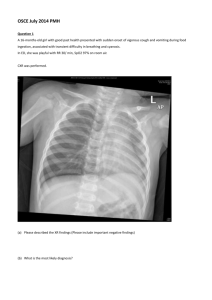
Carol Rivers' Board Review Flash Cards
advertisement

Critical Q’s & As Sixth Edition Behavioral What are the factors associated with an increased likelihood of suicide? Elderly (or adolescent) and male Unmarried (single, divorced, widowed) Recent loss of loved one (usually within 6 months) Family History of suicide Past suicide attempts or a suicide plan Unemployment or severe financial difficulties Severe family stress Recent major depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, alcoholism, drug abuse or loss of a parent in early childhood or adolescence What drug is contraindicated in patients taking MAO inhibitors because of the occurrence of a severe hyperpyrexic reaction? Meperidine (Demerol ®) The diagnosis of malingering may be considered when the patient: Has history of antisocial personality disorder Feigns mental illness or amnesia Fails to cooperate with a history, physical exam and diagnostic evaluation The _______ is often inappropriately calm in the setting of devastating chief complaint, such as acute blindness or paralysis. Patient suffering from a conversion disorder A patient presents with severely agitated, violent behavior. What is the most appropriate management? Physical restraint/seclusion followed by administration of Haloperidol (Haldol®) 5 mg IM, Ziprasidone (Geodon®) or Lorazepam (Ativan®). A patient who has an acute disturbance of consciousness cognition and perception has what type of illness? Acute delirium Which neuroleptic agent reduces agitation, is not very sedation, has a rapid onset but is associated with extrapyramidal side effects? Haloperidol (Haldol®) (Newer neuroleptics, e.g. olanzepine, risperidone, ziprasidone, have less risk of extrapyramidal side effects) What are the symptoms of depression? Sleep disturbance Change in appetite Impaired concentration and memory Reduced level of activity Dysphoria Lack of concern for personal appearance Suicidal thoughts Feelings of hopelessness/helplessness Which organic brain syndrome is characterized by progressive impairment of cognitive function in which recent memory disturbance is the earliest sign? Dementia Which drug should never be used for behavior control in the agitated delirious patient? The opioids, morphine and meperidine, can exacerbate acute brain failure. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) have serious food and drug interactions. What are they? 1. 2. 3. MAOIs + food containing tyramine (aged cheese, chianti wine) or sympathomimetic drugs (pressors, OTC stimulants/decongestants) ACUTE MAOIs + meperidine (Demerol®)COMA MAOIs + SSRIs confusion, diaphoresis, shivering and myoclonus (SEROTONIN SYNDROM) Patients who present with vague symptoms such as weakness, fatigue, headache or pain may have ______ _____. Masked or hidden depression Cardiovascular Which dysrhythmia occurs primarily with severe hypoxia secondary to acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease? Multifocal atrial tachycardia What is the initial ECG abnormality in patients with “torsades de pointes” (a vibrant of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia)? Prolongation of the QT interval. A QT interval 500 msec clearly increases risk of torsades What are the common precipitating factors of torsades de pointes? Most cases are ACQUIRED, as opposed to the less common congenital causes. Acquired causes are: Drug induces (type IA and IC antidysrhythmics, cyclic antidepressants, phenothiazines, organophosphates, droperidol and antihistamines) Drug combinations: astemizole or terfenadine with azole antifungals (fluconazole, ketoconazole) or with macrolide antibiotics (erythromycin, clarithromycin) Electrolyte abnormalities, especially hypomagnesemia and hypokalemia What are the therapeutic consideration for patients with torsades de pointes? 1. Removal and / or discontinuation of the offending drug or correction of the underlying electrolyte disorder; 2. Intravenous magnesium (which shortens the QT interval) is the TREATMENT OF CHOICE; 3. Also effective are overdrive pacing and intravenous isoproterenol (Isuprel®) which has no effect on the QT interval. What is the best initial therapy for the unstable patient with rapid atrial fibrillation? Synchronized cardioversion What is the initial therapy for symptomatic patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (such symptoms include angina, dyspnea, syncope and lightheadedness)? Beta Blockers What are indications for endocarditis prophylaxis? High risk conditions for endocarditis include prosthetic heart valves and valve repair material; history of previous infective endocarditis; unrepaired cyanotic congenital heart disease; repaired congenital heart defect with prosthetic material, or repaired congenital heart disease with residual defects, and cardiac transplant recipients with valve regurgitation due to a structurally abnormal valve. What is usually seen in young, otherwise healthy patients as a result of either accidental or intentional overdose is commonly associated with hyperkalemia, high digoxin levels and bradydysrhythmias as well as AV block; toxicity in these patients most closely correlates with the degree of hyperkalemia (not the serum digoxin level)? Acute digitalis toxicity What is the classic ECG finding in acute pericarditis? Diffuse nonanatomical ST segment elevation with upward concavity is prominent and is seen in all leads except a VR and V1. PR segment depression is often present, most prominent in lead II and often the earliest ECG manifestation of acute pericarditis. Which criterion should be used to distinguish ventricular tachycardia from SVT with aberration? Fusion and capture beats indicate AV dissociation and are practically diagnostic of ventricular tachycardia. A 65-year old woman with a PMH of CAD, CHF and renal insufficiency is brought in by ambulance for evaluation. Her mediations include furosemide, digitalis, sublingual nitroglycerin and baby aspirin. According to family members, she has become progressively more confused and week over the past few days and has not been eating well. The ECG shows a regular wide complex tachycardia with alternating QRS polarity (bi-directional ventricular tachycardia) and laboratory evaluation reveals a digoxin level of 3.5 and a potassium of 3.0. What is the most likely diagnosis? Chronic intoxication with digoxin Transient, episodic chest discomfort that is predictable and reproducible, i.e. familiar symptoms occur from a characteristic stimulus that improves with rest or sublingual nitroglycerin within a few minutes, demonstrates what? Stable angina. These patients are usually sent home or observed briefly in the ED. What is the most common cause of right-sided CHF? Left-sided CHF Which conditions are most likely to predispose a patient to subacute bacterial endocarditis? 1. 2. Pre-existing valvular heart disease especially of the mitral and/or aortic valves. Mitral valve disease is most common (INCLUDING mitral valve prolapsed). Injecting drug users who present with right-sided disease. The tricuspid valve (most commonly involved) is usually normal before onset disease. NOTE: Murmurs are frequently ABSENT What are the reasons for the high mortality rate (>70%) seen in patients with mesenteric vascular occlusion? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Difficulty in early diagnosis Refractory mature of advanced disease Frequent association of other serious diseases Age at which disease occurs has high frequency of comorbid disease Small bowel warm ischemia time is 2-3 hours What is the most common bacterial organism that causes infective endocarditis? Is this the same organism if the patient is an injecting drug user? Non-viridans streptococci (alpha streptococci) No. the organism is Staphylococcus aureus. What are the common conduction disturbance in an acute myocardial infarction? Bradydysrhythmias and AV conduction block Angina that is a new in onset, occurs at rest or is similar but somewhat “different” than previous episodes, is severely limiting or lasts longer than a few minutes, with increased frequency of attacks or resistance to prescribed medications that previously relieved that symptoms (e.g. NTG, the “blockers”) demonstrates what? Unstable angina. Patients are admitted for observation or coronary care. What is the earliest and most common rhythm disturbance seen with digitalis toxicity? PVCs Which drug should be avoided in the therapy of an idioventricular rhythm, because it may obliterate the patient’s only functioning rhythm? Lidocaine What is the treatment of MULTIFOCAL ARTIAL TACHYCARDIA? The MOST IMPORTANT consideration in this dysrhythmia is aggressive treatment of the underlying cause(s) (hypoxia, CHF, sepsis, theophylline toxicity). What are the most common causes of sinus tachycardia? Condition in which catecholamine release is physiologically enhanced (flight, fright, anger, stress, pain) Fever Hypoxia Drugs Anemia Cardiac ischemia, ACS Hypovolemia Sepsis Hypotension Pulmonary embolism Hyperthyroidism Cardiac tamponade Stimulants, illicit drugs What are the ECG findings in digitalis toxicity? PVCs* (often bigeminal and multiform) Junctional tachycardia (common) SA and AV nodal block A-Fib with a slow ventricular response SVT, ESPECIALLY Pat with block Ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation Bidirectional V-Tach 9rare but highly suggestive of digitalis toxicity) Sinus bradycardia/sinus arrest *MOST COMMON Substernal chest discomfort greater than 15 minutes’ duration associated with dyspnea, diaphoresis, lightheadedness, palpitations, nausea and/or vomiting, with pain likely radiating to the inner aspect of one or both arms, shoulders, neck or jaw exhibited within a few hours of awakening in the morning demonstrates what? Acute myocardial infarction. An AMI is classified as a non-STsegment elevation MI (NSTEMI) or an ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI). These patients are admitted to CCU after appropriate treatment. A patient with the chief complaint of “syncope” has a systolic ejectiontype murmur heard maximally either as the lower left sternal border or at the apex that increases with Valsalva maneuver. The ECG shows left ventricular hypertrophy. What is the suspected diagnosis? Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy What is the most common complication of thrombolytic therapy in patients with acute MI? Reperfusion dysrhythmias What are the typical ECG findings in an acute inferior wall MI? Acutely, ST segment elevation occurs in leads II, III and aVF. Reciprocal ST segment depression may occur in leads I, aVL and I V1 –V6. REMEMBER: Q waves may take hours to develop or they may be absent (“non-Q wave” infarctions). Which drugs may be used for hypertensive emergencies in eclampsia prior to delivery? Hydralazine Labetalol Which diagnosis should be excluded in any patient older than 50 years of ago who presents with abdominal pain, back pain, weakness or syncope? Abdominal aortic aneurysm REMEMBER that the absence of a palpable abdominal mass and/or the presence of a palpable femoral pulse DOES NOT exclude this diagnosis Who is more likely to have atypical presentation for acute coronary syndrome? Elderly patients, diabetic patients and women What is a therapeutic contraindication to the administration of IV verapamil? Recent IV administration of propranolol Which drugs are contraindicated in the treatment of ventricular tachydysrhythmias caused by digitalis toxicity? Bretylium Class I antidysrhythmics (procainamide, isoproterenol) Propranolol What electrolyte abnormality is a common cause of dysrhythmias in AICD patients? Hypomagnesemia What is the drug of choice for conversion of a narrow-complex supraventricular tachycardia? adenosine (Adenocard®) Why are alcoholics prone to the development of torsades de pointes and why is this important therapeutically? Chronic alcoholism is associated with hypomagnesmia which can lead to prolongation of the QT interval, a common cause of torsades. Treatment with magnesium is essential because this rhythm may degenerate into V-fibrillation.. Furthermore, if lidocaine or procainamide are given, they may aggravate the dysrhythmia. Which type of angina is classically associated with ST segment elevation (rather than depression) and pain that is usually relieved promptly by nitrates? Prinzmental’s (variant) angina. The other point here is that this type of angina usually occurs AT REST. What is consideration the THERAPY OF CHOICE in the setting of an acute aortic dissection associated with hypertension? Intravenous beta blocker (propranolol, esmolol or labetalol) in combination with nitroprusside. NOTE: The goal of therapy is reduction of aortic wall stress both by lowering blood pressure and by decreasing cardiac output. CLINICAL PRESENTATION: Pain and swelling in the calf and tenderness on AP compression. 