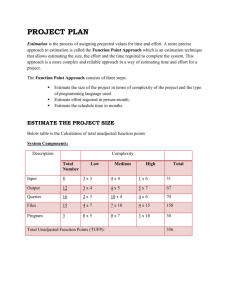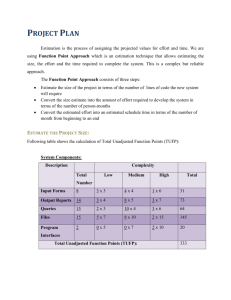
“Index Based Productivity
Benchmarking”
“How Productive
Were Our Teams on
Our Most Recent
Projects?”
Slide 1
Copyright QSMAssociates, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Software Production Equation
Conceptual Form
PRODUCT
SIZE
PROCESS
PRODUCTIVITY
TIME
EFFORT
ESLOC
Function
Points
Objects
Slide 2
=
x
x
Copyright QSMAssociates, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Software Production Equation
Historical Form
PRODUCT
SIZE
PROCESS
PRODUCTIVITY
=
ESLOC
Function
Points
Objects
TIME
EFFORT
x
Slide 3
Copyright QSMAssociates, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Process Productivity Index (PI)
Calculating in Your Environment
In each Development Group, Start by Going
After 1 -3 Past Projects Specific to Your Group
Hold briefing meeting with project managers.
Explain information requirements and lifecycle semantics
Explain what data will be used for
Offer your services in support of data collection
Gather the SEI 4 Core Metrics
Size, Time, Effort, Defects
Slide 4
Copyright QSMAssociates, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Example PI Calculation
Size = 270 Function Points
27,074 LOC
Effort = 24 Person-Months
Time = 6 Months
P ro je c t S ta ffing P ro file
6
5
5
5
5
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
0
J a n-9 7
Slide 5
F e b -9 7
M a r-9 7
A p r-9 7
M a y-9 7
J un-9 7
Copyright QSMAssociates, Inc. All Rights Reserved
How the PI
is Calculated
Step 1 - Note the time for the Main Build phase (Detailed
Design thru Code, Unit Test, Integration, System Accepted
for Deployment). In this case, 6 months.
Step 2 - Record the Full Time Equivalent (FTE) Effort. In
this case, 24 Person-months. This includes design, code,
test, QA, CM staff etc.
Step 3 - Identify the amount of New + Modified Source
Code. In this case, 27,074 SLOC, comprising 270 Function
Points (or about >100 LOC per FP).
Step 4 - Identify B (Integration) Factor from lookup table.
Slide 6
Copyright QSMAssociates, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Lookup Table - Select “B”
(Integration Factor)
Slide 7
Size
B
5k -15k sloc
.16
20k
.18
30k
.28
40k
.34
50k
.37
>70k
.39
Progressively Higher
Values of B allow for
Various Degrees of
Software Integration
Testing
Copyright QSMAssociates, Inc. All Rights Reserved
How the PI is
Calculated (con’t)
Plug Size, Time, Effort, B Factor into SW Equation.
Determine Productivity Parameter (PP). Then Map to a
Productivity Index (PI).
27,074
PP
= (PP) x (6 mos/12) 1.33 x ((24 pm/12)/.28) .33
= (PP) x (.5) 1.33 x (7.14) .33
= 35,422
This Maps to a PI = 17 (See following Table)
Slide 8
Copyright QSMAssociates, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Map Productivity Parameter
to a PI Value
Slide 9
PI
PP
PI
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
754
987
1220
1597
1974
2584
3194
4181
5186
6765
8362
10946
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
PP
13530
17711
21892
28657
35422
46368
57314
75025
92736
121393
150050
196418
Copyright QSMAssociates, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Productivity Index
Industry Baselines - 1997/8
Finance
Retail
Insurance
Others
Slide 10
Category
Business
System Software
Telecom
Scientific
Process Control
Command & Ctrl
Avionic
Real-time
Microcode
PI
17.3
13.7
12.2
12.1
12.1
11.3
8.2
7.8
6.3
STD Dev
+/- 4.1
+/- 4.9
+/- 4.0
+/- 3.5
+/- 3.4
+/- 4.3
+/- 4.8
+/- 3.8
+/- 2.8
Copyright QSMAssociates, Inc. All Rights Reserved
How Does My Org. Compare?
(and What Can I Do to Improve?)
Productivity Index Distribution
BST 1997 Benchmark
3.5
Telecom IT
PI Avg. 17.5
PI Range: 13.5 - 23.6
PI Average: 17.5
3.0
2.5
1.5
Number of Projects
2.0
1.0
0.5
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
0.0
Process Productivity Index (PI)
Slide 11
Copyright QSMAssociates, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Process Productivity Index (PI)
What’s a PI Worth?
Size = 69,000 ESLOC
Burdened Labor Rate = $120,000/PY
Productivity Effort
(PM)
Index
Slide 12
Schedule
(Mos)
Cost
($)
MTTD
(Days)
15
63
14.7
630,000
4.3
14
84
16.4
840,000
3.6
13
120
17.7
1,200,000
2.8
Copyright QSMAssociates, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Process Productivity Index (PI)
Quantifies Team Performance...
Slide 13
Copyright QSMAssociates, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Process Productivity Index (PI)
... In the Environment they are
Working in Day to Day
Management
Methods
Tools
Slide 14
Requirements
Users
Training
Copyright QSMAssociates, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Recommended
Reading
Mah, Michael C., “High-Definition Software
Measurement” © May 1999 Software Magazine
Mah, Michael C., and Putnam, Lawrence H., “Software
by the Numbers: An Aerial View of the Software
Metrics Landscape” © 1997 American Programmer.
Putnam, Lawrence H., and Myers, Ware, “Industrial
Strength Software” © 1997 IEEE Computer Society.
Tufte, Edward, “Visual Explanations, Images and Quantities,
Evidence and Narrative” © 1997 Graphics Press.
Slide 15
Copyright QSMAssociates, Inc. All Rights Reserved