Rich – AAT(H) Name: Semester 2 Midterm Review Date: Period
advertisement

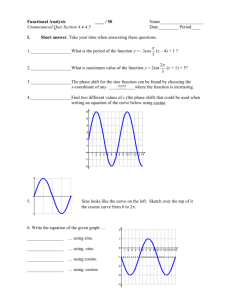
Rich – AAT(H) Name: _________________________________ Semester 2 Midterm Review Date: _____________________ Period: _______ Some things to remember when studying for the midterm: 1. This midterm is designed to be taken during one class period. 2. This midterm will be multiple choice and short answer, all with a calculator. 3. In addition to these example problems, you should also review all previous tests, quizzes, WINKs, and the Unit Circle. 4. This midterm will cover the topics in Unit 3 Part A: Trigonometry and the Unit Circle, and Unit 3 Part B: Graphing Trigonometric Functions. Essential Questions: Think of these EQs as you are studying for the midterm. What is the important information? What do I need in order to start the problem? How is this similar or different from what I have done before? What can I do to retain what I have learned? How can I use this and how does it apply to my life? How do I remember this? Do I need help and where do I go to find it? How would a calculator make this problem easier to do? How do I tell which method to use and how do I apply it? Is there another way to do the problem and which is better? What should this function look like? Learning Targets: These are all of the LTs that have appeared in Unit 3 Part A and Unit 3 Part B. They are all fair game, though it would be impossible for all LTs to appear on the midterm. I would recommend using this as a checklist of skills to help you identify the topics you need help on, and the topics in which you are confident. 3.A.1: evaluate trigonometric functions of acute angles (including special right triangles) 3.A.2: use the fundamental trigonometric identities 3.A.3: use a calculator to evaluate trigonometric functions 3.A.4: use trigonometric functions to model and solve real-life problems 3.A.5: evaluate trigonometric functions of any angle 3.A.6: use reference angles to evaluate trigonometric functions 3.A.7: determine the quadrant of an angle based on the sign of the given trigonometric function 3.A.8: find all trigonometric values of a function with given constraints 3.A.9: use the Law of Sines to solve oblique triangles, including the ambiguous case 3.A.10: find the areas of oblique triangles 3.A.11: use the Law of Sines to model and solve real-life problems 3.A.12: use the Law of Cosines to solve oblique triangles 3.A.13: use the Law of Cosines to model and solve real-life problems 3.A.14: sketch and describe angles 3.A.15: find coterminal angles 3.A.16: convert degrees, minutes, and seconds to decimal form and vice versa 3.A.17: convert between degree and radian measures 3.A.18: use degree and radian measures 3.A.19: use the unit circle to identify trig functions of angles 3.A.20: use angles to model and solve real-life problems 3.B.1: identify periodic functions and their amplitudes 3.B.2: sketch the graphs of basic sine and cosine functions 3.B.3: use amplitude and period to help sketch the graphs of sine and cosine functions 3.B.4: sketch translations of graphs of sine and cosine functions 3.B.5: use sine and cosine functions to model real-life data 3.B.6: write the equation of a sine or cosine function given a graph 3.B.7: sketch the graphs of basic tangent functions 3.B.8: sketch translations of graphs of tangent functions 3.B.9: sketch the graphs of reciprocal trig functions, including translations 3.B.10: write the equation of a tangent or reciprocal trig function given a graph Suggested Book Problems for Review pg. 527 - 530 #3 – 13, 19 – 26, 33 – 39, 50, 51 – 52, 59 – 78, 85 – 99, 101 – 108, 135 – 137, 140, 145 – 149, 151 pg. 644 #1 – 19, 21 – 31