1. What is the INITIAL diagnostic study of choice? 2. What diagnostic study is the most SENSITIVE 1. 2. Duplex ultrasonography Venogram Regarding cardiovascular conditions, nausea and vomiting may be the only presenting sign and symptom of ___ ___ ___. Inferior wall MI “Hypertensive emergency” is defined as an extreme elevation of BP with signs or symptoms of end-organ disease. What is an effective, reliable and safe drug for a hypertensive emergency in the setting of myocardial ischemia or CHF? Sublingual nitroglycerin The most frequent ECG findings in chronic ischemic heart disease are ___________ Nonspecific ST and T waves changes (ST segment elevation/depression<1 mm and T eave flattening or inversion) Persistence of ST segment elevation in the weeks and months after myocardial infarction indicates the development of a ___________. Left ventricular aneurysm What is the most common atrial dysrhythmia seen in the setting if an AMI? Atrial fibrillation A middle-aged patient presents to the ED in acute pulmonary edema. He was seen a week ago for “chest pain” but signed out AMA before an ECG was done. Current ECG shows an inferior wall infarct. What is the most likely cause of this patient’s distress at this time? Papillary muscle rupture ACE-inhibitors are contraindicated in patients with which disorders? Angioedema associated with ACE-inhibitor therapy Significant hyperkalemia Bilateral renal artery stenosis or unilateral with a solitary functioning kidney By far, the most common complication of dilated cardiomyopathy is _________. Progressive CHF What class of drugs are the most effective for the treatment of chronic CHF associated with dilated cardiomyopathies? The ACE-inhibitors Which drug should be avoided in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy? Digitalis (may worsen obstruction) What is the most frequent complication associated with implantable cardioverter/defibrillators (ICDs)? Inappropriate cardioversion is the most frequent complication associated with ICDs. This should be considered if a patient presents in atrial fibrillation or if a patient has received multiple shocks in rapid succession without premonitory symptoms. What are the historical criteria used to evaluate the patient with a normal (or unchanged) ECG for high risk of having an acute coronary syndrome? 1. Documented stenosis ( 50%) in at least major coronary artery 2. 2 episodes resting angina in the last 24 hrs. 3. History of 3 or more cardiac risk factors 4. Presence of chest pain 5. Prior daily ASA intake for CAD prevention What other criteria are used to identify high-risk patients with an unremarkable ECG? Age 65 years Congestive heart failure New ST deviation 0.5 mm in limb and/or precordial leads New pathologic Q waves Sustained ventricular tachycardia Significant elevation of cardiac markers What is the appropriate treatment for symptomatic bradydysrhythmias in a patient with a heart transplant? Isoproterenol is the preferred agent (1-4mcg/min.) because its chronotropic effects are greater than dopamine or dobutamine. Atropine will have no affect on heart rate in these patients because of the lack of parasympathetic innervation in the transplanted heart. What is the appropriate ED management if a small unruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm in a healthy, asymptomatic, elderly patient? Prompt outpatient referral What diagnosis should be excluded in patients with RBBB and ST elevation in the right precordial leads? The Brugada syndrome (Sodium channel dysfunction predisposes patients to ventricular fibrillation. Drug therapy is ineffective. Placement of an internal cardioverter defibrillator is indicated.) Which baseline studies should be ordered prior to anti-coagulation in patients with DVT? CBC INR aPTT Creatinine What are the contraindications to anticoagulant therapy for patients with DVT? Absolute contraindications Active Bleeding Severe bleeding diathesis or platelet count 20,000/mm3 Neurosurgery, ocular surgery or intracranial bleeding within the past 20 days Relative contraindications Mild to moderate bleeding Brain metastases, endocarditis Recent major trauma Major abd. surgery 2 days GI or GU bleeding 14 days Severe hypertension (i.e. Systolic BP 200 mmHg or diastolicBP 120 mmHg at presentation *Mild-to-moderate thrombocytopenia is defined as a platelet count that is normal but 20,000/mm3. Endocrine/Metabolic What are the electrolyte abnormalities seen in Addison’s disease? Hponatremia (most common) Hyperkalemia (next most common) Hyercalcemia CLINICAL PRESENTATION: A patient complains of sudden onset of shortness of breath while dining out in a restaurant; he was swallowing food when the symptoms began. Physical findings include inspiratory stridor and bilateral expiratory wheezing What is the most likely diagnosis? Acute anaphylactic reaction Which therapy should NOT be given to the alcoholic who is actually ill, dehydrated and has the following laboratory values? * Glucose 140 mg/dL * Blood alcohol 0.00 mg/dL * pH = 7.18 * Serum ketones elevated Bicarbonate is not indicated This patient has ALCOHOLIC KETOACIDOSES. The treatment consists of fluids restoration and glucose. Some patients may have even modest hyperglycemia, but “refeeding” unusually corrects this. What is the most common cause (in euvolemic patients) of hyponatremia? SIADH The acronym is for Syndrome of Inappropriate secretion of AntiDiuretic Hormone What are the common precipitating causes of diabetic ketoacidosis? Inadequate administration of insulin, infection or myocardial infarction. In the treatment of patients with delirium tremens, which drugs should be avoided? Phenothiazines (They lower the seizure threshold) The use of high-dose insulin therapy in diabetics is associated with which emergent complications? Hypoglycemia, hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia, ARDS and cerebral edema In the hypotensive patient with hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS) fluid replacement should be initiated with ____ until the patient is normotensive and electrolytes are stable. Then ___ may be used thereafter. Initial fluid replacement is with isotomic or normal saline; thereafter, one-half normal saline may be used. Which diabetic complication may include the following neurologic findings? * Hemiparesis * Hemisensory deficits * Focal or grand mal seizures Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS) Severe hyperkalemia may be associated with which neurologic sequela? Generalized weakness Hyporeflexia Paralysis In the drug therapy of hyperkalemia, which treatment has the most rapid onset and the shortest duration of action? Calcium gluconate or calcium chloride What is the appropriate disposition for a patient taking a sulfonylurea who presents with drug-induced hypoglycemia? ADMISSION. The long half-lie many of these drugs predisposes the patient to recurrent episodes until the drug is metabolized. Chlorpropamide* has a half-life of 36 hours with a duration of effect up to 2-5 days. Second generation drugs (glipizide, glyburide*, glimepiride) have much shorter half-lives BUT the duration of action ranges from 10-16 hours (glipizide) up to 24 hours (glyburide). * Knowledge of these two drugs is ESSENTIAL What is the main contributor to the morbidity in untreated patients with diabetic ketoacidosis? The severity of the acidosis CLINICAL PRESENTATION: A middle-aged female with a history of type I diabetes mellitus presents with periorbital edema, chemosis and dermopathy over lower extremities. What diagnosis should be suspected? Graves’ disease, which is the most common cause of thyrotoxicosis Which endocrinopathy may presents with atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure dominating the clinical picture? Hyperthyroidism/thyrotoxicosis How long after someone stops drinking can symptoms of alcoholic withdrawal syndrome begins? Symptoms may start 6-8 hours after cessation of drinking and include alcoholic tremulousness, seizures and hallucinations. What lab tests are helpful in the diagnosis of alcoholism? 1. 2. 3. Hepatic transaminases * AST ALT suggests alcohol injury * GGT is the most sensitive indicatory of alcoholic liver damage Increased mean corpuscular volume (MCV) is more specific of alcohol abuse than any of the transaminases Carbohydrate-deficient transferrin (CDT) is the most specific and sensitive marker for heavy alcohol consumption; AST ALT (Ratio > 2) What is the treatment for Wernicke’s encephalopathy? 1. Thiamine 100 mg. Administration of glucose prior to thaimine may precipitate Wernicke’s encephalopathy in patients with severe thiamine deficiency. 2. Resistance to thiamine may occur secondary to hypomagnesemia (magnesium is a cofactor for thiamine transketolase) Infants who present at 3-4 months of age with hepatomegaly and hypoglycemia are likely to have _______. What retinal changes are seen in about half of these cases? Glucose-6-Phosphatase Deficiency symmetric, yellowish paramacular lesions Which factors are important in predicting the outcome for a near drowning victim? Age Need for bystander or ED CPR Water characteristics: 1. Clean vs contaminated 2. Temperature 3. Amount aspirated What is the order of tissue resistance to the flow of electrical current? resistance: nerves, blood vessels, muscles, mucous membranes, moist or wet skin LEAST INTERMEDIATE GREATEST resistance: dry skin resistance: bone, tendon, fat Which organ system is LEAST sensitive to an acute radiation exposure? Central nervous system What is the clinical feature that distinguishes heat stroke from heat exhaustion? Central nervous system dysfuntion (In heat exhaustion, mentation is not impaired.) Which injury is most likely to be present in a survivor of a lighting strike? Rupture of the tympanic membranes At what temperature does the hypothermic patient lose the ability to generate heat by shivering? Below 32 C (90 F) A patient complains of severe muscle cramping involving the calves, thighs and shoulders. Questioning reveals that the cramps began after a bout of intensive physical activity and profuse sweating, during which he had been replacing fluid losses with a hypotonic solution. His body temperature is normal. What is the most likely diagnosis? Heat cramps. Inadequate replacement of salt from loss through sweating leads to hyponatremia and muscle cramps. What is the MODIFIED “rule of nines” which may be used in CHILDREN? • • • • • • HEAD = 18% Abdomen = 9% Thorax = 9% Back = 18% Each arm = 9% Each leg = 14% Core temperatures less than ___ are associated with increased myocardial irritability and case cause nearly any tachydysrhythmia, including conduction delays. 30 C (86 F) What is the most important cause of morbidity and mortality in near drowning? Hypoxia In patients with this injury, close observation (sometimes in the hospital) and referral to a plastic or oral surgeon is indicated because there is the possibility of labial artery hemorrhage as the escher separates. Electrical burns of the lip/mouth Rapid rewarming is the key initial therapy for this environmental emergency. Frostbites A patient presents with an acute abdomen. However, you notice that there is no tenderness but there is impressive rigidity. What is the suspected diagnosis? Black widow spider bit (to the lower extremity or genitalia) What is the most common presentation of arterial gas embolization after driving? Air embolus or decompression sickness A scuba diver develops acute confusion and ataxia after an ascent. What is the diagnosis? Cerebral air embolus or decompression sickness (from an ascent that was too rapid) A patient presents with extreme fatigue and profuse sweating on a very hot day. He complains of lightheadedness, nausea, vomiting and a dull headache. He is tachypneic, tachycardic and hypotensive. Body temperature is normal. What is the most likely diagnosis? Heat exhaustion. Salt water depletion from sweat loss leads to hypovolemia and hypoperfusion; neurologic and mental status exams are normal. The whole body dose of ionizing radiation determines the timing of the onset of symptoms. The higher the level of exposure, the _____ symptoms develop. Earlier What is the best predictor of survival in patients with radiation exposure? The absolute lymphocyte count, 48 hours after exposure. What is the treatment of puncture wounds (stings) from sea urchins, stingrays or lionfish? 