Marriages and Families:
Changes, Choices, and Constraints
Seventh Edition
Nijole V. Benokraitis
Chapter Six
Romance, Love, and Loving Relationships
I Love You Man!!
Love, both as an emotion and a
behavior, is essential to human
survival.
The family is usually our first form of
love; it provides not only the
necessary physical things to get by,
but it also provides the necessary
emotional support we need to grow
up.
Self-Love
For social scientists, self-love is an
important part of self-esteem.
Friendship—a friend is someone for
whom you feel affection and respect—
you can count on them for assistance
and they can count on you.
Friends can even help you live a longer,
healthier life.
Eight Important Qualities of
Friendship—by Keith Davis
1. Enjoyment–friends enjoy being
together.
2. Acceptance–friends accept each
other the way they are.
3. Trust—friends trust and look out for
each other.
4. Respect—friends respect each
other’s judgment.
Eight Important Qualities of
Friendship—by Keith Davis
5. Mutual support–friends help each other
without expecting anything in return.
6. Confiding–friends share experiences and
feelings.
7. Understanding–friends are sympathetic
about each other’s feelings and thoughts.
8. Honesty–friends are open and honest.
They feel free to be themselves and say
what they think.
What Is Love?
Love includes all of the qualities of
friendship plus three more:
– Sexual desire
– Priority over other relationships
– Caring to the point of self-sacrifice
Love, like friendship, is a process that
grows over time.
What Is love?
People sometimes make distinctions
between loving someone—like a
family member, aunt, uncle, etc.
Being “in love” for most people is
different—this is about romantic love.
Both types of love nonetheless are
multifaceted, based on respect, and
are often demanding.
Attraction
What attracts people to each other?
Does everyone have “one true love”?
Many cultural norms and values bring
us together and it isn’t necessarily as
“romantic” as it seems.
We are influenced by all those around
us, especially our family, when it
comes to who we “love.”
Love and Lust
There is a distinct difference between love
and lust. Psychologists Pamela Regan and
Ellen Berscheid (1999) differentiated
among sexual arousal (or lust), sexual
desire, and romantic love.
They describe sexual arousal is a
physiological rather than a psychological
state. Sexual desire, in contrast, is a
psychological state.
Romantic love is an intense feeling that can
provide ecstasy when fulfilled or deep
suffering when the feeling isn’t
reciprocated.
Caring, Intimacy,
and Commitment
Love includes caring or wanting to help the other
person. Caring means responding to the other
person’s needs.
Intimacy emphasizes feelings of closeness.
Couples experience intimacy when they have
shared history, an identity as a couple, emotional
interest in each other, and share hopes and
dreams for the future (P.M. Brown, 1995).
Commitment is a person’s intention to remain in a
relationship and work through any problems. It
doesn’t necessarily mean marriage but it may
lead to marriage.
Caring, Intimacy,
and Commitment
– Mutual commitment can arise out
of a sense of loyalty and fidelity
to one’s partner, a religious or
legal belief in the sanctity of
marriage, or a legal contract.
Theories about Love
and Loving
Biological theories maintain that love is
grounded in evolution, biology, and
chemistry. Some evolutionists and
biologists see love as necessary to
form long-term relationships for the
continuation of the species.
They may see love as short-lived
because it is a chemical reaction in
the brain.
Helen Fisher of Rutgers University -3 stages
of love – lust, attraction and attachment
Stage 1: Lust
This is the first stage of love and is driven
by the sex hormones testosterone and
estrogen – in both men and women.
mechanisms that cause you to
constantly think about your
lover, were related to the brain
mechanisms of ObsessiveCompulsive Disorder.
By analysing blood samples
from the lovers, Dr Marazitti
discovered that serotonin levels
of new lovers were equivalent to
the low serotonin levels of
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
patients.
Love needs to be blind
Newly smitten lovers often
idealise their partner,
Stage 3: Attachment
Attachment is the bond that keeps couples
together long enough for them to have and
raise children.
Oxytocin - The cuddle hormone
Oxytocin is a powerful hormone released by
men and women during orgasm.
It probably deepens the feelings of attachment
and makes couples feel much closer to one
another after they have had sex. The theory
goes that the more sex a couple has, the
deeper their bond becomes.
Vasopressin
Vasopressin is another important hormone in
the long-term commitment stage and is
released after sex.
Vasopressin (also called anti-diuretic hormone)
Theories about Love
and Loving
Sociological perspectives and some
psychological theories claim that
culture, not brain chemistry, plays
the role of Cupid.
Theories about Love
and Loving
These theories include:
•Attachment theory
•Reiss’s wheel theory of love
•Sternberg’s triangular theory of love
•Lee’s research on the styles of loving
•Exchange theories
Attachment Theory
This theory proposes that our primary
motivation in life is to be connected with
other people, because this is the only true
security we will ever have.
John Bowlby and Mary Ainsworth are
researchers associated most often with this
theory.
Several studies have tracked attachment
style from toddlerhood through adulthood
and have found that attachment styles can
change over the life course, regardless of a
child’s early experiences.
Reiss’s Wheel Theory
of Love
Sociologist Ira Reiss and his associates
have proposed a “wheel theory” of
love, that generated much research
for several decades. Reiss described
four stages of love: rapport; selfrevelation; mutual dependence; and
personality need fulfillment.
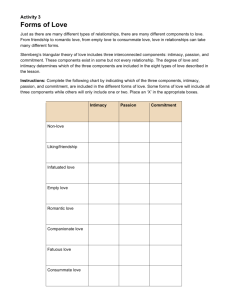
Sternberg’s Triangular
Theory of Love
Sternberg said that love has three important
components:
– Intimacy—encompasses feelings of closeness,
connectedness, and bonding.
