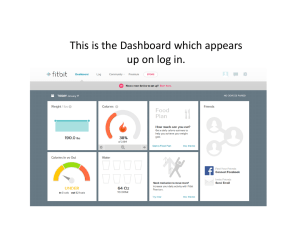
Strategic marketing process
advertisement

In the name of God Developing Successful Marketing and Organizational Strategies Zahra Danieli University of Tehran October 2015 Learning objectives Learn about two kinds of organizations and three levels of strategy in them Learn how core values, mission, organizational culture, business and goals are important to organizations. Learn why managers use marketing dashboards and marketing metrics Learn how an organization assesses where it is now and where it seeks to be Learn the three steps of the planning phase of the strategic marketing process Learn about the elements of the implementation and evaluation phases of the strategic marketing process. Today’s Organizations In studying today’s visionary organizations ,it is important to recognize : 1.The kinds of organizations 2.What strategy is 3.How this strategy relates to the three levels found in many large organizations Kinds of organizations Organizations : Legal entity People Common mission. creating value for both the organization and its customers by satisfying customer need and wants Todays organizations Business firms Nonprofit organizations Business Firm Privately owned organization Serves its customers to earn a profit so that it can survive Profit= total revenues – total expenses Nonprofit Organization A nongovernmental organization that serves its customers but does not have profit as an organizational goal. Its Goals: Operational efficiency Client satisfaction Sustainable Development( SD) Both business firms and nonprofit organizations increasingly seek to achieve sustainable development Sustainable development: "Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.“ Strategy Strategy is an organization’s long-term course of action designed to deliver a unique customer experience while achieving its goals. 1.Delivering a unique customer experience While 2.Achieving its goals ● organizations set strategies and marketing helps to both set this direction and move the organization there. Structure of Todays Organizations Corporate level Corporate level: where top management directs overall strategy for the entire organization. Top management usually means the board of directors and senior management officers with a variety of skills and experiences that are invaluable in establishing overall strategy. CEO ( chief executive officer ) CMOs( chief marketing officer) Strategic Business Unit Level (SBU level) Some multimarket ,multiproduct firms manage a group of businesses. Each group is a SBU which markets a set of related offerings to a clearly defined group of customers. At the strategic business unit level ,managers set a more specific direction for their business to exploit value-creating opportunities. For less complex firms with a single business focus ,the corporate and business unit levels may merge. Functional Level Each strategic business unit has a functional level, where groups of specialists actually create value for the organization. The term Department refers to these specialized functions such as marketing or finance. At this level ,the organizational strategic direction becomes its most specific and focused. It addresses issues usually faced by lower-level managers and deals with strategies for the major organizational functions such as marketing, finance, production, and research, which are considered important to achieving the business strategies and enabling the corporate-level strategy. Strategy in Visionary Organizations Todays organizations must be Forward looking: to anticipate future events and respond quickly and effectively. this requires a visionary organization to specify: Its foundation= why does it exist? Set a direction : what will it do ? Formulate strategies: how will it do it? Organizational Foundation : Why does it exist? Core Values: the fundamental ,passionate and enduring principles that guide its conduct over time Mission: a statement of the organization’s function in society, often identifying its customers, markets, products, and technologies. it should be clear, concise, meaningful, inspirational and long-term. Example: Medtronic's mission statement: to contribute to human welfare by application of biomedical engineering in the research , design, manufacture and sale of instruments or applicants that alleviate pain, restore health, and extend life Organizational culture: set of values ,ideas, attitudes, and norms of behavior that is learned and shared among the members of an organization. Organizational Direction: what will it do? The business : It describes the clear ,broad, underlying industry or market sector of an organization’s offerings. Goals or Objectives : Statements of an accomplishment of task to be achieved, often by a specific time. Profit: to get as high a ROI as possible Sales: to maintain or increase its sales Market share : (Particular firm’s sales revenue in Time Period X) / (Relevant market’s Total Sales Revenue in Time Period X) why it matters? It’s a sign of the firm’s competitiveness Quality Customer satisfaction : to balance the conflicting goals of stakeholders promote their overall welfare, even at the expense of profits . Social responsibility Organizational strategies : how will it do it? Variation by Level : as we come down an organization, strategies become detailed and more specific. Corporate SBU Functional Variation by Offering: the strategy will be far different when marketing a very tangible physical product, a service or an idea. Product Service Idea Tracking strategic performance with Marketing Dashboards Car dashboards and marketing dashboards: a marketing dashboard is the visual computer display of the essential information related to achieving a marketing objective. The idea of marketing dashboard comes from the display of information on a car’s dashboard. on a car dashboard we glance at the fuel gauge and take action when our gas is getting low. With a marketing dashboard we glance at a graph or table and makes a decision whether to take action or to analyze the problem further. Setting Strategic Direction Where are we now? Competencies: what do we do best? its distinguishing competencies→ competitive advantage→ success Customers: providing genuine value to customers with different preferences. Competitors Growth strategies: Where do we want to go? Business Portfolio Analysis Diversification Analysis Business Portfolio Analysis by BCG Business Portfolio Analysis (BCG matrix) Developed by Boston Consulting Group, Business Portfolio Analysis, is a technique that managers use to quantify performance measures and growth targets to analyze their firms SBUs as though they were a collection of separate investments. The purpose: to determine the appeal of SBU or offering and then determine the amount of cash each should receive. The vertical axis : market growth rate The horizontal axis: relative market share BCG Matrix Cash Cows ( Low growth, High market share) stars of yesterday. SBUs that generate large amounts of cash more than required. Located in an industry that is mature ,not growing or declining. Stars( High growth, High market share) leaders in business The may need extra cash to finance their own rapid future growth When their growth slows, they are likely to become cash cows. Question marks:(High growth, Low market share) They require large injections of cash to maintain their market share. Dogs ( Low growth ,Low market share) They do not hold the promise of ever becoming real winners for the organizations. Their numbers should be minimized . Diversification Analysis A technique that helps a firm search for growth opportunities from among current and new markets as well as current and new products. . The Strategic Marketing Process After an organization assesses where it is and where it wants to go ,other questions will emerge: How do we allocate our resources to get where we want to go? How do we convert our plans into actions? How do our results compare with our plans ,and do deviations require new plans? The strategic marketing process is used to answer these questions. Strategic marketing process Planning Implementation Evaluation Strategic Marketing Process STEP 1: SWOT analysis ACTIONS in SWOT analysis phase Build on a strength Correct a weakness Exploit an opportunity Avoid a disaster-laden threat Step 2: market –product Focus and Goal setting Determine which products will be directed toward which customers. Its based on Market Segmentation: aggregating prospecting buyers into groups or segments that have 1.common needs and 2.will respond similarly to a marketing action. Step 2 is a foundation for step 3. The Strategic Marketing Process How do we allocate our resources to get where we want to go? How do we convert our plans into actions? How do results compare with our plans ,and deviations require new plans? Step3.Marketing Program The HOW aspect is developing the program’s marketing mix(the four Ps) and its budget. Product strategy Price strategy Promotion strategy Place strategy The Implementation Phase of the strategic marketing Process Carrying out the marketing plan that emerges from the planning phase. Obtaining resources Designing the marketing organization Developing Planning Schedules Executing the Marketing Program: effective execution requires attention to detail for both marketing strategies and marketing tactics. The Evaluation Phase of the strategic marketing process It seeks to keep the marketing program moving in the direction set for it. Accomplishing this requires the marketing manager to : 1. Compare the results of the marketing program with the goals in the written plans to identify the deviations and 2. Act on these deviations- Correcting negative deviations and exploiting positive ones. Thanks For Your Attention