1. Remove spine (if possible) 2. Wash with sea water or fresh water 3. Submerge wound in hot water for 30-90 minutes Concerning the initial management of patients with radioactive skin contamination, is it preferable only to was or to was AND scrub the skin? Washing with water and mild or nonionic soap is done in conjunction with GENTLE scrubbing. Harsh scrubbing may damage the skin with introduction of radioactive material into the underlying tissues. Does successful recovery from tetanus confer immunity to the disease? No! The patient needs full primary immunization plus boosters through the years as indicated. Which tick-bone illness is characterized by severe retro-orbital headache and photophobia and requires only supportive therapy? Colorado tick fever CLINICAL PRESENTATION: a patient presents ill with fever and a rash. The rash began as discrete red maculopapular lesions on the wrists and ankles. It then spread to the trunk. Early on, the lesions were blanched but later became petechial. What disease characteristically does this? Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) Circular skin lesions with a bright-red to blue-red border and a pale center are characteristic of ___ ___, which is the hallmark of early___ ____. Erythema migrans Lyme disease (stage I) Antibiotic therapy for adults (nonpregnant and nonlactating) and children older than 8 years for Lyme disease stage I is_________. Doxycycline or tetracycline Which animals are most likely to harbor the rabies virus? Which animals are least likely vectors for rabies? MOST common: skunks, bats, raccoons, cows, dogs, foxes and cats LEAST common: rodents (squirrels, chipmunks, rats and mice) and lagomorphs (as in Bugs Bunny and the March Hare) NOTE: Rabies can affect all mammals. What is the management of primate (ape) bite? Careful handwashing for 20 minutes after a bite is the best treatment for prevention of infection with herpes virus simiae (70% fatality rate). Acyclovir should be started at the first sign of infection. There are two types of heat stroke. What are they? Classic heatstroke is envirmentally0induced 9hot, humid weather) and occurs most commonly in those who live in homes without airconditioning (especially the elderly) and those with inadequate fluid intake (e.g. the debilitated). Lab abnormalities are mild. Exertional heat stroke is exercised-induced 9athletes, military recruits) and is associated with significant lab abnormalities: hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia, hyperuricemia, lactic acidosis and rhabdomyolysis. Acute renal failure and coagulopathy (often to a marked) may also occur. Sudden cardiac arrest from electrocution occurs with exposure to ____ or ____. Household AC current Lightning strikes How do you differentiate muscle spasms due to tetanus from those seen in patients with strychnine poisoning? Tetanic muscle contractions are continuous, whereas, muscle spasms associated with strychnin poisoning usually have periods of relaxation between contractions. Also, “lockjaw” is characteristic of tetanus, not strychnine. An elderly patient who lives a sedentary lifestyle and is taking medication for chronic illnesses presents with sweating, then develops hot, dry skin…. The patient lives in an unairconditioned apartment and temperatures have been in the 90s. Lab findings include respiratory alkalosis and mild metabolic acidosis, coagulopathy and CPK elevation; glucose and calcium levels are normal. What is the most likely diagnosis? Heat stroke. This is true medical emergency, characterized by an altered LOC, any neurologic findings and an elevated temperature. You are examining a patient who has a rash that looks like chicken pox. How do you know that it isn’t smallpox? In patients with smallpox (Variola major) all lesions are in the same stage of eruption, unlike chicken pox (Varicella) A young, healthy patient is engaged in strenuous exercise on a warm day in August. The patient is diaphoretic on presentation. The following findings are obtained: respiratory alkalosis and marked lactic acidosis, DIC and rhabdomyolysis (“machine oil” urine), increased BUN/creatinine, hypoglycemia and hypocalcemia. What is the diagnosis? Exertional heat stroke What are the differentiating clinical features that distinguish Crohn’s disease from ulcerative coltis? Crohn’s Disease The majority of patients present with abdominal pain, anorexia, diarrhea and weight loss. The majority of patients have ileum involvement. 30% of patients present with perianal fissures or fistulas, perirectal abscessed or rectal prolapse. Ulcerative Colitis Gradual onset of bloody diarrhea and abdominal pain is the most common presentation Anorexia and weight loss What is the clinical presentation of a patient with Boerhaave’s syndrome and which diagnostic study is likely to be most beneficial? Severe retching or vomiting followed by lower thorax or epigastric pain is the most common; the most common tear site is the left posterolateral wall 2-3cm before the stomach. Occasionally pain is also reported in the restrosternal, left shoulder or upper chest areas. A standard chest radiograph is almost always abnormal and may show left pleural effusion (most common), mediastinal or free peritoneal air, widened mediastinum, or left pneumothorax. Diagnosis may be confirmed by either CT scan or an esophagram using water-soluble contrast (Gastrografin) since barium may cause additional pleura-mediastinal inflammation if a tear is present. What is the general management of ingested foreign bodies that are sharp and pointed? Sharp or pointed objects, as well as objects longer than 5cm and wider than 2cm or oddly shaped foreign bodies such as opened safety pins, MUST BE REMOVED ENDOSCOPICALLY. They should be removed BEFORE passing through the pylorus because 15-35% will cause perforation, usually in the region of the ileocecal valve. What is the management of ingested foreign bodies that are sharp or pointed IN CHILDREN? Initial physical exam and x-ray in ALL children. Labs are usually not necessary. If symptoms are present, obtain surgical consult. If the ingested item is a sewing needle, needles in the stomach need endoscopic removal. Needles that have passed into the intestines require early surgical consult. If no symptoms are present, follow with serial x-rays. No progression past the stomach necessitates contrast x-ray to exclude perforation. Signs of perforation or failure to pass through the GI tract require surgical consultation. A small child swallow a quarter. Where is it most likely to become impacted? The esophagus The three most common site for impaction are: 1. The cricopharyngeus muscle (C6) = 70% 2. Adjacent to the aortic arch and carina (T4) = 15% 3. Lower esophageal sphincter/diaphragmatic hiatus (T10-11) = 15% Which types of hepatitis produce neither a chronic infection nor a carrier state? Hepatitis A and Hepatitis E What pharmacologic agents may be used in the management of esophageal food impaction and how do they work? Sublingual Nitroglycerin relaxes smooth muscle. Sublingual Nifedipine reduces lower esophageal tone. Glucagon relaxes smooth muscle and is most effective at the distal esophageal sphincter. Tartaric Acid and sodium Bicarbonate produce CO2 (which may help advance the food bolus into the stomach.) The clinical presentation of an esophageal foreign body in children may be “dysphagia.” What else is possible? Respiratory distress due to compression of the pliable trachea, including cough or stridor. Food refusal, weight loss, drooling, gagging, emesis/hematemesis, chest pain or sore throat. What is the appropriate therapy for a patient with a cecal volvulus? Is the treatment the same for a sigmoid volvulus? Cecal volvulus requires surgery as soon as possible. No, acute management of sigmoid volvulus in stable patients is detorsion and decompression with a rectal tube via either a sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy (90% success rate). Unstable patients with signs of peritonitis, ischemic bowel or failure of endoscopic decompression requires emergent surgery. Name the most common causes (s) of: 1. All types of intestinal obstruction 2. Small bowel obstruction 3. Large bowel obstruction 1. Adynamic ileus 2. Adhesions, external hernias 3. Carcinoma, sigmoid diverticulitis and volvulus Adhesions are the most common cause of MECHANICAL small bowel obstruction, whereas carcinoma is the most common cause of MECHANICAL colon obstruction. Clinical Presentation: A 45-year-old presents with substernal chest pain following forceful vomiting . Boerhaave’s syndrome (spontaneous esophageal rupture) occurs mainly in MALES between the ages of 40-60 and usually involves the LEFT SIDE of the esophagus. Both Mallory-Weiss syndrome and Boerhaave’s syndrome involve tears of the esophagus. How do these tears differ anatomically? Mallory-Weiss syndrome involves a partial thickness tear of the MUCOSAL layer. Typically, upper GI bleeding is the presentation. Boerhaave’s syndrome involves a complete rupture with ALL LAYERS of the esophagus involved, typically presenting as left-sided chest pain. A patient has recently returned from a back-packing trip in Colorado and presents with abdominal pain, bloating and gas. He also complains of postprandial abdominal cramping, an urgency to defecate and has diarrhea that is frothy and foul-smelling. A stool specimen sent to the lab is negative for ova and parasites. What is the most likely etiology. Giardia lamblia Clinical Presentation: A 43-year-old woman presents with epigastric discomfort after eating dinner. She is tender in both the epigastrium and RUQ. Which radiographic study is the “gold standard” in establishing the diagnosis? Diagnostic confirmation of cholecystits requires nuclear scintigraphy (HIDA), which demonstrates 95% senisitvity and specificity for acute cholecystits, while ultrasound or CT scanning can assess anatomy and secondary signs, which may guide therapy, but the HIDA scan can relay information of the biliary tree. What are poor prognostic signs in patients with pancreatitis? Ranson’s criteria On admission: * Age > 55 years* Glucose > 200 mg/dL * WBC > 16,000 mm3 * LDH > 350 IU/L * AST > 250 Sigma-Frankel* 48 hours later: Calcium < 8 mg/dL * pO2 < 60 mmHg * > 10% fall in Hct * > 5% mg/dL rise in BUN Base deficit > 4 mEq/L units/L* Sequestration of > 6L of fluid Name the most common causes of bright red rectal bleeding. Anal lesions, particularly fissures and hemorrhoids Name the most common cause of bloody diarrhea. Shigella Name the most common cause of upper GI bleeding. Peptic ulcer disease (duodenal ulcer is most common) A patient with diagnosed ulcerative colitis demonstrates a traverse colon measuring > 8 cm on an abdominal film. What is the significant of this finding? Toxic megacolon What is the drug of choice in patients with severe pseudomembranous colitis? Oral metronidazole or vancomycin. If critically ill, intravenous metronidazole and oral vancomycin. What is the most common complication of upper GI endoscopy? Esophageal trauma What is the chief complaint of patients with Boerhaave’s syndrome? Chest pain, which is usually severe and lancinating. Patient history may include vomiting or other Valsalva maneuver, including cough or heavy lifting. Clinical Presentation: A patient with a recent history of CAD, MI or peripheral vascular disease develops sudden onset of abdominal pain. There is also diarrhea that is positive for occult blood. What is the suspected diagnosis? Mesenteric vascular occlusion A young woman presents with recurrent episodes of altered bowel function (diarrhea or constipation). The episodes are usually precipitated by stress and the pain is described as crampy or achy and is confined to the lower abdomen. In association with constipation, it is relieved by defecation or gas passage. Extracolonic symptoms (bloating, belching, reflux) are common. The patients denies anorexia, fever and weight loss. Nonspecific exam findings may include vague lower abdominal tenderness and a palpable stool-filled sigmoid colon. Labs are unremarkable. What is the likely diagnosis? Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) Which abnormal electrolyte finding is seen in patients with acute pancreatitis? Hypocalcemia Hemorrhagic shock is a potential complication of which inflammatory GI disorder? Pancreatitis What are the historical findings consistent with the diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome? Rome II criteria Abdominal pain or discomfort > 12 weeks over the past year accompanied by two of the following * Relief of discomfort with defecation * Association of discomfort with altered stool frequency * Association of discomfort with altered stool form What are the most likely causes of lower GI bleeding in children? Meckel’s diverticulum is the most common cause of significant lower GI bleeding in children. Anal fissure is the most likely cause of minor lower GI bleeding in a healthy infant beyond the neonatal period without previous GI history. What is the most common cause of upper GI bleeding in pregnancy Esophagitis (secondary to reflux and repeated vomiting) A patient presents with sudden onset LUQ pain associated with violent retching (but no vomiting). Upright films of the chest and abdomen reveal a distended stomach with one or two air0filuid levels. What is the diagnosis? Gastric volvulus presents with sudden onset of severe abdominal pain with retching or vomiting. Upright films of the chest and abdomen may reveal stomach distension with one or two air fluid levels or a large, gas-filled loop of bowel in the abdomen or chest. What is the most common cancer of the small intestine? Adenocarcinoma Usually occurs in the proximal small bowel Higher incidence in patients with long-standing Crohn’s disease What is the most frequent site for aortoenteric and ileoenteric fistulae? The distal duodenum (Consider this diagnosis in patients with GI bleeding and a history of aneurysms) What is the carcinoid syndrome? Carcinoid tumor cells (usually in the distal small bowel) secrete 5hydroxytryptophan→ wheezing/shortness of breath, intermittent flushing, abdominal pain, diarrhea, signs and symptoms of right-sided valvular heart disease. Diagnosis is confirmed by obtaining a urine level of 5hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA). What is the etiology of hepatic abscesses? Pyogenic ( usually E. Coli) → 90% Amebic (Entamoeba histolytica) → 10% What is the most common presentation of cholelithiasis? 1. 2. 3. RUQ No fever Relatively normal lab studies What is the most common cause of portal hypertension worldwide? Schistosomiasis What is the most common bloodborne viral infection in the United States? Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) What are the two most common causes of esophageal bleeding? Varices Mallory-Weiss tear UGI bleeding due to a ruptured esophageal varix can be controlled in 90-95% of cases with what type of treatment Endoscopic sclerotherapy Pharmacologic agents (octreotide) Clinical Presentation: a middle-aged male with cirrhosis who is confused and unable to hold an assumed position (asterixis). What is the diagnosis and appropriate management? Hepatic encephalopathy is the diagnosis. Management includes: Lactulose Decreased protein intake (especially animal protein) Avoidance of all sedatives and tranquilizers Avoid bicarbonate (alkalosis may precipitate or worsen encephalopathy) Correction of hypokalemia Rifaximin When is the insertion of a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube for esophageal varix hemorrhage contraindicated? What procedure should be done prior to insertion of the tube? Contraindications include: Hiatal hernia (precludes proper tube placement) Peptic ulcer disease with stricture of the esophagus Bleeding from esophageal lacerations Inability of the patient to protect the airway Endoscopy should precede insertion (if at all possible) so that the diagnosis may be confirmed Bloody diarrhea should warrant testing for which bacteria? Shigella Salmonella Campylobactor Hemorrhagic E. Coli Protozoal pathogens most frequently associated with diarrhea that persists for more than 7-10 days are _____ and _____. Giardia Cryptosporidium Patients with refractory cryptosporidiosis, cyclosporiasis or isosporiasis should be tested for _________. HIV infection Head and Neck What is the distinguishing clinical feature which helps differentiate croup from epiglottitis? Mode on onset Symptoms of croup start gradually, whereas symptoms of epiglottitis tend to begin abruptly, particularly in children. What is the appropriate initial study in a patient with headache, lethargy, nuchal rigidity and papilledema? Computed tomography (CT) of the head should be done initially to exclude the presence of mass lesions prior to lumbar puncture. The important consideration here is subarachnoid hemorrhage, secondary to a ruptured aneurysm. If meningitis is a possibility, administration of antibiotics should be delayed. A “teardrop”-shaped pupil in a patient with a history of trauma to the eye suggests what injuries? Corneoscleral perforation or laceration Rupture of the globe What is the most common precipitating factor in the development of Ludwig’s angina (cellulitis of the floor of the mouth)? Dental disease (infections, extractions, trauma) Clinical Presentation: An adult male was struck in the eye by a fist 3 days ago. Over the past 24 hours, he has developed redness, pain and photophobia. 1. How would you confirm the diagnosis? 2. How is this treated? The diagnosis is traumatic iritis. This is conformed by a slit lamp examination which demonstrates cells and flare in the anterior chamber. treatment consists of long-acting topical mydriatic-cycloplegic drops (dilate the constricted pupil, relax ciliary spasm) and topical corticosteroids (reduce inflammation). Of all patients with epistaxis, the ones who must be admitted are those treated with _____. Posterior packing The feared complications are: Hypoxia and hypercarbia Sudden death due to dislodgement of the pack Dysrhythmias and coronary ischemia List the complications of a hyphema. Rebleeding, which occurs 2-5 days after the initial clot loosens, is a major complication. Blood staining of the corneal epithelium Secondary glaucoma Anterior and posterior synechiae Optic atrophy from increased IOP associated with hyphema. What is the most common direct source of posterior nosebleeds? Posterior branches of the sphenopalatine artery A patient presents within 3 days of a tooth extraction complaining of severe pain and of foul breath odor. What is the diagnosis? Acute alveolar osteitis (“dry socket”) What is the diagnosis in patients who complain of “flashing lights” in front of the eyes, especially at night and in the peripheral visual field? Retinal detachment Slit-lamp exam of a painful eye reveals a fluorescein-positive are with a branching or dendrite pattern. What is the diagnosis and treatment of this disease? Herpes simplex keratitis Treatment: 1. Topical and oral antiviral agents 2. Topical cycloplegic drops 3. Emergent ophthalmologic consultation Clinical Presentation: A patient complains of weakness of an upper extremity as well as numbness and tingling of the forearm and middle finger. When the patient is asked to extend the elbow against resistance, he is unable to do so and complains of pain in the upper back. Where is the lesion located? C7 What is the unusual cause of bacterial parotitis? Staphylococcus aureus What is the most common presenting symptom of a brain abscess? Headache Which abnormal laboratory findings is associated with temporal arteritis? Markedly elevated sedimentation rate (usually over 50mm/hour). Maximum normal sedimentation rate can be calculated as age (10+ if female)/2. Compressive dressing applied to an external ear injury may cause _____. Necrosis of the ear cartilage What are the complications of ethmoid sinusitis? • Periorbital/orbital cellulitis • Brain abscess What is a complication of sphenoid sinusitis? Cavernous sinus thrombosis Mastoiditis is usually a complication of which disorder? Untreated or inadequately treated acute otitis media What is the treatment of mastoiditis? 1. 2. 3. Admission Parental antibiotics (Adequate coverage from gram negative and positive organisms usually entails combination therapy, ceftazidime OR cefepime OR piperacillin-tazobactam PLUS vancomycin.) Immediate ENT consultation regarding surgical drainage and/or mastoidectomy A patient complains of a severe sore throat, muffled voice as well as difficulty swallowing and opening the mouth. What is the suggested diagnosis? Peritonsillar abscess What are the two most common supportive complications of group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis? Acute otitis media Acute sinusitis They are caused by spread of organisms via the eustachian tube (otitis media) and direct spread to sinuses (sinusitis) A patient with a history of blunt trauma to the face has enophthalmos (recognizable as slight ptosis) on physical examination. Which diagnosis should be considered? Blowout fracture of the orbit What is the currently recommended emergency treatment for complete laryngeal obstruction due to trauma? Tracheostomy Cricothyrotomy is usually not feasible because the injury is frequently below the cricothyroid membrane Blind nasotracheal intubation attempts mat penetrate the mediastinum Percutaneous transtracheal insufflation is currently under investigation What is the most common cause of “pink eye”? Conjunctivitis (bacterial and viral) Bacterial causes include N. gonorrhoeae in the newborn as the most vision-threatening, but C. trachomatis is the most common in newborn. In adults, the most common bacteria is S. aureus. The most common virus is adenovirus. Acute bacterial conjunctivitis in adults is most commonly doe to ____ and ____. S. Aureus* S. pneumoniae * The most common cause of mucopurulent conjunctivitis What are the characteristic fluorescein uptake patterns in keratitis due to exposure, acanthamoeba and herpes simplex? Exposure keratitis → horizontal band Acanthamoeba keratitis → ring shape Herpes simplex keratitis → branching dendritic pattern How do you differentiate between central retinal artery occlusion and central retinal vein occlusion on funduscopic exam? Patients with central retinal artery occlusion have a cherry-red spot in the center of the fovea; those with central retinal venous occlusion have a “blood and thunder” fundus. What causes acute thermal epiglottitis? A direct thermal insult from ingestion of hot food or liquid (or from smoking cocaine) may precipitate thermal epiglottitis. Neonatal conjunctivitis (ophthalmia neonatorum) occurs in the first 3-15 days of life. Which organisms are likely to be responsible? If it occurs on the first 3-5 days → N. gonorrhoeae and/or HSV should be suspected If it occurs between 5-15 days → Chlamydia trachomatis, *HV, H. influenzae, S. pneumoniae, S. aureus or Staphylococcus should be suspected. *Concomitant pneumonia may be present Spontaneous hyphemas are associated with __________. Sickle cell disease Diabetes and neoplasms should also be considered An acute cranial nerve III palsy with pupillary dilation is a ____ until proven otherwise. Posterior communicating artery aneurysm You are examining a patient who seems to have a Bell’s palsy. When you check EOMs, he is unable to abduct the ipsilateral eye. What is the diagnosis? A CVA masquerading as a Bell’s palsy Which diagnosis should be considered in a patient with an isolated cranial nerve palsy (III, IV or VI) associated with pupil sparing? Diabetic/hypertensive cranial nerve palsy Name the condition in which the iris has an unusual curved shaped at the periphery, placing it closer to the cornea and creating a congenitally narrow angle. Plateau iris (predisposes the patient to the subsequent development of acute, narrowangle glaucoma) What medications have produced sudden attacks of narrow-angle glaucoma? Topical cycloplegics Anticholinergic agents Beta-agonists (including inhaled agents) Sulfa, MAO inhibitors, trycyclics The most common acute optic neuropathy in patients > 50 years old is _____. Visual loss is often described as altitudinal (only the upper or lower half of the visual field is missing); inferior loss is more common. Nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy Which potentially life-threatening disease should be excluded in patients in their sixties who complain of dull, aching eye pain that extends to the temple? Ocular ischemic syndrome (Light-induced amaurosis should alert the clinician to possibility of significant carotid occlusion) What is the most common cause of acute visual reduction due to optic nerve dysfunction in patients w20-40 years old? Optic neuritis A patient with a corneal ulcer presents with an adherent