Martsolf #2
advertisement

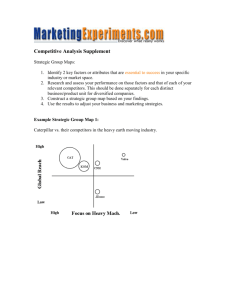
Industry and Competitive Analysis Questions to Answer: What are the dominant economic traits? What are the competitive forces at work? What are the drivers of change? Which companies are the strongest and the weakest? Who will make the next competitive move? What are the key factors of success? How attractive is the industry for profitability? Industry’s Dominant Economic Traits Market size Geographic scope of competitive rivalry Market growth rate & growth cycle Number & size of rivals Number & size of buyers Pace of product innovation Ease of entry and exit Pace of change of technology Degree of differentiation Capacity & demand Industry’s Dominant Economic Traits Economies of scale offer companies lower costs & competitive advantage Available economies of scale: Manufacturing Research & Development Purchasing Transportation Advertising Industry’s Dominant Economic Traits Need for high capacity utilization Whether there exists a strong learning and experience curve Prevalence of vertical integration Capital requirements Industry profitability: above or below average? Porter’s 5 Competitive Forces Rivalry among competing sellers Firms with substitute products Potential entry of new competitors Leverage of suppliers Leverage of buyers Competitive Forces at Work: Competitive Rivalry Increases when… Increase in the number of competitors Competitor size becomes more equal Slow growth in demand High proportion of cost is fixed Product is costly to hold in inventory Customer cost to switch is low Competitor(s) dissatisfied with market position Size of the payoff for strategic move Increase in exit costs Diversity of competitors Takeovers of weaker firms Competitive Forces at Work: Substitute Products… Place ceiling on prices and profits Customers compare: Price Quality Service Performance features Other costs Competitive Forces at Work: Substitute Products… Cost of switching products Retraining Additional equipment Technical help Testing quality and reliability Severing old relationships Establishing new relationships Competitive Forces at Work: Threat of New Entrants Determined by… Economies of scale Access to technology Learning curve Brand preference & customer loyalty Capital requirements Cost disadvantage or access to suppliers Access to distribution channels Regulatory, licensing & permit policies Tariffs & restrictions Competitive Forces at Work: Power of Suppliers Determined by… Size of the customer Number of suppliers Demand for products Availability of substitutes Standardization of commodity Economies of scale: make or buy Quality Competitive Forces at Work: Power of Buyers Determined by… Size of the customer Number of buyers Demand for products Cost of switching Buyer bargaining power is not equal Threat of vertical integration by buyer Discretion over when to purchase Drivers of Change Internet Globalization Long-term industry growth rate Who buys the product and how it is used Product innovation Technological change Marketing innovation Drivers of Change Entry or exit of major firms Diffusion of technology Changes in cost and efficiency Emerging buyer preferences Regulatory, social and political influences Reduction in uncertainty and risk “Flattening” of the world Key Success Factors Technology Manufacturing Distribution Marketing Skills Organizational capability Miscellaneous Strongest & Weakest Companies Strategic Group Mapping Identify competitive characteristics Plot firms on a 2variable map Assign firms to strategic groups Circle groups proportional to size Variables Not correlated Expose differences in rival strategies Need not be quantitative or continuous Multiple pairing may provide several maps Who Will Make the Next Move? Identify competitor strategies Which are strong & which are weak Evaluate who will be the major players Predict competitors’ next moves Strategic changes Moves into new markets Acquisition- targets or movers Competitor Strategies: Competitive Scope Local Regional National Multi-country Global Competitor Strategies: Strategic Intent Dominant leader Overtake the leader Among the top 5 Among the top 10 Move up a notch, or two Overtake a rival Maintain position Just survive Competitor Strategies: Market Share Objective Aggressive expansion via: Internal growth Acquisition Expansion via internal growth Expansion via acquisition Hold on to present share Give up share if necessary Competitor Strategies: Competitive Position Getting stronger Well entrenched Stuck in the middle of the pack Seeking different market position Struggling, or losing ground Retrenching Competitor Strategies: Strategic Posture Mostly offensive Mostly defensive Combination of offense and defense Aggressive risk-taker Conservative follower Competitor Strategies: Generic Competitive Strategies Low-cost leadership Market niche High end Low end Geographic Special needs buyers Other Differentiation based on: Quality Service Technological superiority Breadth of product line Image and reputation Value Other attributes Attractiveness of Industry Growth potential Impact of prevailing driving forces Potential entry or exit of major firms Stability of demand Trend of competitive forces Severity of problems confronting industry Future risk or uncertainty Potential for impact on profitability trend