File
advertisement

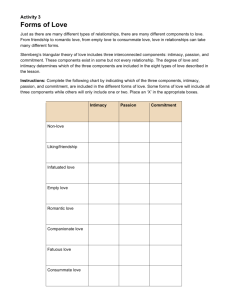
• Love • Love—a ______________ and _______________ emotion that satisfies certain needs, motivates human behavior, and is coupled with caring for and acceptance of the beloved resulting in an intimate relationship • Components of Love • Deep and Vital Emotion—a strong feeling, arising without __________ ___________ effort emotions motivate individuals to behave in particular ways • Satisfies personal needs—fulfills human’s basic needs for recognition and affection satisfies ‘legitimate’ needs of ________ support, understanding, ______________, and emotional sharing does not satisfy ‘illegitimate’ needs of ______-_________, unworthiness, or ________________ • Involves caring and ____________________ • Theories of Love • Evolutionary Perspective • Psychological Perspectives • Attachment Theory • Reiss’s Wheel Theory of Love • Evolutionary Perspective • Love serves to draw men and women into long-term relationships for the purpose of bearing children • Duration of love: – 4 years for 1 child – 7 years for 2 children • Psychological Perspective • Sternberg Triangular Theory – Love has 3 dimensions • Intimacy • Intimacy is the _____________ component – Includes sharing ___________ and providing emotional support – Increases as closeness grows and relationship _____________ • Passion • Passion is the ____________ component – Expressed by ______________ and feeling – Develops quickly and can fade ____________ • Commitment • Commitment is the ___________ component – Moving toward a more advanced stage in the relationship – Involves staying in a relationship over ______ times – Begins slowly, but rapidly increases if the relationship is ______________ • Sternberg Theory • There are 8 love relationships: – Non-love—absence of all 3 dimensions – Infatuation—passion only – Liking—intimacy only (emotion) – Romantic love—intimacy + passion – Companionate love—intimacy + commitment – Fatuous love—passion + commitment – Empty love—commitment only (staying for the kids) – Consummate love—intimacy + passion + commitment • Attachment Theory • Your early relationship with your primary caregiver (most often mothers) serves as the __________ for later ____________, including romantic relationships • 3 types of attachment: – Secure • • • • • • • • • • • • – Anxious/ambivalent – avoidant Secure Attachment Mother was responsive – Secure adults: easy time getting close to others, more comfortable and satisfied in their relationships – Key word: satisfied Anxious/Ambivalent Attachment Mother was _______________ – Worried more often that partners will ________ them – More obsessive in relationships – Key idea: think that partner will leave Avoidant Attachment Mother was ________________ – Distrustful and fearful of becoming ______________ on others – Key idea: no trust Reiss’s Wheel Theory of Love Reiss’s Wheel Theory of Love Love is maintained through 4 processes: – Rapport—rests on ___________ trust and respect – Self Revelation—the disclosure of __________ feelings – Mutual Dependency—become dependent on one another 1. When that person is missing, you _______ them – Personality Need Fulfillment—we have a basic need for _______________ that is fulfilled by our partners Sex differences in Love and Romance Men fall in love easier than women Men stay in love longer than women – Men have a harder time recovering from breakups – Men are more resistant to breaking up • Men are more likely to idealize their partners – Men often see partners as ‘love of their lives’ • Women experience more emotional symptoms of love • Where do you fall in love? • Most common place is _________ – 6-8 million Americans per year become romantically involved at work