mucopurulent exudate and a “ground glass” appearance of the cornea. What is the most likely infecting organism? Pseudomonas aeruginosa Hematology/Oncology In which area of the body is central cyanosis likely to be detected? The tongue and oral mucous membranes In which clinical entity is there severe tissue hypoxia but no peripheral cyanosis? Carbon monoxide poisoning What are the causes of central cyanosis? Methemoglobinemia V/Q mismatches High altitude NOTE: Cold exposure causes peripheral cyanosis. With which blood disorder would one associate the common appearance of aseptic necrosis of the femoral head? Sickle cell disease Why are O-negative packed cells preferable to O-negative whole blood prior to cross-match? O-negative packed cells are less concentrated with anti-A and anti-B antibodies. What is the most common cause of a prolonged PTT with a normal PT? Hemophilia A What are the potential complications of auto-transfusion? Air embolus Dilutional coagulopathy, if volume is > 4000 mL Sepsis, if contaminated blood is infused Hemolysis, if the blood has pooled within the pleural cavity for more than 6 hours What is the best test for platelet function (aggregation and adhesion) onto injured vascular surfaces? Bleeding time Clinical Presentation: A patient is seen with shortness of breath, swelling and plethora of the face and upper extremities, and headache. What is the diagnosis? Superior vena cava syndrome Which drug should you avoid in patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency? Sulfa Pyridium® Nitrofurantoin Antimalarials Dapsone Methylene blue Aspirin NSAIDs Can thrombocytopenia result from an exchange transfusion? Dilutional thrombocytopenia occurs in cases of massive transfusion, exchange transfusion or extracorporeal circulation. You are seeing a child who took some of Grandpa’s coumadin. There is no evidence of bleeding and the PT is normal. Do you administer vitamin K or just observe him? Observe. Vitamin K is indicated for serious bleeding since the result of overdose is a functional deficiency of vitamin K. What is the most severe from of congenital anemia? (clinical features include bronze skin discoloration and patients are transfusion-dependent). β-Thalassemia (Thalassemia major, Cooley’s anemia) This is often misdiagnosed as iron deficiency anemia on blood smear (hypochromic, microcytic red cells). Clinical Presentation: A neutropenic patient develops sepsis associated with nonproductive cough and fever with rales at both bases. He also has an infected sacral decubitus ulcer. What is the likely offending organism? Pseudomonas aeruginosa What is the most common organism causing life-threatening infection in patients undergoing bone marrow or solid organ transplants? Cytomegalovirus Major Trauma What is the most appropriate diagnostic study in trauma patients with blood at the urethral meatus? Retrograde urethrogram In the setting of acute trauma, this test should be performed if renal artery injury is suspected or needs to be excluded. CT scanning with 3-D reconstruction and IV contrast In a trauma patient with signs of intramural duodenal hematoma (gastric outlet obstruction), which is the most sensitive diagnostic study? Upper GI air-contrast study What are the classic signs of compartment syndrome? The 6 Ps Pain out of proportion to what is expected Pallor Piokilothermia Pulselessness Parenthesia Paralysis What is the role of hyperventilation in the management of elevated intracranial pressure secondary to trauma? The role is very limited (which is a change from previous practice). Hyperventilation should only be considered for herniation or clinical deterioration despite adequate resuscitation and mannitol; if used, the pCO2 should be maintained between 25-30 Torr. What is the immediate cause of death from an untreated tension pneumothorax? Relative hypovolemia The tension severely impedes venous return which results in a fatal reduction in cardiac output. In a patient presenting with a periorbital hematoma or a hyphema, what diagnosis should be excluded? Orbital fracture At what age can surgical cricothyroidotomy be performed on a child? When the cricothyroid membrane is palpable, around age 12. When viewing cervical spine films in a child with possible injury, what are normal variants? Wedging of the anterior cervical bodies, (especially C3 which is seen up to age 12) Anterior pseudosubluxation of C2 over C3 or C3 on C4 A patient with a head injury is unresponsive both to verbal and painful stimuli. There is no eye opening whatsoever. What is the Glasgow coma score? “3” The patient scores 1 point each for eye opening, speech and best motor response…even when there is none. What is the leading cause of death in patients sustaining pelvic fractures? Hemorrhagic shock Where are the children (< 11 years old) with cervical spine injuries most commonly injured? The upper C-spine What is the most common cause of sudden death following a MVC or fall from a great height? A traumatic aortic rupture Clinical Presentation: A patient has a facial laceration that requires suturing. He claims an allergy to procaine. Which of the following is the safest choice for local anesthesia? (a) Benoxinate HCI (b) Benzocaine (c) Cocaine (d) Tetracaine (e) Mepivacaine (e) Mepivacaine Procaine is the prototype “ester” local anesthetic. All of the anesthetics listed are chemically related to procaine except mepivacaine is an “amide.” The amide anthesthetics are associated with far fewer allergic reactions. The other amides are lidocaine, bupivacaine, etidocaine and prilocaine. Pelvic fractures are associated with bladder injury. What should you check for? Hematuria; do a urethrogram/cystogram if appropriate. How does one differentiate pulmonary contusion from adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) on chest x-ray? Pulmonary contusion occurs within minutes to hours of the injury and is seen on x-ray as an infiltrate or consolidation that is usually localized to a pulmonary segment or lobe. ARDS is associated with delayed onset (12-72 hours after injury) with diffuse patchy infiltrates seen on chest x-ray (24-72 hours after injury) Death from drowning is due to _________. Hypoxia What are the contraindications for the use of MAST/PASG? Pulmonary edema is an absolute contraindication to use of the MAST garment. Relative contraindications for MAST use are pregnancy, impaled objects, evisceration of the abdominal contents, and thoracic and diaphragmatic injuries. What is the most common cause of fetal death following blunt trauma? Second only maternal death, abruptio placentae is the most common cause of fetal death. What are the NEXUS criteria? No posterior midline cervical tenderness No evidence of intoxication Normal level of alertness No focal neurologic deficit No distracting painful injuries What is the most common ureteral injury in the setting of blunt trauma? Ureteropelvic disruption Should be suspected with fractures of the lumbar spine: urinalysis may be normal) What is the best radiographic modality for the evaluation of renal trauma? Contrast-enhanced CT has become the study of choice because it provides more information than the IVP. (Current literature recommends that adults with microscopic hematuria < 100 RBCs/HPF do not require emergent CT unless it is accompanied by hypotension…including in the field) What are the most common sequela following blunt abdominal trauma during pregnancy? Preterm contractions What is the most common site of penetrating trauma to the heart? The right ventricle A multiple-injured patient without a head injury and multiple long-bone fractures undergoes a dramatic worsening of his neurological status? What diagnosis should be considered in this scenario? Fat Embolism syndrome (The classic triad of symptoms is: acute respiratory failure, global neurologic dysfunction and a petechial rash) When assessing indications for thoracotomy in trauma arrest patients, signs of life in the field or on arrival in the ED include: Blood pressure or Pulse or Cardiac rhythm or Respiratory effect or Echo cardiac activity or tamponade Sensory loss on the chest or abdomen is presumptive evidence of _________. Spinal cord injury/involvement What percent of patients with a C-spine fractures have a second, noncontiguous vertebral fracture? 10% If one fracture is present, complete radiographic screening of the entire spine is needed. In a woman with an orbital fracture, what is the incidence of sexual assault/domestic violence? Greater than 30% Which reversible conditions can mimic the appearance of brain death? Hypothermia Barbiturate coma What should you be looking for on AP and lateral films of the thoracic and lumbar spine in trauma patients? AP: vertical alignment of the pedicles as well as the distance between them (unstable fractures commonly cause widening of the interpedicular distance) Lateral: subluxations, compression fractures and Chance fractures. Patients in hypovolemic shock are usually ______, while those in neurogenic shock are typically ________. Tachycardic Bradycardic CT scanning of the thoracic and lumbar spine is particularly useful for detecting which injuries? Fractures of the posterior elements (pedicles, laminae + spinal processes) and the degree of canal compromise causes by burst fractures. True or false: corticosteroids should not be used to treat head injury (whatever the severity)? True…according to a 2006 LLSA article* *Lancet, 2004; 364: 1325 In mild traumatic brain injury and no loss of consciousness, a head CT is indicated for: Focal neurologic deficit Severe headache or vomiting Age > 65 years Physical signs of basilar skull fracture GCS less than 15 Coagulopathy Dangerous mechanism of injury *ACEP Clinical Policy Important factors for identifying children at low risk for traumatic brain injury after blunt head trauma include the absence of: Abnormal mental status Clinical signs if skull fracture History of vomiting and/or headache Scalp hematoma in children < 2 years old *LLSA reading Neurology Clinical Presentation: An elderly woman arrives at the Emergency Department after an automobile accident. She has neck pain. You saw her walk in unassisted. Examination reveals a weak handshake but relatively good proximal arm strength. What is the diagnosis? Central cord syndrome What is the most common spinal cord syndrome and what are its clinical features? Central cord syndrome usually occurs in patients with pre-existing cervical stenosis from degenerative arthritis or cervical canal narrowing from protrusion or tumor. Weakness is greater in arms than in legs and distal muscles are affected more tham proximal. In addition to the central cord syndrome, there are two other incomplete spinal cord injury syndromes. What are these syndromes and what are their clinical features? BROWN-SÉQUARD’S SYNDROME is a unilateral cord problem (usually from penetrating trauma) with ipsilateral paralysis and loss of positionvibratory sensation with contralateral pain and temperature loss. ANTERIOR CORD SYNDROME (from anterior spinal artery injury or from anterior cord compression usually from hyperflexion injury) is characterized by paralysis and pain-temperature loss distal to he lesion with sparing of the posterior columns (position-vibratory sensation). What is the most common intracerebral bleed following head injury? Subarachnoid hemorrhage 20% of late post-traumatic seizures (those that occur one week to 10 years after head injury) are _________ seizures. Temporal lobe What are the early signs of phenytoin toxicity? Somnolence Sedation Slurred speech Diplopia/blurred vision Coarse tremor Nystagmus A post-viral acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy with ascending paralysis and decreased or absent DTRs is the ___- ____ ____. Guillain-Barré syndrome Unilateral facial never paralysis that involves the muscles of the forehead and is differentiated from a stroke by the absence of focal neurologic deficits is know as _____ _____. Bell’s palsy. Bell’s palsy affects the forehead, while central CNVII deficits spare the forehead. Clinical Presentation: A middle-aged male complains of muscle weakness after he climbed a flight of stairs. He also complains of double vision. On examination, there is ptosis. What is the diagnosis? Myasthenia gravis What are the most frequent initial symptoms/signs in myasthenia gravis patients? Visual sign/symptoms (ptosis, diplopia, blurred vision) If a “regular” alcoholic ED patient is confused (or more confused than usual) _____ _____ must be