Cuyahoga Falls OH 2.27.09sendam
advertisement

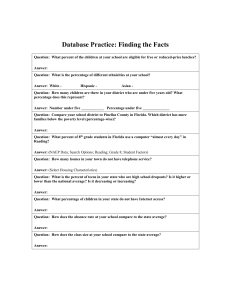
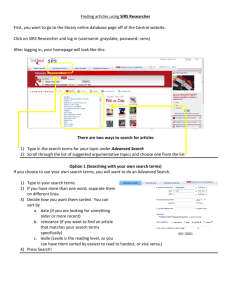
Preparing Students for the 21st Century February 27, 2009 Dr. Willard R. Daggett International Center for Leadership in Education Application Model 1. 2. 3. 4. Knowledge in one discipline Application within discipline Application across disciplines Application to real-world predictable situations 5. Application to real-world unpredictable situations Challenges • Globalization Wal Mart • Largest Corporation • 8 times Size of Microsoft • 2 % of GDP • 1.4 Million Employees • More Employees than: • GM, Ford, G.E. and IBM Combined Source: The Post-American World “China today exports in a single day more than exported in all of 1978.” Source: The Rise of India and China . . . Savings Rate 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. India -- 25% Japan -- 28% Korea -- 30% China -- 50% United States -- (-4%) U.S. – 2nd Half of 20th Century • Only Superpower • Highest per Capita Income • 1st in Economic Growth • 5% of Population > 24% of Consumption Source: National Academy of Science Challenges • Globalization • Technology Information Technology • Processing • Communications 1983 – A Nation at Risk • • • • • • • • E-mail Web pages Google iPODs Laptops Digital cameras Doppler radar Cell phones 2000 • • • • • • • Blogs Wikis Tagging Text messaging MySpace Podcasts PDAs Content Creation & Social Media • • • • • • Facebook MySpace Flickr YouTube Blogs Personal Web Pages SPOT • Microsoft – Citizen – Fossil – Suunco SPOT • Integrated Projection • Projection Keyboard Projection Keyboard Projection Keyboard and Projector Language Translation Translation Goggles Emotiv • 16 embedded sensors • Detect facial expressions and emotions • Push, pull, lift, and drop http://emotiv.com/INDS_3/inds_3.html Bio Technology • Biological Science • Practical Application Nano Technology • Atom Up 2000 Info Tech Nano Tech Bio Tech 2009 Info Tech Nano Tech Bio Tech 2012 Info Tech Nano Tech Bio Tech Chinese Science Elementary Schools 6 Years Integrated Science Biology / Chemistry Grade 7 Biology / Physics Grade 8 Physics / Chemistry Grade 9 Integrated Science Grades 10 - 12 Source: Ed Week 6/6/07 Challenges • Technology • Globalization • Demographics Start Working End Working Longevity 77 62 107 62 47 21 14 18 1900 2000 2100 Retirement 55 is not an economically sustainable policy Demographics / Economic • 1910 3.0 / 100 • 1946 4.6 / 100 • 2010 1.4 / 100 Population of the US (in millions) 2000 4 2050 2 8% 13 % 5 White Black 13 % 68 % Hispanic Asian 24 % Other 14 % 49 % Medicare • 2004 • 2020 • 2040 9% 25 % 50 % Challenges • • • • Technology Globalization Demographics Work Employment 1970’s High Skill Low Skill Employment 1990’s High Skill Semi Skill Low Skill Employment 2010 High Skill Semi Skill Low Skill 1970’s 1990’s 2010 Industrial Base 1900 American Cotton Oil American Steel American Sugar Continental Tobacco Federal Steel General Electric National Lead Pacific Mail People’s Gas Tennessee Coal and Iron Industrial Base 1998 General Motors Wal-Mart Exxon Ford General Electric IBM Citigroup AT & T Phillip Morris Boeing Industrial Base 2010 Software Aerospace Genomics Bioinformatics Nanotechnology Photonics Micro Material Finance IT Robotics Lexile Framework® for Reading Study Summary of Text Lexile Measures Interquartile Ranges Shown (25% - 75%) Text Lexile Measure (L) 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 High School Literature College Literature * Source of National Test Data: MetaMetrics College High School Textbooks Textbooks Military Personal Entry-Level Use Occupations SAT 1, ACT, AP* Expectations have Changed 20th Century 21st Century # of Jobs Job Requirements Teaching Model 1 – 2 Jobs 10 – 15 Jobs Mastery of One Field Flexibility And Adaptability Subject Matter Mastery Life Long Learners U.S. % of World Scientists / Engineers 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 1990 2020 We need to do what