Honey, I Blew Up
advertisement

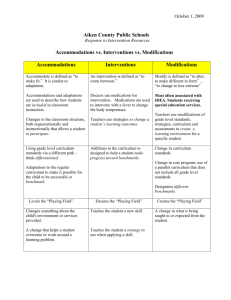
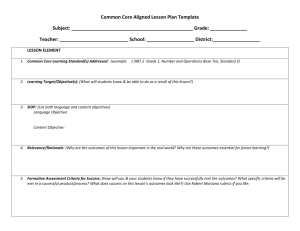
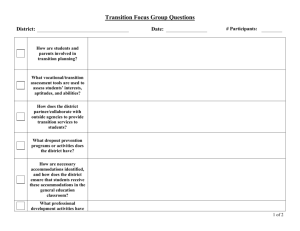
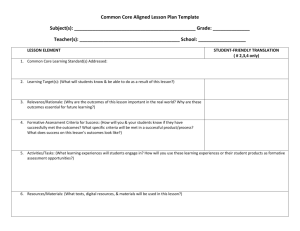
Adapting and Accommodating for all Learners OUTCOMES FOR TODAY ~ Everyone will expand their thinking when it comes to adaptations and accommodations. Participants will learn some new tools and strategies that they can use immediately. OUTLINE Introduction ~ Bridget & Nancy What does she need? Adaptations How to get started learner curriculum environment Tools and Strategies Mini books graphic webs preview technology My Experience We never segregate the people • we value . Inclusion – What would she be doing if she did not have Down Syndrome? • How can we address both academic learning & Social inclusion? • How will she learn? • What will she learn? • How can we accommodate for her needs and include her? WHAT DOES SHE NEED? • Supportive community that accepts and supports her. • Academic adaptations so she will have access to the curriculum • Opportunities to participate in the full educational experience. Why ADAPT? WHY do we Need to think about ADAPTATIONS & ACCOMMODATIONS? • IDEA • Diverse students in our classrooms • Inclusion IDEA ’97 Says . . . Each public agency shall ensure that: A child with a disability is not removed from education in age-appropriate regular classrooms solely because of needed modifications in the general curriculum. 34 CFR #300.352(e) “The IEP for each child with a disability must include--A statement of the program modifications…that will be provided for the child – To advance appropriately toward attaining the annual goals; – To be involved and progress in the general curriculum – To be educated and participate with other children with disabilities and non-disabled children…” IDEA Regulations, 34 C.F.R.§300.347(a)(3) Evolution of Supports and Services in General Education Prerequisite Home base Services Standards Mainstream Near grade level in academics & social Special Education Minor adaptations, consultation, collaboration Same as general education Integration Near grade level in academic or social Special Education Special Instruction, Merged classes, Adaptations Same as general education or modified General Education Full Continuum of services Varies with each student Inclusion 80 % of time spent in Gen ed. Classes. NONE with age appropriate peers with access and equity to the gen. ed curriculum and activities. Bill Peters 1991 WHAT MAKES IT WORK? Professional Development Teaming Adapt Curriculum What Makes Inclusion Work Build Relationships Resources Vision And Attitude Effective Instructional Strategies Get Started ~ Take a look at … Learner Environment Curriculum A LOOK AT THE LEARNER THE LEARNER … Is Exposed to The General Curriculum Is accountable and Tested on some of the Curriculum (essential and enduring concepts) will demonstrate their Learning by … What does the learner need to be part of the educational process? Organization, Previewing, a system for learning Student LEARNER PROFILE • • • • Strengths Needs Areas for improvement Support needed to be part of the process The student is successful when… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. He previews the information He has pictures He has a picture schedule He can work with a group He can relate the concept to something concrete. 6. He receives direct reading instruction 7. He has writing supports 8. He has math supports (manipulatives, touch math, with assistants) BIG QUESTIONS • WHAT is the student going to learn? • WHEN is the student going to learn the information? • WHERE is the student going to learn? • WHO is going to teach the student? • HOW is the student going to learn? IEP at a Glance Student’s Name: Areas of Focus Reading: Math: Communication (Oral or Written): Behavior: Assessment: Support Teacher (s): Accommodations Recommended Notes Individual Educational Program & General Education Matrix Regular Class Schedule Name:____________ Grade:____________ MGMT. Needs IEP Goals Writing simple sentences Morning Meeting Reading X Spelling/ LA X PE/Music/ Library Lunch Math X Science/ SS X Journal X TAKE A LOOK AT The CURRICULUM • Adaptations • Accommodations • Modifications Adaptations Accommodations Modifications • Changes in HOW a student accesses or demonstrates learning • Changes in WHAT a student is expected to learn. • Does not substantially change instructional level, content or performance level • Changes may be made in instructional