prominent in the differential diagnosis. Subdural hematoma What is the most common cause of focal encephalitis and leading cause of intracranial mass lesions in AIDS patients? CNS toxoplasmosis The clinical picture: fever, headache, focal neurological deficits, altered mental status or seizures. CT scan with contrast shows ring enhancing lesions (the signet ring sign). What early sign in a head injury patient indicates that delayed posttraumatic epilepsy is a likely sequela? Acute intracerebral hematoma or a depressed skull fracture What must be considered if a patient presents with vertigo associated with neurologic complaints? Occlusion of posterior inferior cerebellar artery (Wallenberg’s syndrome) A patient with subtle meningeal sign has the following CSF findings: *Protein = elevated *Glucose = low *Cell count = lymphocytes (about 80%) Which type of meningitis is this? CSF findings of increased protein, decreased glucose and a lymphocytic predominance of WBCs suggest chronic or subacute meningitis either from tuberculosis or fungal infection. In addition to TB and fungal cultures, acid-fast smear, India ink preparation and cryptococcal antigen should also be ordered. What is the most likely bacterial organism causing meningitis in an 8-year-old girl? Streptococcus pneumoniae predominates from the ages of 3 months up to 10-12 years of age. Neisseria meningitides is more common up to the age 19. Hemophilus influenzae meningitis has declined significantly since the advent of routine immunization. What is the most common presenting neurologic manifestation of diphtheria? Paralysis of the palatal muscles What is the primary consideration for the etiology of meningitis in an AIDS patient? Cryptococcus neoformans Concerning patients suspected of cryptococcal meningitis, which studies should be ordered on the cerebrospinal fluid examination? Cryptococcal antigen and An India ink preparation Where does the spinal cord originate and terminate? The spinal cord begins at the medulla oblongata (approximately at the atlanto-occipital junction) and ends between T12 and L3. What is the main cause of radioculopathy in patients > 65 years old? Spinal stenosis is an unusual narrowing of the spinal canal that impinges on the cauda equina and nerve roots. This results in pain in one or both extremities brought on by walking, relieved by rest and exacerbated by back extension. An elderly woman who was rear-ended in a motor vehicle collision sustains a cervical injury. She complains of neck pain. You find upper extremity weakness that does not localize to any particular spinal level. What is the diagnosis? Central cord syndrome An absent deep tendon reflex at the ankle suggests a lesion of which nerve root? S1 What is suggested when there is: * Inability to flex the DIP joint of a finger and * There are signs of traumatic tenosynovitis, such as swelling and tenderness in the flexor tendon sheath and a mild flexion deformity? Rupture of the flexor digitorum profundus tendon What are the physical findings of nerve root involvement in patients with lumbar disk compression? L3 – L4 = decreased/absent knee jerk L5 = decreased/absent dorsiflexion of great toe S1 = decreased/absent Achilles reflex (decreased or absent plantar flexion) plus numbness of the lateral foot What cervical spine injury occurs as the result of axial loading? Jefferson fracture or C1 ring blowout fracture What is the most common cause of focal intracranial mass lesions in patients with HIV? Toxoplasma gondii. Common signs and symptoms include headache, fever, altered mental status and seizures What psychiatric disorder is most often confused with stroke? Conversion disorder A young woman presents with papilledema and recurring headaches. CT reveals slit-like ventricles. Diagnosis? Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. This is seen primarily in young, obese women of childbearing age. Risk factors include oral contraceptive use, anabolic tetracyclines and Vitamin A use. CSF pressures are > 200 mm H2 O if not obese and > 250 mm H2 O if obese. How does mannitol work in treatment if cerebral edema? Mannitol causes an osmotic diuresis, increasing GFR so that volume is rapidly excreted decreasing hydrostatic pressure. What reflex should be checked in patients with a neurogenic bladder? The Bulbocavernosus Reflex This is a normal cord-mediated reflex elicited by placing a gloved finger in the rectum and squeezing the glans penis (or gently tugging the Foley catheter). Contraction of the anal sphincter is the normal response; absence indicates the presence of spinal shock: concussive injury to the spinal cord that results in total neurologic dysfunction distal to the site of injury. Orthopedics What is the mechanism whereby infectious tenosynovitis occurs in the flexor tendon of a finger? Penetrating trauma, particularly a puncture wound, along the volar aspect of the finger or in the palm of the hand. Clinical Presentation: A young athlete complains of lower leg pain with no history of trauma. The lower leg is firm and tender lateral to the tibia, but it is of equal girth when measured against the opposite leg. What diagnosis must be excluded? Acute compartment syndrome Remember the “6 Ps” Note that all need not be present. Pain out of proportion to what is expected Pallor Piokilothermia • Pulselessness • Paresthesia • Paralysis If untreated, ischemia of the nerves + muscles lead to the end stage known as Volkmann’s Ischemic Contracture. Which nerve injury is most commonly associated with anterior glenohumeral dislocations? Axillary (C5 – C6) 5-54% incidence of axillary nerve damage and is more frequent when age > 50. test lateral shoulder sensation. Fractures of the clavicle are most likely to occur on which region of the bone? Middle third (80%) A fracture at the base of the second metatarsal is pathognomonic for what type of injury? Lisfranc’s fracture This is a fracture of the base of the second metatarsal with separation of the first and second metatarsals. What is the most immediate concern in patients with fractures of the tibia and fibula? The development of a compartment syndrome Calcaneus fractures may be associated with what other fracture or injury? Lumbar spine fracture (10%) Bilateral calcaneal fracture (10%) Calcaneus injuries are most commonly caused by axial load by a fall from a height. Damage to which nerve is frequently associated with acetabular fractures? Sciatic What is the most common dislocation of the patella? Lateral usually occurring from a twisting injury on an extended knee. Answer the following concerning hip dislocation: 1. What is the most common type of hip dislocation? 2. What are the expected physical findings? 3. What is the most serious complication? Posterior dislocation occurs in 90% of cases The leg is shortened, adducted and internally rotated. The most serious complication is avascular necrosis of the femoral head. The chance of this problem occurring is in direct proportion to delays in reduction. A patient with a history of knee injury states that he heard a “popping” sound at the time of injury. On examination, you find hemarthrosis of the joint. There is a positive anterior drawer test. What structure is most likely injured? Anterior cruciate ligament (70%) Where are the tendinous insertions of the muscles comprising the rotator cuff The subscapularis inserts on the lesser tubercle of the humerus. The supraspinatus, infraspinatus and teres minor all insert on the greater tubercle. All four originate from the scapula. Clinical Presentation: A patient complains of a painful shoulder after a fall. There is no fracture. On examination, there is weak and painful abduction with tenderness over the greater tuberosity. What is the diagnosis? The rotator cuff is injured. Partial tears are more common than complete and the supraspinatus is the most commonly involved muscle. The supraspinatus is essential for the first 30 degrees of abduction. The posterior fat pad sign seen in the lateral radiographic view of the elbow of an adult is presumptive evidence of which injury? Fracture of the radial head What are the signs of flexor tenosynovitis? The following are known as Kanavel’s four signs of flexor tenosynovitis: The finger is held in slight flexion Symmetric swelling of the finger Tenderness along the flexor tendon sheath Pain with passive extension of the finger Fracture of the lateral tibial plateau may be associated with injury of the ________? Anterior cruciate and medical collateral ligament In patients with calcaneus fractures, what other injuries are commonly used? Lumbar spine fracture (10%) Bilateral calcaneal fracture (10%) Calcaneus injuries are most commonly caused by axial load by a fall from a height. Why is it important to obtain an early orthopedic referral for infants with congenital hip dislocation? Treatment should consist of splinting or casting in flexion/abduction to avoid later instability, chronic dislocations and need for surgery. What is the most common midfoot fracture? The most common fracture is a navicular bone fracture. What is a Toddler’s fracture? Toddler’s fractures are nondisplaced spiral fractures of the distal tibia, and are usually accidental. Note: mid-shaft fractures in children who are nonambulatory generally occur as a result of nonaccidental trauma. When is angiography with embolization indicated in the treatment t of severe hemorrhage secondary to pelvic fracture? Angiography with embolization is used to manage hemorrhage when fluid resuscitation has failed and the patient is continuing to hemorrhage. Signs of ongoing bleeding from pelvic fractures include: (1) > 4 units of blood are required in < 24 hours or > 6 units were needed in < 48 hours (2) Persistent hemodynamic instability with a negative evaluation for other sources of hemorrhage or a pelvic hematoma on CT (3) Large (or expanding) retroperitoneal hemorrhage Name the tests used to assess the stability of the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments of the knee. ACLS Tests PCL Tests Anterior drawer sign Posterior drawer sign Lachman test Posterior sat test Pivot shift Consider the following questions regarding amputations involving the hand: 1- Which amputations have the best prognosis for reimplantation? 2- How should the amputated part(s) be preserved? Amputations at the level of the middle phalanx, wrist and distal forearm have the best chance of a functionally successful reimplantation. The part(s) should be handled as aseptically as possible. Wrap the part(s) in a plastic bad and place in iced water in an insulated container. Never freeze the amputated part. Fluid analysis of knee joint aspirate reveals the presence of positive birefringent crystals. What is the diagnosis? Pseudogout Uric acid crystals are negatively birefringent Pediatrics What is the best screening test for the diagnosis of Reye’s syndrome? Serum ammonia level Clinical Presentation: A young boy (3 to 9 years of age) presents with a limp. There is no history of trauma. There is no recent or current febrile illness. On examination, the hip is noted to be slightly flexed, externally rotated, and abducted. What is mot likely the diagnosis? What other diagnosis must be considered? Transient synovitis is the most common cause of a nontraumatic limp. If the condition is chronic, exclude LeggCalvé-Perthes disease (avascular necrosis of the femoral head) What are the most common pathogens causing pneumonia in children after the newborn period? Viruses (age < 5 years) Mycoplasma pneumonias (ages 5-15 years) What is the most common cause of bacterial pneumonia in children after the newborn period? Streptococcus pneumoniae Slipped capital femoral epiphysis occurs most frequently in which group of children? Obese males, ages 10-16 or slender, rapidly-growing adolescents (usually male) Note: The slipped epiphysis is best seen on the frog lateral x-ray of the pelvis. Which organism causes the majority of cases of occult bacteremia in children under 24 months of age? Group B streptococcus (0-2 months) Streptococcus pneumoniae (3-36 months) What is the most primary dysrhythmia in children? Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) What is the most common pre-arrest rhythm disturbance seen in the setting of pediatric arrest? Bradyarrhythmias, especially sinus bradycardia; asystole is the most common arrest rhythm. Note: Epinephrine is the drug of choice (after oxygenation and ventilation) for treating bradycardia in the pediatric population. In which age group are radial head subluxations most commonly seen? Children less than 6 years of age; peaks between 2-3 years Which fractures are most commonly seen in children who fall on an outstretched arm? Distal radial fracture (epiphyseal fractures and/or torus fractures) Clinical Presentation: A 1-year-old presents with intermittent abdominal discomfort and a palpable sausage-shaped mass in the right midabdomen. What is the most appropriate therapeutic course of action? Air insufflation or barium enema (BE) These studies are useful both diagnostically and therapeutically since 90% of intussusception cases may be corrected if it is performed within the first 12-24 hours; air insufflation has some advantages over BE and is being used with greater frequency today. What are the most common signs/symptoms of hypothermia in infants? Lethargy Decreased feeding In addition to the rash, what are the characteristic physical findings if rubella (German measles)? Lymphadenopathy involving the postauricular, posterior cervical and suboccipital nodes. Early findings include a 1-5 day prodome of fever, malaise, headache and sore throat. Clinical Presentation: A child known to have a ventricular septal defect develops sudden onset of agitation and cyanosis. What is the most likely explanation? Reversal of the shunt has occurred This is the Eisenmenger complex. Congenital heart lesions causing shunts are best corrected before this point, since pulmonary hypertension may not reverse after surgery. Because of the unique nature of the blood supply to the skeletal system, ______ and _____ ______ frequently occur together in infants. Osteomyelitis Septic arthritis What is the initial fluid therapy for children in shock? Rapid infusion of crystalloids, 20mL/kg In the setting of an acute upper respiratory infection occurring in unimmunized children less than four years old, what is an important disease to include in the differential diagnosis? Pertussis (whopping cough) What is the most common complication of pertussis (whooping cough)? Secondary bacterial pneumonia Is the discovery of an inguinal hernia in an infant a surgical emergency? No, unless the child is symptomatic and/or the hernia is not reducible. Otherwise, these hernias should be repaired on an elective basis. A child without a spleen is particularly susceptible to which illness? Bacteremia or sepsis from gram-positive encapsulated organisms Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus) heads the list. Which respiratory tract infection is most commonly confused with asthma? Bronchiolitis This is a viral disease. 70% of cases are caused by the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Less commonly implicated viruses are parainfluenza, adenovirus and influenza. Which infection generally occurs from seeding during sepsis or from spread of a contiguous infection, such as otitis media? Meningitis What diagnosis should be considered in children between the ages of 5 and 12 months who present with abdominal pain? Intussusception Why is the funduscopic examination important in the suspected child abuse victim? Retinal hemorrhages may be seen in the “shaken baby syndrome” Prior to vaccinations, in the early stages if this illness, symptoms are indistinguishable form a nonspecific upper respiratory infection with rhinorrhea, low grade fever, cough, conjunctivitis and anorexia. As the disease progresses, the cough becomes the diagnostic and dominant clinical feature. What is the disease? Pertussis or whooping cough Two lessons are to be learned here. First, there are a lot of children less than 1 year old who are under immunized or not immunized. Be wary of those with respiratory illness and cough. Second, people immunized more than 12 years ago for pertussis can acquire the disease if exposed. Note that the current Dtap vaccine reduces the incidence of pertussis in the United States thereby preventing pertussis epidemics. What are the Ottawa Knee Rules for ordering knee x-rays in children > 5 years old with an injury? A knee x-ray is only required for children > 5 years old if any of these findings are present on physical exam: Isolated patellar tenderness Tenderness at the head of the fibula Inability to flex knee 90º Inability to bear weight and walk up 4 steps (immediately and in the ED) What is the current drug of choice for the treatment of GABHS tonsillopharyngitis in children? Penicillin remains the drug of choice for GABHS infection. If treatment failure or penicillin allergy, consider a cephalosporin. Do children with pos-traumatic seizures following blunt head trauma require admission? In otherwise healthy children with a single post-traumatic seizure, normal neurologic exam and head CT, discharge to home with the usual head injury instructions is appropriate. What type of fracture occurs because the bone at the metaphysealdiaphyseal junction fails to compress? Torres fracture is a fracture without cortical disruption Pulmonary You are viewing the chest x-ray of a patient who is a traveler from overseas that reveals a diffuse pneumonia associated with a moderate pleural effusion and lymphadenopathy. What is your diagnosis? Tuberculosis What diagnosis is suggested by rust-colored sputum associated with an infiltrate in the right middle or right lower lobe on chest x-ray? S. pneumoniae (pneumococcal) pneumonia This is the most common cause of community-acquired bacterial pneumonia in normal hosts, which peak incidence in winter and early spring. A pulse oximetry reading would not be helpful in a patient with __________. carbon monoxide poisoning or methemoglobinemia Clinical Presentation: An ill-looking child is brought in because if earache. Examination reveals bullous myringitis, as well as rales and rhonchi on the chest exam. What is the causative organism? Mycoplasma pneumoniae The triad of fever, nonproductive cough, pleuritic chest pain and exertional dyspnea in a patient who is HIV-positive should suggest what diagnosis? Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia It is the most common etiology , but bacterial pathogens and tuberculosis must be considered. Although patients with PCP may present with typical features of subacute onset of nonproductive cough, fever, shortness of breath, diffuse interstitial infiltrates on chest radiography and arterial hypoxemias, 10-20% of patients subsequently proven to have PCP lack these findings. PCP usually has a subacute presentation characterized by nonproductive cough, exertional dyspnea and weight loss. Tachypnea and tachycardia are usually present. What is the initial drug of choice for patients with Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia? TMP-SMX is treatment of choice; the usual regiment is 20mg/kg of TMP and 100mg/kg of SMX daily in four divided doses, to be continued for 21 days. For most adult patients, a regimen of three ampoules (80mg of TMP and 400mg of SMX per ampule) every 6 hours is appropriate. For patients allergic to sulfa, pentamidine can be given, 4mg/kg over 1 hour. An elderly, debilitated patient with a history of diabetes, alcoholism and COPD presents in early spring with a cough and sputum production that has been getting worse. He complains of fever, shortness of breath and pleuritic-type chest pain. There are rules but no signs of consolidation with breath sounds. What is the most likely etiology? H. influenzae pneumonia Which diagnosis should be considered in a patient with who presents with a cough productive of fetid and bloody sputum? Lung abscess You have just intubated a 70kg asthmatic. The pH is 7.0, pO2 5o and pCO2 100. What are your initial ventilator settings? The vent setting should allow for permissive hypercapnia. A ventilator strategy providing adequate oxygenation and ventilation while minimizing high airway pressure, barotrauma and systemic hypotension must be instituted. The technique of permissive hypercapnia (also know as controlled hypoventilation) is common. Oxygenation is maintained by using a high fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO 2); hypercarbia and respiratory acidosis (pH maintained at 7.15-7.2 using sodium bicarbonate) and tolerated. Airway pressure is kept low by providing low tidal volumes (6-8 mL/kg), thus preventing excessive increases of intrinsic positive endexpiratory pressure, stacking of ventilations and barotrauma. Low ventilation rates (< 10 breaths/min) and high inspiratory flow rates provide prolonged time for expiration. Adjunctive therapies (in-line beta2-agonists and anticholinergics, IV corticosteroids, IV ketamine, and possibly magnesium) to decrease airway pressure and airway obstruction are delivered simultaneously. A middle-aged patient presents with sudden onset of cough followed by shaking chills and shortness of breath. The patients complains of pleuritic-type chest pain and is noted to be cyanotic. Signs of pulmonary consolidation are present. What is the most likely etiology? Klebsiella pneumonia Which two pathogens are the most common cause of a lobar infiltrate on chest x-ray? Klebsiella (upper lobe) and S. pneumoniae A patient presents with fever, multiple chills and pleuritic chest pain. He had the flu which was followed by the insidious onset of a cough productive of purulent sputum. Course rhonchi and rales are heard on the chest exam. There are no signs of consolidation. What is the most likely etiology? Staphylococcal pneumonia What are the most common pathogenic causes of lung abscesses seen on x-ray? Anaerobic bacteria is the most common cause in an immunocompetent patient and S. aureus, e. coli, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas and Streptococcus are most common in compromised patients. What is the classic (as well as most common) x-ray finding of sarcoidosis? Bilateral mediastinal lymphadenopathy A patient present looking ill, diaphoretic and febrile. He has a sudden onset of shaking chills, high fever, myalgias, severe headache and a nonproductive cough. Chest findings are minimal. Hepatomegaly is present. What is the most likely diagnosis? Q Fever pneumonia Toxicology What is the most common initial symptom of botulism in adults? Visual Difficulties There are present on more than 90% of cases and result from abducens (VI) nerve palsy. Severe cases may exhibit fixed dilated pupils from oculomotor (III) never involvement. In a poisoning patient with an increased anion gap metabolic acidosis, which etiology is likely with the finding of calcium oxalate crystals in the urine? Ethylene glycol poisoning In patients with propranolol overdose, which drug may produce dramatic improvement in heart rate and blood pressure? Glucagon Glucagon, which does not depend on beta receptors for its action has both inotropic and chronotropic effects. It helps to counteract the hypoglycemia induced by beta blocker overdoes. Glucagon is given as a 5 to 10 mg IV bolus. Because of its short (20 minutes) half life, an infusion of 2-5 mg/hour for adults should be started immediately after the bolus. With cumulative large doses, glucagon should be diluted in 5% glucose in water for constant infusion. Side effects include nausea and vomiting in most patients, mild hyperglycemia, hypokalemia and allergic reactions. Which blood gas measurement is likely to be normal in a patient with carbon monoxide poisoning? pO2 For what drug ingestions would alkalinize the urine? Salicylates Barbiturates Withdrawal from which substance produce the distinctive clinical findings of yawning, lacrimation and piloerection? Opiates What are the features of Wernicke encephalopathy? At least 2 of 4: dietary deficiency, oculomotor abnormalities, cerebellar dysfunction, and either altered mental status or mild memory impairment. Clinical Presentation: A 21-year-old male presents with nystagmus and extremely bizarre aggressive behavior. What is the diagnosis Phencyclidine (PCP) toxicity The nystagmus may be horizontal, vertical or rotatory. Other symptoms of PCP intoxication: At doses 1-6 mg (typical street dose): hallucinations, euphoria disinhibition At doses 6-10 mg: pupils can be paradoxically small, psychosis/sympathetic stimulation seen 150-200 mg ingestions can cause death What are the features of Korsakoff’s psychosis (aka alcoholinduced persisting amnestic disorder) Features include recent memory impairment, inability to learn new information, apathy and possible confabulation. What is the appropriate disposition for a child who ingest a petroleum distillate but demonstrates no signs or symptoms of toxicity? Observation for 6 hours (in the ED or at