Supplemental Digital Content 1: CURRICULLUM OF
advertisement
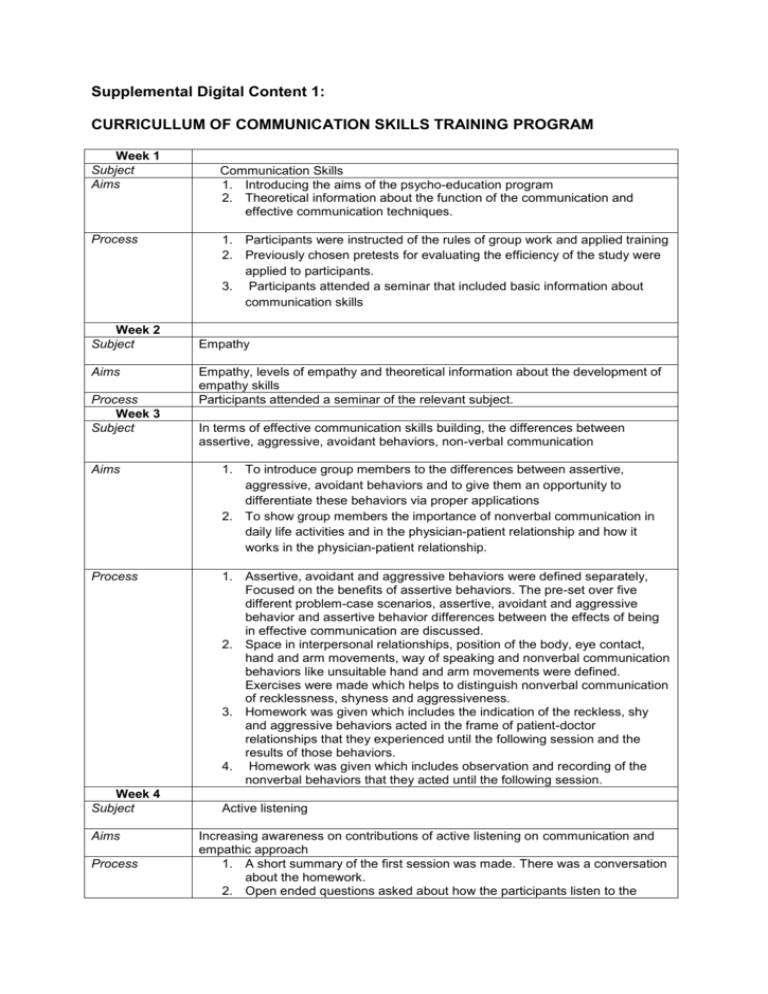
Supplemental Digital Content 1: CURRICULLUM OF COMMUNICATION SKILLS TRAINING PROGRAM Week 1 Subject Aims Process Week 2 Subject Aims Process Week 3 Subject Communication Skills 1. Introducing the aims of the psycho-education program 2. Theoretical information about the function of the communication and effective communication techniques. 1. Participants were instructed of the rules of group work and applied training 2. Previously chosen pretests for evaluating the efficiency of the study were applied to participants. 3. Participants attended a seminar that included basic information about communication skills Empathy Empathy, levels of empathy and theoretical information about the development of empathy skills Participants attended a seminar of the relevant subject. In terms of effective communication skills building, the differences between assertive, aggressive, avoidant behaviors, non-verbal communication Aims 1. To introduce group members to the differences between assertive, aggressive, avoidant behaviors and to give them an opportunity to differentiate these behaviors via proper applications 2. To show group members the importance of nonverbal communication in daily life activities and in the physician-patient relationship and how it works in the physician-patient relationship. Process 1. Assertive, avoidant and aggressive behaviors were defined separately, Focused on the benefits of assertive behaviors. The pre-set over five different problem-case scenarios, assertive, avoidant and aggressive behavior and assertive behavior differences between the effects of being in effective communication are discussed. 2. Space in interpersonal relationships, position of the body, eye contact, hand and arm movements, way of speaking and nonverbal communication behaviors like unsuitable hand and arm movements were defined. Exercises were made which helps to distinguish nonverbal communication of recklessness, shyness and aggressiveness. 3. Homework was given which includes the indication of the reckless, shy and aggressive behaviors acted in the frame of patient-doctor relationships that they experienced until the following session and the results of those behaviors. 4. Homework was given which includes observation and recording of the nonverbal behaviors that they acted until the following session. Week 4 Subject Aims Process Active listening Increasing awareness on contributions of active listening on communication and empathic approach 1. A short summary of the first session was made. There was a conversation about the homework. 2. Open ended questions asked about how the participants listen to the people they communicate with in their daily lives. Listening skill was emphasized. For that aim, participants were exercised: Participants were requested to talk about a subject that they decided for five minutes, and the remaining participants requested to get a nonlistening position. After the talks, there was a conversation about the effects of the non-listening situation. Then, the same exercise was repeated with the listening position. 4. After the exercise finished, the relationship between active listening and active communication, empathy was described and the activity terminated 3. Week 5 Subject Aims Process Week 6 Subject Aims Process Recognition and understanding of emotions and indicating negative emotions 1. To learn how recognizing emotions, distinguishing emotions from thoughts and behaviors and how emotions affect behaviors helps to form empathy 2. To provide telling the positive and negative emotions directly and accepting the negative emotions with tolerance. 1. Exercises were made which aimed participants to distinguish emotion, thought and behaviors with example cases and role playing technique. 2. An exercise was made about participants’ telling positive and negative views directly about each other without hurting the other. During this exercise the importance of using ‘I language’ and differences between ‘I language’ and ‘you language’ from the perspective of communication conflicts were discussed. 3. Homework was given which includes case examples about the subjects which was exercised until the next session. Establishing empathy and placing oneself in someone else’s shoes Establishing the concept of empathy, differences between the concepts of empathy and sympathy, increasing awareness on placing oneself in someone else’s shoes and understanding the emotions and thoughts By reading the participants a patient-doctor relationship scenario prepared previously, emotions and thoughts (both the patient’s and the doctor’s) of the characters of the scenario were attempted to be decided and understood. 1. Similarly, by reading another scenario, participants were requested to put themselves into the characters’ shoes. By this way, empathic perception tried to be developed. 2. After the psycho-education, effectiveness of the exercise was discussed. 3. To evaluate the results of the psycho-education, with the tests which were used in first session posttest application was made.








