CHAP 13: Spectroscopy II. NMR, part 4
advertisement

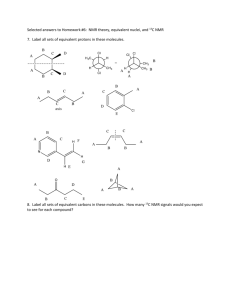
13.18 Carbon-13 NMR SALIENT FACTS ABOUT 13C NMR 12C is not NMR-active however…. 13C 13C I= 0 does have spin, I = 1/2 (odd mass) signals are 6000 times weaker than 1H because: 1. Natural abundance of 2. Magnetic moment of 13C 13C is small (1.08% of all C) is small PULSED FT-NMR IS REQUIRED The chemical shift range is larger than for protons 0 - 220 ppm COUPLING TO ATTACHED PROTONS COUPLING TO ATTACHED PROTONS 3 protons 2 protons H 13 C 0 protons H H H n+1 = 4 Methyl carbon 1 proton 13 C H n+1 = 3 Methylene carbon 13 C H n+1 = 2 Methine carbon 13 C n+1 = 1 Quaternary carbon The effect of attached protons on 13C resonances ( n+1 rule applies ) (J’s are large ~ 100 - 200 Hz) ETHYL PHENYLACETATE 13C coupled to the hydrogens DECOUPLED SPECTRA ETHYL PHENYLACETATE 13C coupled to the protons 13C decoupled from the protons in some cases the peaks of the multiplets will overlap this is an easier spectrum to interpret CHEMICAL SHIFTS OF 13C ATOMS 200 150 100 50 0 RANGE R-CH3 Saturated carbon - sp3 no electronegativity effects 8 - 30 R-CH2-R 15 - 55 R3CH / R4C 20 - 60 40 - 80 C-O Saturated carbon - sp3 35 - 80 C-Cl electronegativity effects C-Br C Unsaturated carbon - sp2 C=C C 25 - 65 Alkyne carbons - sp 65 - 90 100 - 150 Aromatic ring carbons C=O C=O 200 110 - 175 Acids Amides Esters Anhydrides Aldehydes Ketones 150 100 155 - 185 185 - 220 50 0 Correlation chart for 13C Chemical Shifts (ppm) Some useful information! • sp3 carbons are upfield (shielded), 15 to 75 • When the carbon has electronegative groups, appear further downfield, 50 to 75 • sp2 carbons appear down field, 120 to 170 • C=O carbons appear furthest to the left, 170 to 220ppm SPECTRA Toluene CH3 WWU Chemistry 1-Propanol HO-CH2-CH2-CH3 c b a PROTON DECOUPLED 200 150 100 50 Proton-decoupled 13C spectrum of 1-propanol (22.5 MHz) 0 Cyclohexanol Cyclohexanone 1,2-Dichlorobenzene b a a b c Cl c Cl 1,3-Dichlolrobenzene Cl Cl 1,4-Dichlorobenzene Cl Cl Some Unknowns! • The next three slides are carbon-13 spectra for: • Cyclohexanol • Cyclohexanone • 2-Methylcyclopentanone • Assign them! Hit the enter key to see • the answer. 2-methylcyclopentanone cyclohexanone cyclohexanol The next slide shows some structures. Predict the number of carbon peaks you would observe in the 13C NMR. Hit the enter key for answers. O Br 8 peaks 6 peaks O CH 3 OH CH 3 4 peaks 4 peaks 3 peaks O 10 peaks 7 peaks The following four slides show carbon spectra for four isomers. They all have the formula C7H14O. They all show strong peaks at 1715 cm-1 in the infrared spectrum. Determine the structures for each. Possible answers: 4-heptanone 2-heptanone 2,4-dimethyl-3-pentanone 5-methyl-2-hexanone C7 H14O Compound 1 C7 H14O Compound 2 C7 H14O Compound 3 C7 H14O Compound 4 Answers to the previous four spectral questions: 1) 2,4-dimethyl-3-pentanone 2) 4-heptanone 3) 2-heptanone 4) 5-methyl-2-pentanone