Cell - ColemanBio

Biology
Summer 2009
Read page 41 and answer the following questions.
Your body is made of trillions of cells.
Cell – the smallest unit that can carry out all the activities necessary for life; smallest unit of life
Most organisms are made of a single cell.
Cell Membrane – outer surface of the cell that shields the delicate internal machinery of a cell
Read page 50 and answer the following questions.
What is an example of a single-celled organism?
Bacteria
Nucleus – contains DNA within chromosomes; control center of the cell; the boss
Eukaryote – organisms that have cells with a nucleus
Prokaryote – organisms that do not have a nucleus
Cytoplasm – fluid internal environment of the cell; everything between cell membrane and nucleus
Ribosomes – where proteins are made
Eukarytoic
Cell
Prokaryotic
Cell
Read pages 51 -54 to answer the following questions.
Cytosol – aqueous (watery) space in the cytoplasm; like jello holding fruit in place
Organelle – specialized compartment that carries out one or more specific functions
How do organelles benefit eukaryotic cells? the separate compartments alow specialized activities to be restricted to particular places; organization
Organelle Function
Mitochondria
Endoplasmic Reticulum
(ER)
Golgi apparatus
Chloroplast makes energy for the cell; power house used to transport materials throughout the cell packages and labels proteins to be shipped out of the cell makes food for plant cells
Cell Wall
Vacuole provides structure and support for plant cells storage for food and water
Kind of Like A…
Plant Cell Animal Cell
Complete Cell Worksheet; Identify Function of Part and Identify Part in a Diagram
Compound Light Microscope – microscope used to see inside of transparent objects (example: cells, pond water)
Magnification
Magnification is the measure of how much larger the object appears through the microscope than it actually is. For example if you are looking at leaf using a stereomicroscope with 3x magnification, the parts of the leaf will appear 3 times larger than they actually are.
Magnification can be determined by multiplying the magnification of each lens used to see the object.
10x X 4x magnification magnification of eyepiece of objective lens
= 40x total magnification
Complete the chart below to calculate the total magnification of an object.
Total Magnification Eyepiece Lens
15x
10x
20x
Objective Lens
15x
10x
40x
Bromthymol Blue Demonstration
Observations
What do we think we know about photosynthesis?
What do we think we know about respiration?
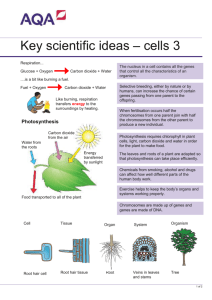
Photosynthesis – process by which organisms use the energy of light to make food in the form of carbohydrates (glucose)
Word Equation for Photosynthesis
Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis
Respiration – process by which organisms use food energy (glucose) to make chemical energy (ATP); make batteries that run each cell
Word Equation for Respiration
Chemical Equation for Respiration
Photosynthesis & Respiration are Cellular Processes.
Where in the cell do they take place?
Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplast of plant cells only. Organisms that perform photosynthesis are called producers . Organisms that cannot perform photosynthesis are called consumers.
Respiration takes place in the mitochondria of every living organism.
Anaerobic Respiration (Fermentation) – respiration without oxygen; additional “waste” will be produced
Word Equation for Respiration
Word Equation for Anaerobic Respiration (Humans)
Photosynthesis & Respiration Demonstration
Test Tube
Empty tube with bromthymol blue
Sunlight
Initial Observation Observation after 24 hrs
Conclusion (What happened in the test tube?)
Blue
Bromthymol Blue
Snail Only
Sunlight
Blue & Living Snail
Blue & Living Plant Bromthymol Blue
Plant Only
Sunlight
Bromthymol Blue
Snail & Plant
Sunlight
Blue & Living Snail and
Plant
Photosynthesis & Respiration as Cellular Processes/Review
Photosynthesis: Chloroplast
Respiration: Mitochondria
Cellular Processes: Mitosis & Meiosis
July 2, 2009
Read and take notes on pages 101-103
The set of instructions that determines that you are a human and not another type of organism is a long molecule found inside the nucleus called DNA.
Chromosomes (use glossary on page 858) – compact structure of tightly coiled DNA that forms prior to mitosis (and meiosis)
If a strand of DNA from a single chromosome were laid out in a straight line, it would be about 5 cm long.
DNA must be wound around proteins so that it can fit inside the cell’s nucleus.
Karyotype – a visable set of chromosomes for an organism; human karyotype below
Most cells of your body contain 46 chromosomes.
Diploid Cell – cell which contains pairs of chromosomes; human diploid cells have 23 pairs of chromosomes or 46 total chromosomes; almost all body cells are diploid cells.
Haploid Cell – cell which contains only one set of chromosomes; human haploid cells only have 23 total chromosomes; reproductive cells are haploid cells.
Sex Chromosomes – a pair of chromosomes that determines your gender.
Females have two X chromosomes. Males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome.
Mitosis – process by which identical copies of cells are made; necessary for growth and repair
•Start with a cell that has 46 chromosomes. End with a cell that has 46 chromosomes.
•Each new cell must be identical to the original cell.
•For one original cell 2 new cells will be made.
Meiosis – process by which genetically different cells are made that have half the number of chromosomes as a normal body cell; necessary for making reproductive cells
•Start with a cell that has 46 chromosomes. End with a cell that has 23 chromosomes.
•Each new cell must be genetically different than the original cell.
•For one original cell 4 new cells will be made.