C1 Esterase Inhibitor (human)
advertisement

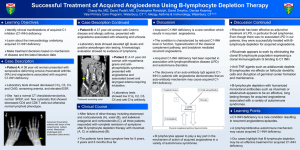
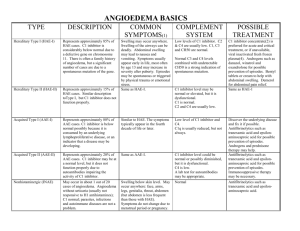
C1 ESTERASE INHIBITOR (HUMAN) For the prevention and treatment of acute attacks of Hereditary Angioedema Reid Nakagawa November 31, 2013 OUTLINE Hereditary Angioedema Definition Clinical Manifestations Epidemiology Treatment Pathophysiology C1 esterase inhibitor (human) Indications & Usage Dosing & Administration Mechanism of Action Pharmacokinetics Drug Interactions Adverse Effects Precautions Pregnancy & Lactation Reconstitution Place in Practice ANGIOEDEMA Angioedema is the result of localized blood vessel dilation and increased permeability that causes rapid swelling of the subcutaneous, mucosal, and submucosal tissues. Hereditary Angioedema Triggers: Dental work, trauma, anxiety, stress, etc. Attacks can occur spontaneously in the absence of triggers EPIDEMIOLOGY Affects approximately 1 in 50,000 individuals (1:10,000 – 1:150,000) Males and females are affected equally The prevalence of HAE is highest in Europe and North America Mean age of onset is 8 to 12 years 75% experience first attack by the age of 15 years PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Hereditary Angioedema (HAE) is an autosomal dominant disorder where there is a deficiency or dysfunction in endogenous C1 esterase inhibitor (C1-INH) Type 1: deficiency in C1-INH (~85%) Type II HAE: dysfunctional CI-INH (~15%) HAE with normal C1-INH: mutations in Factor XII? Acquired C1-INH deficiency: associated with autoimmune disorders C1 esterase inhibitor (C1-INH) is a member of the serine protease inhibitors “serpin” superfamily. It is an inhibitor of the kinin-generating, coagulation, and fibrinolytic pathways. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS Prodromal symptoms: fatigue, irritability, nausea, myalgias, flu-like symptoms, erythema marginatum Affected areas: Skin, GI tract, GU tract, and upper airway Edema involves the subcutaneous, mucosal, and submucosal tissues Urticaria and pruritis are absent, Severity: inconvenient cutaneous edema - life-threatening laryngeal edema Duration of attacks: 48-96 hours TREATMENT Patients with HAE tend not to respond to epinephrine, antihistamines, or glucocorticoids Plasma kalikrein inhibitor Ecallantide (Kalbitor) Bradykinin receptor antagonist Icatibant acetate (Firazyr) C1 esterase inhibitor C1 esterase inhibitor, human (Cinryze, Berinert) C1 ESTERASE INHIBITOR C1 ESTERASE INHIBITOR INDICATIONS & USAGE: For routine prophylaxis against angioedema attacks in adolescent and adult patients with Hereditary Angioedema (Cinryze). For the treatment of acute abdominal, facial, or laryngeal attacks of Hereditary Angioedema in adult and adolescent patients (Berinert). MECHANISM OF ACTION PHARMACOKINETICS / DYNAMICS Single Dose Double Dose Cbaseline (units/mL) 0.31 +/- 0.20 0.33 +/- 0.20 Cmax(units/mL) 0.68 +/- 0.08 0.85 +/- 0.12 Tmax (hours) 3.9 +/- 7.3 2.7 +/- 1.9 T1/2 (hours) 56 +/- 36 62 +/- 38 Onset of action: 1 hour or less Vd: 0.43 dL/kg No known drug-drug interactions PRECAUTIONS Severe hypersensitivity reactions may occur. CONTRAINDICATION Thrombotic Events Thrombotic events have been reported following the administration of high doses of CI-INH Transmissible Infectious Agents C1-INH has the risk of transmitting infectious agents, e.g. HIV, HepC, CJD, etc. ADVERSE EFFECTS Common Headache 7.0% - 28% Nausea 1.8% - 18% Rash 3.5% - 10% Sinusitis 5% or greater URI 1.8% or greater Serious Hypersensitivity MI DVT CVA PE PREGNANCY & BREASTFEEDING Pregnancy Category: C (All Trimesters) No animal data are available No adequate and well-controlled studies were conducted in pregnant women C1-INH should be given to pregnant women only if clearly needed Breastfeeding: It is not known