level, content or performance level. • Goal = provide equal access to learning • Goal = provide meaningful & productive learning experiences Accommodation? or Modification? Instead of writing a complete paragraph, have the student draw a picture and label it. Allow the student to come in before school to work on a project. Provide the student with an uncluttered version of an assignment/test with additional space to write. Instead of completing a research paper, have the student locate library materials for the class on the topic. Provide audio versions of textbooks, and have the student follow the text while listening. Accommodation? or Modification? Instead of writing a complete paragraph, have the student draw a picture and label it. Allow the student to come in before school to work on a project. Provide the student with an uncluttered version of an assignment/test with additional space to write. Instead of completing a research paper, have the student locate library materials for the class on the topic. Provide audio versions of textbooks, and have the student follow the text while listening. Accommodation? or Modification? To assist with note-taking, provide an outline with main points. Allow student to use the computer to take a spelling test instead of writing the words. Allow student to provide a verbal response to an essay question on a science test. Instead of writing a five paragraph essay, have the student write one paragraph with at least five sentences. Have student be accountable for a few main concepts of a unit, rather than all the material. 8 Types of Adaptations Types of Adaptations Adapted from the Center for School & Community Integration, Institute for the Study of Developmental Disabilities, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN Size Time Level of Support Adapt the number of items that the learner is expected to learn or complete. Adapt the size of the information by enlarging. Adapt the time allotted and allowed for learning, task completion, or testing. Increase the amount of assistance for a specific learner. Input Difficulty Output Adapt the way instruction is delivered to the learner. Adapt the skill level, problem type, or the rules on how the learner may approach the work. Adapt how the learner can respond to instruction. Participation Alternate Goals Adapt the extent to which a learner is actively involved in the task. Adapt the goals or outcome expectations while using the same basic materials. SORT THE 8 TYPES SUBJECT : WATER CYCLE GOAL: Students will be able to describe the water cycle INSTRUCTIONAL PLAN: The students will draw the water cycle and write a paragraph describing how it works Types of Adaptations Adapted from the Center for School & Community Integration, Institute for the Study of Developmental Disabilities, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN Goal for Most learners: The students will be able to describe how the water cycle works. Instructional Plan for Most Learners: The students will draw the water cycle and write a paragraph describing how it works. Size Allow the student to write a few sentences rather than a complete paragraph. Input Provide the student with a model and pre-labeled cards to place on the diagram as s/he listens to the classroom explanation. Time Allow the student to use free time or come in before school to work on the project. Difficulty Provide the student with a “word bank” to assist in writing the paragraph. Participation Alternate Goals Have the student go to the school library to locate materials on the water cycle for the class to use during the unit. Change the goal to learning that water exists in different forms. Have the student locate magazine pictures of water in all its forms. Level of Support Have a peer work with the student on the paragraph to brainstorm ideas, formulate sentences and edit the end product. Output Allow the student to type the paragraph on the computer, using a word prediction program. Maintain the INTEGRITY of the curriculum Reduce the DENSITY of the material Be ECLECTIC ACCOMMODATE the child’s learning needs Remember the LEARNING STYLES DENSITY Accommodate the child’s learning needs And Assess Appropriately Backward Design Logic From Understanding by Design Begin with the end in mind! Universal Design Access for everyone CURRICULUM It is good to look at CURRICULUM with a birds eye view! Planning Pyramid Incidental Concepts What SOME students will learn More complex, abstract, & detailed Next Most Important Info. Additional