Exporting
advertisement
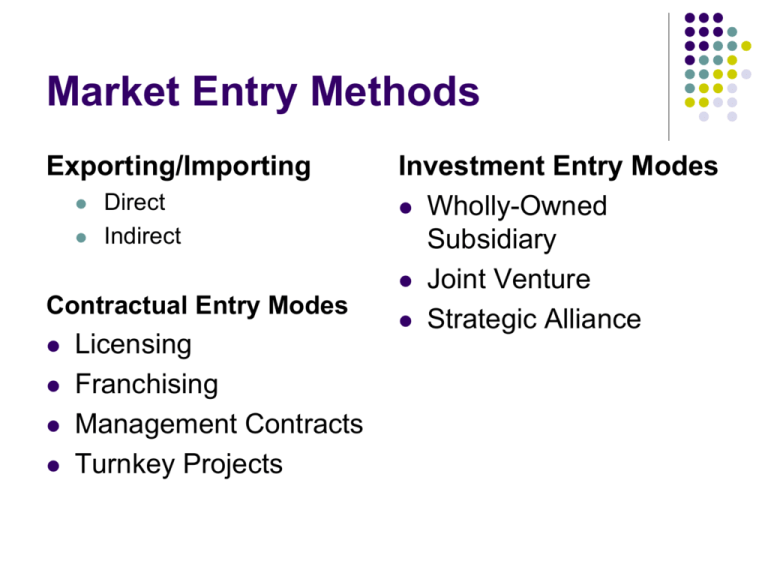
Market Entry Methods Exporting/Importing Direct Indirect Contractual Entry Modes Licensing Franchising Management Contracts Turnkey Projects Investment Entry Modes Wholly-Owned Subsidiary Joint Venture Strategic Alliance Exporting Selling and shipping products across borders Easiest and most common first step All size companies use this strategy Direct exporting: Company actively seeks exporting Indirect exporting: Casual exporting which uses agents or intermediaries Advantages: Risk of loss minimized because not much is invested Product can remain unchanged Can be used to get rid of excess inventory or gain additional sales Disadvantages: May not make the most of an opportunity Strongly dependent on exchange rates Examples: Producer sells to Wal-Mart which ships overseas Stora Enso sells paper products to Canada Intermediaries Agents Export Management Company Representatives of one or more indirect exporters in a target market Exports products on behalf of exporters Export Trading Company Provides services to indirect exporters Licensing Domestic company allows foreign company to use trademarks, patents, copyrights, processes, or technical knowledge for a fee Establishes foothold in foreign market without a big investment Favorite strategy of small to medium size companies Often use in addition to exporting Advantages: Foothold in foreign marketing without big investment Formal agreement in licensing contract Avoids import restrictions Disadvantages: Hard to protect intellectual property May be least profitable means of entry Examples: Nestle makes food products with Disney characters Franchising Franchisor provides standardized products and management processes while franchisee provides capital, management personnel and knowledge of local markets Fastest growing market entry strategy More than 30,000 franchises throughout the world Advantages: Allows skills to be located with franchisor while operations are spread over franchisees Expands company quickly with little investment by franchisor Foreign laws are friendly because of local ownership Disadvantages: Must share profits Poor franchisee can ruin image Management Contracting Company sells management skills and runs a foreign operation Main advantage is that it’s low risk Main disadvantage is that there is low profit potential and lack of a long-term presence in market Example: DBS Asia (Thailand) awarded a contract to Favorlangh Communication (Taiwan) to set up and run digital tv programming in Taiwan Turnkey Operation One company designs, constructs and tests a production facility for a client firm for a fee Often used by governments Ex: Turkey’s government had two consortiums of international firms build four hydroelectric dams Wholly-Owned Subsidiary Domestic company owns 100% of the stock of another company Can buy an existing business (easiest method that takes advantages of existing strengths) or start from scratch Advantages: Can take advantage of low cost labor Avoid high import taxes Can gain access to raw materials May cut transportation costs to market Disadvantages: High investment High risk May suffer backlash from country Many countries restrict foreign direct investment Examples Nike Stora Enso Joint Ventures Legal agreements between two or more companies to conduct business together Separate company is created and jointly owned Creates an alliance that combines strengths and accomplishes goals more efficiently 2nd most frequently used strategy behind exporting Advantages: Less capital investment required from each partner Shared risks Access to skills of partner With a local partner may allow access to markets which are forbidden to foreigners Disadvantages: Shared control complicates decision making Agreements require frequent review Could create competitor Share revenue Strategic Alliance Relationship between two companies to cooperate to achieve strategic goals Similar to joint venture except a new company is not formed Unz & Co. Guide to Exporting http://www.unzco.com/basicguide/toc.html Small Business Administration Guide http://www.sba.gov/OIT/info/Guide-ToExporting/ Inc. equivalents Canada, Japan, England – Ltd. (limited) France, Belgium – Sarl Spain, Mexico, Portugal and Brazil – S.A. Germany, Switzerland – GmbH Netherlands – N.V. Italy – Srl Denmark – A/S What method of market entry is this?? A company from Singapore is working with businesses in Kenya to help organize and run hospitals A British toy company allows a Japanese company to create clothing and school supplies with one of the British company’s doll characters on the products. An example of this would be Nike making shoes in Asia and Honda producing cars in the United States. A small food-packaging firm cannot afford to sell in other countries, so it asks an export agent to obtain orders for the company. A Vietnamese company decides to obtain assistance from an Israeli company to share production costs and profits of a chemical manufacturing enterprise. An Italian restaurant is planning to allow a company in New Zealand to operate several restaurants using the same name and menu items. A company in Egypt has purchased 51 percent of the stock of a company in Peru. A disadvantage of this entry method is that it is strongly dependent on exchange rates between countries and may not make the most of of an international opportunity. Advantages to this method are that it requires less capital, and risks are shared Which method of entry is the costliest? Which method of entry is the easiest and most common first step for businesses to go international? Which is the fastest growing market entry method with over 30,000 possibilities worldwide?











