSIS -- 1.0 / 2.0 / 3.0) Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification Shared down trunk line (slowdown) Information service / no open access Fiber to the home/premises (FTTH/P) FTTN -- fiber to the node (last mile is coaxial cable for cable & twisted-pair copper for DSL Broadband over power line (BPL) Interference State approval Broadband delivery -- wireless Fixed wireless broadband (FWB) (from MMDS) 3G mobile wireless (4G / pre-4G) Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11) (‘WLAN’) Wi-Max (802.16) Satellite HughesNet & WildBlue (several now) Latency problem (VoIP, games) “a time delay between the moment something is initiated, and the moment one of its effects begins or becomes detectable” Home Networks Residential gateway (aka - cable/DSL router) ‘the key device in most home networks’ Wired (server / hub / router) LAN Wireless (wi-fi / WLAN / 802.11) Interconnects all computers and other IP devices Connects the home network to the broadband connection ‘Specs’ Technical specifications or standards Like all issues – establish technical standards HPNA -- Home Phoneline Networking Alliance -- technology, built on Ethernet, allows all the components of a home network to interact over the home's existing telephone wiring without disturbing the existing voice or fax services IEEE -- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Proprietary or agreed-upon? VHS vs. Beta (home) DVD-R / DVD-RW vs. DVD+R / RW vs. RAM SD cards or compact flash cards HD-DVD vs. BluRay WMA vs. RealPlayer vs. Quicktime etc. codecs HDTV (8-VSB / COFDM) Home ‘hot spot’ Applications? Multiple networked computers Computers share one printer Integration of phone / cable or satellite systems / DVR, Slingbox, etc. with IP Security system connections Home ‘hot spot’ Applications? Control any IP device -- Microsoft has been working with Whirlpool to allow users to monitor their laundry with their home network, computer, TV, and cell phone. Continuing growth in American homes operating a wireless network, making the US the leader in adoption of wireless home networks. What else? RFID (ubiquitous?) Smart Home (video) / robotics Speech recognition Types: Discrete, continuous & complete Speech recognition gone awry Better success demo (click screen when page loads) Ultra HD video (cinema--replace film projection) Electronic paper (Kindle, iPad) (e-paper demo) Wikis GIGO conundrum? LA Times experiment Google docs as collaborative authoring? Virtual / Augmented Reality (RWWW) Second Life (promo/commercial) Google Earth and other competitors Education, Entertainment, etc. in a ‘virtual world’? Computer speed, power and storage How to simulate touch, smell, taste HMD, haptics, immersive environment