facts, extensions of base concepts, more complex concepts and vocabulary What MOST students will learn Most Important Concepts to Lesson/Unit Broad concepts, relevant applications, key vocabulary What ALL students should learn Foundational Concepts, Selected Higher Order Concepts Adapted from: Schumm, J. S., Vaughn, S. & Harris J., “Pyramid Power for Collaborative Planning” Plate Tectonics 1 week science 8th grade • The earth changes over time • There are ocean plates and land plates that change the earth when they move TRY IT OUT ! The seven most dangerous words: “HE WON’T GET ANYTHING OUT OF IT !!!” Research Project Junior year • ALL students will write a research paper that includes sources, appropriate documentation, and clear accurate information. Bridget’s paper will: • be 3 pages long • 3 sources documented • Include a graphic web of ideas, and a short presentation. Bridget will have assistance and support so she can successfully participate in this project. I learned : • • • • • • About Martin Luther King Jr. Rosa Parks & the Bus Boycott The 9 students In Little Rock About the civil rights movement Segregation Non Violence IEP GOALS – Demonstrated learning • • • • • Bridget learned: About the history of segregation and the civil rights movement. – she can discuss the issues she learned about, – she can ask questions, – she can put ideas in a graphic web – she can discuss her research project – she read two books about the subject That American Issues (Civil Rights) were linked to world wide issues – She understands that Gandhi and Martin Luther King Jr. work on behalf of human rights. used lessons from Civil Disobedience King Jr. Information about some key leaders in history. – She learned about Martin Luther King Jr. – She learned about Rosa Parks – She learned about the 9 students in Little Rock • Experience with a research Project – – – – – She learned what a source was How to write a source – from writers Inc. How to find information on the internet How to find information in books. How to organize her thoughts in a web Standards • Standards • Analyze events, trends and individual movements shaping the history of the USA. • Describe and explain contributions of selected individuals through history. • Explain major social, economic and political events throughout history. • Analyze the roles played by groups in the development of a pluralistic society in the U.S. Bridget’s learning outcomes • Bridget’s learning outcomes • Learned that the bus boycott, brown vs. board of education and little rock nine were movements that shaped history • She learned about martin Luther King Jr., Rosa Parks and the 9 students in Little Rock. Made contributions • She learned about the civil rights movement as a major social event through out history. • She learned how the civil rights movement helped create a more pluralistic society Bridget’s Individual Goals and outcomes for participation in her research project. • • • • • • • • Bridget’s Individual Goals and outcomes for participation in her research project. Learn what a research project is Learn how to plan for a Project. Learn what a source is, how to locate a source, and record the information Learn that sources can come from books, magazines, article, and internet information Learn to put her ideas in a graphic web. Learn – with assistance – how to take her ideas and make one paragraph per idea Learn basic information about little rock 9, brown vs. the board of education and the bus boycott so that she can discuss this topic, ask questions and link information to other issues. (civil rights movement = disability issues) A Planning Structure General ed teacher prepares an outline of upcoming curriculum. General & special ed teachers jointly decide how to arrange teachers & students to accomplish curriculum priorities. Special educator (with assistance from regular educator) makes accommodations & modifications for students with special needs. Student Participation Options in General Education Classroom Activities Minor Accommodations Same activities Same objectives Accommodations Major Modifications Same activities Same objectives (may prioritize) Accommodations & modifications for success Same curricular area Different objectives Significant modifications (using same or different materials) Assessment & Grading Options Minor Accommodations Major Modifications “General Education” “Blended” “Modified” Assessment/Grading Model Assessment/Grading Model Assessment/Grading Model Minor Accommodations Major Accommodations / Minor Modifications Major Modifications General Education Teacher General & Special Education Teachers Special Education Teacher ENVIRONMENT Adapt the environment by: • • • • • • • • • Creating cooperative learning groups Using stations or centers Discussion groups Co-teaching Groups based on interest Individual conferencing time Learning contracts Partners Peer Guides • PAIR AND SHARE – OTHER WAYS TO ADAPT THE ENVIORNMENT TOOLS & STRATEGIES Uses for Graphic Webbing Reduce the density Note taking Tool Find out what’s important Preview & Review Sort Information Use pictures to help retrieve information Discussion tool: Retrieve Contribute WHAT IS THE BIG IDEA? Sense Organs Touch See Taste Hear Smell The BRAIN Central Nervous System Note Taking Tool ROCKS SHOW HOW THE EARTH HAS CHANGED IGNIOUS SEDIMENTARY METAMORPHIC WATER BIRDS PAPYRUS TRANSPORTATION 4 GIFTS OF THE NILE RIVER EGYPT RICH MUD Graphic Relationships 10 20 NOTE TAKING TOOLS • Cloze notes, Graphic Webs, Flip books Main idea Details Cloze Notes Activity • There are 3 major Rocks. • The ____________________ rocks change over time. • _____________rocks are layered sand and rock. • Rocks that come from _____________ are called ______________rocks. Writing Template The important thing about _____ is that it is _______________________. It is ___________________________. It is ___________________________. But the most important thing about ______ is that it is ______________. Tomlinson, C. (1999). The Differentiated Classroom: Responding to the Needs of All Learners. Alexandria, VA: ASCD. Study Guides Some of the colonists were so angry that they wanted to form an assembly. An assembly is a group of people who make rules or laws. They thought as assembly would help them get new rules. The governor of the colony did not always agree with these rule. Sometimes he would veto, or reject, the rules. What is an assembly? _________________ What did the colonist think the assembly would do for them?__________________________________ What does veto mean?________________________________ www.picsearch.com www.pics4learning.com www.classroomclipart.com Taped Books www.talkingtapes.org $2.50 (rent) $4.50 (buy) www.rfbd.org Recording for the Blind & Dyslexic yearly fee Digital Books www.bookshare.org yearly fee http://www.accessiblebookcollection.org yearly fee www.promo.net/pg/ Project Gutenberg – public domain books Text-to-Speech Software www.textassist.com $50 www.readplease.com free Auto Summarize Helpful Sites • http://www.help4teachers.com Kathie Nunley’s Site for Layered Curriculum Examples of layered units for many subject areas • http://www.windows.ucar.edu/ Windows to the Universe Earth and space science site, with information at 3 levels of difficulty • www.uwm.edu/~caberg/access Science lessons with built in accommodations for behavior, academics and assistive technology • http://www.historyalive.com Teachers’ Curriculum Institute: History Alive! Dynamic, enticing history materials which consider various learning styles. Low cost Activity Samplers available. Technology • BrainPOP www.brainpop.com • Thinkfinity www.thinkfinity.org • http://teacher.scholastic.com/p roducts/bookflixfreetrial/ BrainPOP Jr. - K-3 Educational Movies, Quizzes, Lessons, and More! • Provides educational movies for K-3 students. Homework Help, leveled quizzes, games and activities for kids. Exceptional resource for teachers and homeschools • Thinkfinity • Thousands of Free Lesson Plans and Educational Resources for Teachers ... • Over 55,000 Free Lesson Plans in Math Social Studies Art Language Arts Music Physical Education Reading Writing Geography Science Projects Science Lesson Plans and Thematic units. http://teacher.scholastic.com/products/bookflixfreetrial • This is by scholastic - called book flix. • It has tons of books and activities online. Students can read and have books read to them. Many libraries have a subscription, so children can use it for free and access tons of classic children's books. Check it out! MODELS OF SUPPORT • • • • PEER GUIDES CIRCLE OF FRIENDS YES I CAN PROGRAM SOCIAL CIRCLES Additional Important Information • • • • Social Emotional Learning Self determination Behavior Person Centered Planning Thanks and have a great day! Inclusion is like Lattice: an open framework made of interwoven strips of metal or wood. It provides a structure upon which plants can grow and thrive. It is not a solid, rigid structure, but rather one that is adaptable and able to withstand changes in wind and weather.