workers abroad cannot do equally well for less money… Forging relationships, tackling novel challenges, synthesizing big picture. Business Reality Foreign owned companies and foreignborn inventors account for nearly half of U.S. patents (Japan, Korea and Taiwan more than one-fourth) “Innovate America,” Council on Competitiveness Workplace Trends Unskilled Work to Worker Large to Small 16 Career Clusters Department of Education Agriculture and Natural Resources Arts, Audiovisual Technology, and Communications Business and Administration Architecture and Construction Education and Training Finance Health Science Hospitality and Tourism Human Services Information Technology Law and Public Safety Manufacturing Government and Public Administration Retail, Wholesale, and Service Scientific Research and Engineering Transportation, Distribution, and Logistics Reading Requirements Findings Entry-level Highest in 6/16 Second Highest in 7/16 Consistent Across Country Advanced Lexile Reading Level Range: 850-930 Intermediate Lexile Reading Level Range: 940-1090 Entry Level Human Services Lexile Reading Level Range: 1000-1140 Advanced Lexile Reading Level Range: 1310-1390 Intermediate Lexile Reading Level Range: 1250-1340 Entry Level Construction Lexile Reading Level Range: 1310-1350 Advanced Lexile Reading Level Range: 1310-1440 Intermediate Lexile Reading Level Range: 1280-1310 Entry Level Manufacturing Lexile Reading Level Range: 1280-1330 Proficiency Grade 4 Reading Proficient Wisconsin Texas Iowa Florida Massachusetts California South Carolina 83 % 81 % 77 % 71 % 48 % 48 % 35 % Required NAEP Score Proficiency Grade 4 Reading Wisconsin Texas Iowa Florida Massachusetts California South Carolina Proficient Required NAEP Score 83 % 81 % 77 % 71 % 48 % 48 % 189 190 197 202 234 210 35 % 228 Proficiency Grade 8 Reading Proficient North Carolina Wisconsin Iowa Florida California South Carolina 88 % 86 % 72 % 44 % 39 % 30 % Required NAEP Score Proficiency Grade 8 Reading North Carolina Wisconsin Iowa Florida California South Carolina Proficient Required NAEP Score 88 % 86 % 72 % 44 % 39 % 217 229 250 265 262 30 % 276 Proficiency Grade 4 Mathematics Proficient North Carolina Texas Wisconsin Michigan Florida California South Carolina Massachusetts 91 % 82 % 74 % 73 % 63 % 51 % 39 % 39 % Required NAEP Score Proficiency Grade 4 Mathematics North Carolina Texas Wisconsin Michigan Florida California South Carolina Massachusetts Proficient Required NAEP Score 91 % 82 % 74 % 73 % 63 % 51 % 39 % 203 219 225 222 230 231 246 39 % 255 Proficiency Grade 8 Mathematics Proficient North Carolina Iowa Wisconsin Michigan Florida Massachusetts South Carolina 84 % 76 % 75 % 61 % 58 % 42 % 24 % Required NAEP Score Proficiency Grade 8 Mathematics North Carolina Iowa Wisconsin Michigan Florida Massachusetts South Carolina Proficient Required NAEP Score 84 % 76 % 75 % 61 % 58 % 42 % 247 262 263 269 269 301 24 % 305 Improving Student Performance in Times of Declining Resources Bases of ICLE Position • International Center with Nation’s most Successful Schools • Funding Student Learning – Report • States – Florida – New Jersey Framework Vs. Index Efficient and Effective Framework High Cost Low Cost Efficient and Effective Framework High Student Performance High Cost E f f e c t i v e n e s s Low Student Performance Low Cost Efficient and Effective Framework High Student Performance High Cost C A E f f e c t i v e n e s s D B Low Student Performance Low Cost Efficient and Effective Framework High Student Performance High Cost High Performance High Cost C High Cost Low Performance A Low Cost High Performance D Low Cost Low Performance B Low Student Performance Low Cost Example • Class Size – – – – 25 to 24 4 % increase Payroll Equals 80 % Total Cost = 3.2 % of Budget • Professional Development Ohio English Language Arts Learning Standards Tested Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Grade 9 Grade 10 High 16 36 7 22 18 14 28 34 Medium 5 10 16 6 41 7 17 18 Low 70 38 62 54 22 58 31 24 Levels Bloom’s 6 5 4 3 2 1 C D A B 1 2 3 4 5 Application Gold Seal Lessons Efficient and Effective Framework High Student Performance Focused Professional Development High Cost Reduce Class Size Low Student Performance Low Cost Empower Staff Empower Staff 1. Team of teachers Empower Staff 1. Team of teachers 2. Given group of students Empower Staff 1. Team of teachers 2. Given group of students 3. Agree to their present performance Empower Staff 1. 