– Passion—leads to romance, physical attraction,
and sexual consummation.
– Decision/commitment—has a short- and longterm dimension. A couple makes a short-term
commitment to love each other, which can turn
into a long-term commitment to stay in love.
Sternberg’s Triangular
Theory of Love
• According to Sternberg, the mix of
intimacy, passion, and commitment can
vary from one relationship to another.
Love can vary from one relationship in which
there is no love to another relationship in
which all kinds of love are present.
Lee’s Styles of Loving
John Lee developed one the most
widely cited and studied theories of
love. According to Lee, there are six
basic styles of loving: eros, mania,
ludus, storge, agape, and pragma, all
of which overlap.
Exchange Theory
Social scientists often describe love as a
social exchange process. Romantic love
and long-term relationships involve
exchange and negotiation.
Functions of Love
and Loving
Love ensures human survival—loving
someone and being loved ensures the
survival of our species.
Love enhances our physical and emotional
health—numerous studies have shown a
connection between our emotions and
our physical and emotional health, and
love is certainly one of those essential
emotions.
Functions of Loveand Loving
Love improves the quality of our lives—
love fosters self-esteem. From a solid
basis of love, children can then go out
and face the world with the emotional
support of their families.
Love is fun—love doesn’t appear out of
nowhere, to get and keep love, one
has be active and take some chances.
Experiencing Love
Who is most likely to be in love?
According to recent research, it is men
between the ages of 30-49 and people
who are married. Surprised?
For most people caring, trusting,
respect, and honesty are central to
loving.
Are Men or Women
More Romantic?
According to research, men are more
likely to fall in love quickly. Both men
and women tend to link love and sex.
Men can be very romantic, but not see
love as necessarily leading to
marriage.
Are Women or Men
More Intimate?
Men and women show intimacy
differently. Women link intimacy with
being held, cuddled, and with
communication.
Men link intimacy with sex.
For women, sex comes after intimacy,
for men, sex is their way of expressing
intimacy.
Same-Sex Love
Homophobia—the fear and hatred of
homosexuals—has decreased in the
past decade. Gay men and lesbian
women are more likely to openly display
their relationships and feelings for one
another.
Breakups and all the relationship problems
that heterosexual couples go through
also haunt homosexual couples.
Barriers to
Experiencing Love
A number of obstacles can block our search for
love:
– Mass society and demographic factors—because
we live in a media age, our face-to-face
conversations and lives have changed. We no
longer need to see people face-to-face to chat or
even to purchase something at a store—we can
do it online, which diminishes our chances of
meeting people.
Barriers to
Experiencing Love
– The double standard—our society still
discriminates against women in the sense that if
men have premarital sex it is OK, but if a
woman does that she is labeled a “tramp” (or
worse).
– “Me First” individualism—we are a “me first”
generation. We want our own needs to be met
first and then we are willing to meet the needs
of others—a real relationship cannot be that one
sided.
Barriers to
Experiencing Love
– Personality and family characteristics—those
around us have a large influence on who we are
attracted to and with whom we have
relationships.
– We are responsible for our own relationships,
but we still look to others for advice, especially
family members, and when our family does not
approve of our dating partner, it makes it more
difficult to pursue that relationship.
When Love Goes Wrong
Narcissists are people who have
exaggerated feelings of power and selfimportance. They believe that they are
unique.
Narcissistic partners can be dangerous in
a relationship. Depending, of course, on
the person, they may become intensely
jealous over meaningless things and try
to control the partner.
Jealousy
Jealousy is a form of control of one
partner over another. The person
exhibiting the jealousy or control tries
to isolate the victim by becoming
jealous of every minute they spend
doing something besides paying
attention to them.
Are Men or Women More Jealous?
One researcher found that women are
more jealous of emotional infidelity
than of sexual infidelity.
– This could be for two reasons:
1. They could blame themselves—“Maybe I
wasn’t there enough for him.”
2. They see an emotional affair as more
threatening because it could develop into a
long-term relationship.
Jealousy and Stalking
Some jealous lovers become obsessed and
stalk their former lovers. Stalking
behaviors include telephone harassment,
following a person, threatening a person
or their family, or now even cyberstalking.
Many women live in fear for their lives
because the men they once thought loved
them are being abusive.
Other Controlling Behaviors
Threats of homicide or suicide, threats
against family members or children,
guilt trips, emotional abuse, and
physical abuse.
How Couples Change: Romantic
and Long-Term Love
Long-lasting love provides security and constancy.
– Love usually starts as romantic love which is
characterized by:
• Finding it impossible to do anything but
think about that one person.
• Wildly fluctuating moods.
• Finding it impossible to believe that they will
ever love again.
• Fantasizing about how their partner will
declare their love.
• Caring so desperately for the other person
that nothing else seems to matter.
• Being willing to do anything for the beloved.
Love in Long-Term Relationships
Romance is just a stepping stone to
long-term love. Some characteristics
of long-term and romantic love
overlap.
Love in Long-Term Relationships
Romantic love is fairly simple compared to
long-term love.
Romantic love is often self-centered, whereas
long-term love is altruistic.
Romance is typically short-lived because love
changes over time.
Long-term love grows and develops, whereas
romantic love is typically immature.
Companionate love is more characteristic of
long-term relationships compared with
passion and game-playing in romantic love.
A Global View of Love
The meaning and expression of love
differs from culture to culture.
Romantic love is an important
component of marriage in about
89% of countries, whereas in some
cultures kinship ties take
precedence over romantic love.
In some countries arranged
marriages still exist.