Powerpoint Slides
advertisement

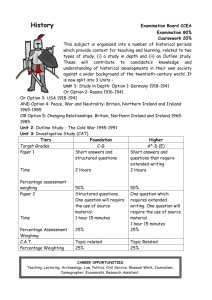
Teaching a Course on Government Statistics in a University Statistics Department Patrick Murphy University College Dublin Ireland Outline of Talk 1. Introduction 2. Background: Department & Students 3. Course Development 4. The Course: Content 5. The Course: Presentation 6. Assessment 7. Students’ View 8. Lessons Leaned/Alterations 9. Conclusions Introduction STATISTICIANS: Who are we? ACADEMIC Statisticians OFFICIAL Statisticians INDUSTRY Statisticians Introduction COLLABORATION? Academics <--> Industry Academics <--> Official Statisticians UCD Statistics: 8 Academics 7 have collaborations with Industry Introduction 26 Fe “Statistics” Definition now slightly IRONIC “Facts for the use of the State” “State Arithmetic” Introduction Graduate Employment National Statistical Offices are significant Employers of Statisticians Consider... Ireland: Central Statistics Office Small NSO But largest employer of Statisticians in Ireland >70 Permanent Statisticians Introduction Training for such Graduates Statistics, Mathematics Economics, Social Science, Politics What about specific training in Official Statistics? Introduction Graduate Training continued... 1999 Web search of Universities revealed University of Southampton, UK MSc in Official Statistics Monash University, Australia Later I discovered University of Ljubljana University of Helsinki Introduction Real Official Statistics Training “On the Job” From International Organisations – Training of European Statisticians TES Institute – International Monetary Fund Introduction Background: Department & Students University College Dublin Largest University in Ireland >20,000 Students Department of Statistics formed in 1986 8 full time Academic members Background Statistics’ Students Level 1 Statistics: – Approximately 120 Students Degree through Arts or Science Faculties Arts – 3 years combined with another subject Science – 4 year single honours degree or – 4 year joint honours with another subject Background Final Year Undergraduate Courses included: Time Series Survey Sampling Design and Analysis of Experiments Survival Analysis Bio-statistics Actuarial Statistics Regression Theory Non-Parametric Statistics Background Higher Diploma in Statistics One year graduate diploma Conversion course for graduates of cognate disciplines e.g. Psychology, Politics, Economics, Computer Science M.Sc., M.A. One year taught Masters Degree Available to Students with a good honours degree in Statistics, Mathematics or Actuarial & Financial Studies Background Course Development Course Development 1: Goals To provide students with an appreciation of the extent to which Official Statistics pervades the lives of citizens of a state To describe the process by which data are collected, processed, analysed and disseminated by an NSI To introduce some techniques used extensively in NSI’s that are not taught in other courses in the Department of Statistics Course Development Course Development 2: Logistics Students: – Final Year Undergraduate – Graduate Diploma – Masters Degree One-Semester course 24 hours of lectures 6 extra computer practical hours Course Development Course Development 3: Problems Existing Courses: Time Series, Survey Sampling Arts Students may be studying – Economics, Politics, Sociology etc. Science Students – unfamiliar with these subjects 1999 Web Search revealed few, if any, similar courses Textbook? My own background in CSO Course Development Course Development 4: Course Materials Books used by official statisticians National Accounts UN System of National Accounts Eurostat - European System of Accounts Balance of Payments IMF - Balance of Payments Manual, Compilation Guide and Textbook Course Development Course Development 4: Course Materials Other Irish official statistics sources That Was Then, This is Now - Change in Ireland 1949-1999 – Published by the CSO Journal of the Statistical and Social Inquiry Society of Ireland – Articles by TP Linehan Ex Director General CSO Course Development Course Development 4: Course Materials Some parts of the course were easy to prepare For Example: Index Number Theory Databases Course Development The Course Course Content 1. History Domesday book IMF, Eurostat Ireland 1800 - 2000 CSO Background reading on UK The Course Course Content 2. Legal and Institutional Statistics Act in Ireland, NSB International Organisations – IMF, OECD, ILO, Eurostat etc. CSO as an example of an NSI Including Processing of statistics – Non-response, Missing data, Quality Control, Confidentiality, CAPI, Edifact The Course Course Content 3. The Statistics National Accounts Balance of Payments External Trade Demography Agriculture Building Buisness register Vital Statistics Data Bank Industry Labour Market Prices Retail Sales Services Transport & Tourism Non CSO data The Course Course Content 4. Index Numbers History of Cost of Living Indices Laspeyres & Paasche Substitution Bias Fisher Index Chain method CPI calculation - Household Budget Survey Purchasing Power Parities The Course Course Content 5. Databases RDBMS Normalisation, SQL etc... MS ACCESS The Course Course Content 6. Additional Topics Guest Lecturers to reinforce relevance of official statistics Regional Accounts CPI for Pensioners The Course Presentation of the Course Content not Mathematical but Discursive Statistics Students not used to this Lot of material covered in class Wanted to encourage interaction in class Hence... Course home page on W W W Course notes on web as PDF files Links to external sites, NSI’s etc. The Course Assessment Course Assessment 30% Continuous Assessment 70% Final Exam Continuous Assessment consisted of projects to be completed by students in groups of two or three Six weeks to complete Oral Presentation Written Report Assessment Projects in Year One Projects were based on CSO statistics Unemployment Statistics Agricultural Accounts BOP40 - Balance of Payments Survey Tourism Statistics Consumer Price Index and Household Budget Survey Assessment Projects in Year One Content Descriptions of concepts measured Descriptions of data collection procedures International comparisons Students should also act as consumers and analyse recent statistics Assessment Students’ Views Students’ Views Course unlike others in Statistics Department Arts students acclimatised faster Reaction generally positive Some students very interested in area which was new to them Two students chose careers in Official Statistics directly because of this course 3 science students didn’t perform well Student’s Views Lessons Learned/ Alterations Lessons Learned/Alterations Course content changed slightly Examination format changed Projects revised to be more relevant to daily life New projects did not concentrate on one are but combined many to answer a question Report writing was flawed in first year so guidelines were introduced for second year Lessons Projects in Year Two Project 1. Economists warn that the Irish economy is in danger of overheating. They cite the recent increase in inflation as one piece of evidence. Discuss, using as many sources as you can find to back up your opinion. Lessons Projects in Year Two Project 2. Using at least five different indicators compare Ireland’s economic performance since 1990 with the rest of the world and explain why the Irish economy has become known as “The Celtic Tiger” Lessons Projects in Year Two Project 3. There is currently a housing crisis in this country. Construction firms are booming but a few years ago builders couldn’t find jobs. Using as many official statistics as you can, describe the extent of this situation and explain what you think is its cause. Lessons Project Guidelines Size 15 pages 12pt font No photocopied material One page Introduction & Conclusion International Comparisons Remainder of 15 pages discretionary Appendix 1: – Methodologies & Sources used by the NSI’s Appendix 2: Sources for report No Plagiarism, Complete Group Participation, Deadline Lessons 2003 Changes in UCD caused cancellation of this course Future Likely amalgamation of Survey Sampling course with this Official Statistics course Lessons Conclusions Conclusions Goals met Students have better understanding of – work done by official statisticians – how the results of that pervade society Textbook ??? Graduates employed in official statistics Guest lecturers Conclusions Conference on Official and Public Statistics Centre for Official Statistics at UCD? Recommend similar courses elsewhere FOR MORE INFO... Patrick.Murphy@UCD.IE Hopefully this hasn’t been too boring...