2. 3. 4. Team of teachers Given group of students Agree to their present performance Give total budget (fixed and variable) Empower Staff 1. 2. 3. 4. Team of teachers Given group of students Agree to their present performance Give total budget (fixed and variable) 5. Give % of savings if student performance improves Successful Examples 1. Teachers in teams with a group of students --- They get 50% of reduced cost if students maintain student performance. If they dramatically improve student performance they get 80% of reduced cost Efficient and Effective Framework High Student Performance X Teacher-Designed Program High Cost Low Cost Existing Program X Low Student Performance Examples 1. Department Chairs Efficient and Effective Framework High Student Performance Interdisciplinary Chairs High Cost Low Cost Low Student Performance Examples 1. Department Chairs 2. Looping Efficient and Effective Framework High Student Performance Looping High Cost Low Cost Low Student Performance Examples 1. Department Chairs 2. Looping 3. Electives to 9th Grade Efficient and Effective Framework High Student Performance High Cost Electives to 9th Grade Low Cost Low Student Performance Technology Efficient and Effective Framework High Student Performance I CAN Learn High Cost Low Cost Low Student Performance Efficient and Effective Framework High Student Performance READ 180 High Cost Low Cost Low Student Performance Examples Coordinate Professional Development with Graduate Degrees Online and Best Practices • • 3 credit hours = 45 contact hours 6 hour days = 7.5 days (45 contact hours) Cost of Graduate Programs 1. Temple University -$573 per credit hour ($837 out of state) 2. State University of New York at Albany -$338 per credit hour ($573 out of state) 3. RPI - $1,285 per credit hour Online and Best Practices • course 3 credit hours = 45 contact hours • 6 hour days = 7.5 days (45 contact hours) • Cost of $450 = $60 per day compared to: - $1,014 - $3,855 per course for Graduate Credit - Cost of Professional Development Day $36,000 per year/180 days = $200 per day Online and Best Practices • • • • 3 credit hours = 45 contact hours 6 hour days = 7.5 days (45 contact hours) Cost of course $450 = $60 per day Tied to nation’s most successful schools and their practices Online and Best Practices • • • • • 3 credit hours = 45 contact hours 6 hour days = 7.5 days (45 contact hours) Cost of course $450 = $60 per day Tied to nation’s most successful schools and their practices Based on district priorities Online and Best Practices • • • • • • 3 credit hours = 45 contact hours 6 hour days = 7.5 days (45 contact hours) Cost of course $450 = $60 per day Tied to nation’s most successful schools and their practices Based on district priorities No travel Online and Best Practices • • • • • • • 3 credit hours = 45 contact hours 6 hour days = 7.5 days (45 contact hours) Cost of course $450 = $60 per day Tied to nation’s most successful schools and their practices Based on district priorities No travel Cost savings to teachers and district PLUS best practices tied to district priorities Relevant and Cost Effective for Teachers Relevant and Cost Effective for District Efficient and Effective Framework High Student Performance X Online Graduate Course High Cost Low Cost Traditional Professional Development X Low Student Performance WHY - WHAT - HOW International Center for Leadership in Education, Inc. 1587 Route 146 Rexford, NY 12148 Phone (518) 399-2776 Fax (518) 399-7607 E-mail - info@LeaderEd.com www.LeaderEd.com