whether C1-INH is excreted in breast milk Caution should be exercised when C1-INH is administered to a nursing mother STORAGE AND HANDLING Storage: 2 C – 22 C (36 F – 77 F) O O O O Do not freeze Store the vial in the original container to protect it from light RECONSTITUTION DOSING & ADMINISTRATION For intravenous use only. Can be given as either an IV push over 10 minutes or as an IV drip over 10 minutes Administer within 3 hours of reconstitution HAE, Prophylaxis (Cinryze): 1,000 Units IV push/infusion over 10 minutes Q3 - 4 days HAE, abdominal, facial, or laryngeal attacks (Berinert): 20 International Units/kg IV infusion at a rate of approximately 4 mL/min TRADITIONAL PLACE IN PRACTICE Prophylaxis The use of C1-INH for prophylaxis against Hereditary Angioedema attacks has been established C1-INH can either be administered by a healthcare provider in clinic or self-administered by the patient at home Treatment For acute attacks of HAE in patients presenting to the Emergency Department Cinryze is FDA approved for treatment of HAE, but has been studied Dosing: 1,000 units IV over 10 minutes; 2nd dose may be administered 60 minutes after first dose if no improvement in symptoms is seen - or 20 units/kg IV; rate not to exceend 4 mL/min EFFICACY EFFICACY TREATMENT TRIAL 37 sites, N = 68 patients Study drug : 35 patients 1,000 units (10 mL) IV over 10 minutes; repeat x 1 if no symptomatic relief after 60 minutes Placebo: 33 patients 10 mL NS over 10 minutes Primary Endpoint Time from administration of the study drug to unequivocal relief of symptoms at the defining site Secondary Endpoints Percentage of subjects who had an onset of unequivocal relief of symptoms w/in 4 hours after receiving treatment Time to complete resolution of the attack TREATMENT TRIAL Median time to symptom relief 2 hours VS 4 hours (CI: 1.17 – 4.95) P =0.02 Percentage of subjects with onset of relief within 4 hours 60% VS 42%; P =0.06 Time to complete resolution of attack 12.3 hours VS 25.0 hours; P =0.004 PROPHYLAXIS TRIAL N = 22 patients 24 week crossover Primary Endpoint Number of attacks of angioedema during each treatment period Average severity of attacks (on a scale of 1-3) 1-mild 2-moderate 3-severe Average duration of attacks Number of open label injections of C1-INH Total number of days of swelling PROPHYLAXIS TRIAL Number of angioedema attacks 6.26 VS 12.73 (CI: 4.21 – 8.73) P<0.001 Average severity of attacks 1.3 +/- 0.85 VS 1.9 +/- 0.36 P<0.001 Average duration of attacks 2.1 +/- 1.13 d VS 3.4 +/- 1.39 d P=0.002 Number of open-label injections 4.7 +/- 8.66 VS 15.4 +/- 8.41 P<0.001 Total number of days of swelling 10.22 +/- 10.73 d VS 29.6 +/- 16.9 d P<0.001 NEXT FRONTIER C1-INH in patients with HAE with normal C1-INH levels Patients are usually refractory to epinephrine, antihistamines, and glucocorticoids C1-INH has been used in these patients to presumably raise the set point for activation of kallikrein and generation of bradykinin. Further research is needed to validate its use in this patient population C1-INH in patients with Idiopathic Angioedema 2 main types Histaminergic angioedema Bradykinergic angioedema Most patients do not respond to epinephrine, antihistamines, and glucocorticoids The use of C1-INH in this patient population is currently being discussed by experts QUESTIONS REFERENCES Berinert [package insert]. Kankakee, IL: CSL Behring LLC; 2012 Cinryze [package insert]. Exton, PA: ViroPharm Biologics, Inc.; 2010- 2013. Lang DM, Aberer W, Bernstein JA, et al. International Consensus on Hereditary and Acuired Angioedema. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2012;109:395-402. Zuraw BL, Busse PJ, White M, et al. Nanofiltered C1 Inhibitor Concentrate for Treatment of Hereditary Angioedema. N Engl J Med 2010;363: 513-22.