The House of Representatives
advertisement

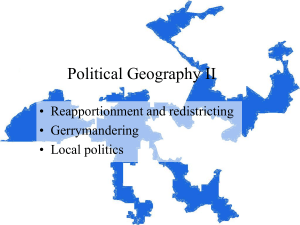
The House of Representatives population-based representation Article I, Section 2 Size and Terms 435 members – determined by Congress Representation apportioned (distributed) based on population Representatives serve 2 year terms No limit on the number of terms Every state is guaranteed at least one seat in the House of Representatives, no matter how small their population is. Small States with 1 Representative Alaska Delaware Montana North Dakota South Dakota Vermont Wyoming How does the government know how many people live in each state? Census: Constitution requires the government to count all of the people in the country every 10 years After the census, Congress decides the number of representatives each state will have. Reapportionment After every census, the representation is reapportioned or redistributed Number set at 435 - The Reapportionment Act of 1929 2010 was the last Census The number of people counted was 308,745,538 divided by 435 = 705,760 people per representative The US grows – number of people each representative speaks for grows. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Gerrymandering Districts with unusual shapes Gerrymandering draws districts to favor one political party - governor’s responsibility The original gerrymander was created in 1812 by Massachusetts governor Elbridge Gerry, who crafted a district for QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. political purposes that looked like a salamander. How has Congress regulated redistricting? In 1967, Congress passed a law requiring all U.S. representatives to be elected from single member district - the system we use today. Congress in 1982 amended the Voting Rights Act to protect the voting rights of protected racial minorities in redistricting. Within those laws, states have great leeway to draw districts, which often leads to gerrymandering. How Has the Supreme Court regulated redistricting? Wesbury v Sanders 1964 Bush v Vera 1996 One man, one vote: each voting district must be of similar size Struck down race based districts as unconstitutional - race can not be the controlling factor in drawing district lines Hunt v Cromartie 2001 Race can be one of the mix of factors that shape the process Congressional Elections Held the first Tuesday after the first Monday in November of an even numbered year Senate - continuous body House - up for election every even numbered year Districts Single-member districts People in a district vote for their representative At-large? People in a state vote for all representatives in that state