Unit 3: Revolution PPT astro_unit_3-revolution
advertisement

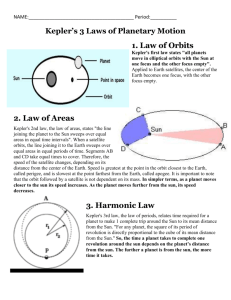
What does the word eminent mean? APOD Famous and respected within a particular sphere or profession. Write down: o Name of each scientist o Their discovery/contribution to the study of astronomy Who first discovered other moons in the Solar System? Which planet do they orbit? APOD We will be learning about important and “Revolutionary” astronomers Working in groups of 2 You will create a brochure about your scientist Today you will read about your scientist and begin organizing information o using the “Eminent Eight: Astronomer Biography Form” Tomorrow we will be in the library so you can fill in the gaps of information. What is one major difference in our understanding of the universe now as compared to a few hundred years ago? APOD Todayo Work on your brochures- you should finish with all research today o Fill in information on your brochure- include all information from the research sheet. Be as detailed and clear as possible! o Your brochures are due tomorrow. o If you print to the library-only print ONCE Tomorrow-Food If we get over 60 items, we could win donuts and KR sunglasses! That’s only 2 cans per person! Wh0 is your brochure about? What was his major contribution to astronomy? APOD Today- o Finish your brochures o Your brochures are due TODAY o If you print to the library-only print ONCE When done w/ brochure: o “Astronomical Scientific Models” o Bring your book and notebook to the library What does it mean when we describe a scientist’s view of the Solar system as heliocentric? APOD Your brochures are placed around the room Each scientist should have at least 2 brochures describing their lives and work. Your job is to use only the brochures to answer the provided questions. Which scientist described the 3 laws of planetary motion? APOD Who was the “Greatest naked-eye observer in the world”? Why was he called that? APOD Should be in the form of a flow chart Each Scientist/group should have its own box describing: o Their model or theory or law/formula that describes the solar system or universe. Use the flow chart to show the chronological order of the theories/models. Central African: The Moon and weather Took careful observations of the moon Figured out that the orientation of the points on the crescent moon coincided with the seasons. Used the moon to keep track of the wet and dry seasons. Ancient Greek: Pre- Aristotle, Geocentric Described the Solar system with the Earth at center“Celestial Sphere” Each planet was attached onto a sphere Why was Copernicus’s Heliocentric theory not widely accepted? Who provided the evidence to change that? APOD Earth is spherical-its shadow showed on the moon during an eclipse Said the Earth can’t be moving or clouds and birds and other objects would be left behind Orbits must be circular because the heavens are perfect Stellar parallax would exist if the Earth moved All of these were proved false by Kepler Earth centric Improved accuracy of celestial predictions Stated that each planet moved in a circle within its orbital path Remained the standard for 1400 years, until Copernicus Heliocentric-First to propose that Sun is the center, not Earth This more easily explained the motion of the planets However, he still held the belief that the orbits were perfect circles wasn’t able to improve the prediction of planetary movementstill had the circles within circles Not widely accepted Built on the work of Copernicus and Brahe Attempted to find a model that would work based on circular orbits His calculations were 8 arc minutes off of Tycho Brahe’s, but he couldn’t ignore it-he needed a new model of the Solar system “Those eight minutes pointed the road to a complete reformation in astronomy” Summarized his ideas in 3 laws of planetary motion 1. Each planet’s orbit is an ellipse, with the Sun as one focus 2. As a planet moves around the Sun, it sweeps out equal areas in equal times 3. The orbital period is related to the distance from the Sun Using the new laws, Tycho Brahe’s observations were now explained This was strong evidence in favor of Copernicus’s idea of a Sun-centered solar system What are the aphelion and perihelion? APOD How is the angular momentum of a planet conserved? (Kepler’s 2nd law) APOD How is the angular momentum of a planet conserved? (Kepler’s 2nd law) Use your book help answer!! to APOD Kepler’s law worksheet-only do #1-7 of the first page, don’t do the rest of the packet. Answer in your notebooks: o Pg 149 #9-13, 15 Restate Kepler’s 3rd law in your own words. How is this law useful to scientists? APOD Kepler’s laws of motion vocabulary Kepler’s law worksheet-only do #1-7 of the first page Book questions: Pg 149 #9-13, 15 Unit review