home) Which type of caustic ingestion is worse, acid or alkali? Alkali The liquefactive necrosis of alkali ingestion penetrates deeper than the coagulation necrosis of acid ingestion. In patients with organophosphate poisoning, large doses of this drug are frequently needed and may be repeated until tracheobronchial secretions dry up. What is this drug? Atropine The doses are: Adult – 2 mg IV Q 5-15 minutes prn Child – 0.05 mg/kg Q 15 minutes prn Intoxication with this drug of abuse may cause hyperthermia which may be sudden and lethal. What is the substance? Cocaine In patients with hydrofluoric acid burns, effective therapy includes? Calcium gluconate (2.5%) gel is the preferred topical agent and can be made by mixing 3.5 g calcium gluconate power in 150 mL of a water soluble lubricant (e.g glycerin hydroxethyl cellulose jelly). The gel should be secured by an occulsive cover (power free latex glove). Because the skin is impermeable to calcium, topical treatment is effective only for mild, superficial burns. Subcutaneous. Infiltrative therapy is necessary to treat deep, painful HF burns. Calcium gluconate is the agent of choice and can be administrated by either direct infiltration or intra-arterial injection. Despite its wide acceptance, the infiltration technique had disadvantage, especially when treating digits. Vascular compromise can occur if excessive fluid is injected into skin exposure sites, and unbound calcium ions have a direct toxic effect on tissue. Because of these disadvantages with subcutaneous infiltration intra-arterial infusion of calcium is now recommended in most instance. What is the major hazard of barbiturate abuse? Unintentional overdose (Abuse of barbiturates does not lead to tolerance of its toxic effects. As larger doses are taken, the greater the likelihood of an unintentional overdose.) What are the signs of benzodiazepine toxicity? Central nervous system depression, ranging from mild drowsiness to coma. Significant respiratory depression is rare, but can be seen with large oral overdoses or during intravenous conscious sedation, particularly when the benzodiazepine is combined with an opioid such as fetanyl. Hypotension is uncommon. Other implications include aspiration pneumonia and pressure necrosis of skin and muscles. Ataxia is the most common sign of toxicity, occurring in 90% of patients. Most potentially lethal ODs/poisonings demonstrate clinical manifestations within several hours of ingestion. Common exceptions to this rule are: Acetaminophen Mushrooms (amatoxin, gyromitrin, Cortinarius) Sulfonylureas Sustained-release Ca++ channel blockers Ant metabolites (e.g. methotrexate) Lomotil Paresthesias (mouth, face and limbs), ataxia, weakness and an odd floating sensation are associated with_______. Paralytic shellfish poisoning Dystonias and buccolingual (or perioral) dyskinesia (“rabbit syndrome”) are signs of ______ toxicity. Phenothiazine Profound weakness (especially in patients with myasthenia gravis) is a sign of toxicity of which drug group? The aminoglycosides Other important points Ototoxicity to vestibular and cochlear cells Nephrotoxicity causing proximal tubular damage and ATN Peripheral neuropathy in association with constipation suggests toxicity to what agent? Vincristine Urogenital What is the principle component of renal calculi? Calcium ( 75% of cases) Calcium oxalate is the main substance in 70% of stones, with calcium-phosphate mixtures present in 10%. Less common substance include struvite (magnesium ammonium phosphate) and uric acid. What is the differential diagnosis of pain at the right costal margin during the third trimester of pregnancy? Appendicitis Gall bladder disease Pyelonephritis Pulmonary disease The lesson here is that appendicitis is a very important consideration since the appendix is displaced (usually superiorly) as the pregnancy progresses. What is the most likely diagnosis of a malodorous vaginal discharge in a 6-year-old girl? Vaginal foreign body Describe the role of oral acyclovir in Herpes simplex infection. Acyclovir predictably decrease the duration of viral shedding. The duration of viral shedding accelerates healing and shortens the duration of symptoms. Antivirals do not affect the frequency of severity of recurrence. What is the most common cause of acute urinary retention in males over the age of 50? Benign prostatic hypertrophy Clinical Presentation: A 65-year-old diabetic male patient complains of pain “down there.” Examination reveals a scrotum that is swollen, edematous with an area of necrosis. He has no current or prior urinary problems. What is the diagnosis? Fournier’s gangrene (idiopathic scrotal gangrene) Name the most common etiology for dysuria in school age girls. Vulvovaginits Infections-Garderella vaginalis, Candida, Trichomonas Irritant and allergic contact Local response to vaginal foreign body Testicular torsion is most frequently misdiagnosed as _______. Epididymitis What is the treatment for Gardnerella vaginitis? The standard route of therapy has been oral, but there is also an intravaginal preparation available. Bacterial vaginosis (formally known as Gardnerella vaginitis or Haemophilus vaginalis) is an overgrowth of multiple endogenous vaginal bacteria, in some cases producing excessive discharge and vaginal malodor. Prevalence rates in pregnancy are estimated at 15-20%. Bacterial vaginosis is associated with an increased risk of chorioamnionitis, subclinical PID, premature rupture of membranes, fetal prematurity, and postpartum endometritis after vaginal delivery. Therapy during the second trimester is recommended even when the patient is asymptomatic to prevent the sequelae of premature rupture of membranes. Management includes a day course of metronidazole or a 7 day course of clinedamycin. Intravaginal treatment is not recommended on pregnant patients. Which cause of genital infections has the greatest propensity for permanent tubal obstruction and infertility? Chlamydia trachomatis The presentation of this clinical problem may be indistinguishable from a ruptured ectopic pregnancy.. There is a sudden onset of lower abdominal pain in a patient with amenorrhea or one in early pregnancy. What is the diagnosis? Hemorrhagic corpus luteum cyst Elevation of both the systolic and diastolic blood pressure after the 20th-24th week of pregnancy is known as _______. Pre-eclampsia The other important components of this disease are proteinuria (30 mg in 24 hour collection) and edema. Hyperreflexia, if present, suggests impending eclampsia 9seizures and/or coma), since 80% of eclamptic patients have pre-existing hyperreflexia. Other common presenting symptoms for pre-eclampsia include headache, visual disturbances and abdominal pain. What is the usual cause of fetal death following blunt trauma to the mother? Maternal death and abruptio placentae A prolapsed umbilical cord is a true obstetrical emergency. What should the emergency physician do while awaiting the arrival of the obstetrician? The examiner’s hand should be used to elevate the presenting fetal part until a cesarean section can occur. 90% of renal calculi that are up to______ man in diameter will pass spontaneously. 4-5 mm 90% of stones less than 4 mm will pass spontaneously while 50% of stones 4-6 mm in size will pass spontaneously. What is the treatment of Fournier’s gangrene? Mandatory treatment includes immediate surgical debridement and administration of broad spectrum parental antibiotics that cover gram positive, negative and anaerobic etiologies. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and IV fluid resuscitation should also be employed if available. Mortality is about 20%. What is the emergency treatment of paraphimosis if the foreskin cannot be reduced manually? Local anesthesia is administered followed by a superficial dorsal midline incision of the band. This will decompress than glans and allow foreskin reduction. In the third trimester of pregnancy, this antibiotics should not be used in therapy of urinary tract infections. Sulfonamides The risk to the fetus is kernicterus because of a rise in serum bilirubin. What is the most frequent opportunistic bacterial infection in patients with AIDS? Mycobacterium avium What is the most common cause of cancer in HIV-infected patients? Kaposi’s sarcoma Which is the only opportunistic infection in patients with AIDS that is transmitted by respiratory route to both immunocomprised and immunocompetent hosts? Tuberculosis What is the most common organism causing septic arthritis in patients less than 50 years-old, particularly teenagers and young adults? Neisseria gonorrhoeae Which antibiotics should be avoided throughout pregnancy? Tetracyclines, quinolones and aminoglycosides What is the most common opportunistic infection in AIDS patients? Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) What are the most common causes of vaginal bleeding for permenarchal girls, women in their reproductive years and those after menopause? Premenarch: Trauma/foreign body, infection, anovulation Reproductive years: Pregnancy Post-menopause: Neoplasms, malignancy, atrophic vaginitis. Miscellaneous Administration of magnesium is dangerous in the presence of which electrolyte abnormality? Hyperkalemia. Magnesium replacement enhances potassium retention. What is the most frequent cause of malpractice claims against emergency physicians? Failure to diagnosis fractures and/or dislocations How should an error in a medical chart be corrected? If the patient is still present in the Emergency Department, draw a single line through the incorrect statement(s), noting the reason for the change, initialing the correction(s) and time the change. If the patient left the Department, add a signed, dated and timed addendum to the chart. What is the purpose of off-line (indirect) medical control? Development of protocols In a disaster situation, a patient with a barely palpable blood pressure would be categorized as ________. First priority. The START disaster triage criteria classification are expectant, immediate, delayed and minor. In the hospital phase of disaster management, where should the control center be located? Near but not in the Emergency Department; a staging are for incoming personal and equipment should be established on the outer perimeter. What are the strategies/recommendations used in scheduling night shifts that will be least disruptive to the body’s natural circadian rhythm? 1- The “gold standard” is not to change shifts at all; work the same shift all the time and keep the same sleep pattern. 2- Working only one or two night shifts in a row is the next best strategy because it minimizes circadian disruption. 3- If rotating shifts cannot be avoided it is best to rotate all shifts in a clockwise direction with a minimum of one month per rotation. Scalded skin syndrome is usually caused by a _____ in children (generally less than 6-years-old). Toxic epidermal necrolysis, on the other hand, is most often caused by a ___ ___ in adults. Staphylococcal infection (children) Drug/toxin reaction (adults) What is the most common cause of erthema multiforme? Herpes simplex is the most common cause in children. Drugs, connective tissue disorders, malignancies and HIV have a significant association with Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN). The “herald patch” is most closely associated with ________. Pityriasis rosea Clinical Presentation: A patient presents with a rash. He was given a thiazide diuretic recently by the family physician. The rash is scaly or flaking and is erythematous and warm to the touch. What is the most likely diagnosis? Exfoliative erythroderma Clinical Presentation: An elderly male has a history of prostate disease with urinary tract infections. He presents with fever, a systolic BP < 100 mmHg and a rash. The lesions are erythematous with necrotic centers. Which organism is the likely offender? Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The rash is called ecthyma gangrenosum. The same presentation could occur in a patient with pneumonia or COPD. In other words, think about Pseudomonas with a possible gram-negative sepsis and this particular rash. Wood’s light examination is helpful in diagnosing which skin disorders? Erythrasma Tinea versicolor Porphyria cutanea tarda Some pseudomonal skin infections The most costly cause of malpractice is? Failure to diagnose MI Name the leading cause of septic shock. Gram-negative bacteremia Regarding Pseudomonas infections: 1-What is /are the drug(s) of choice? 2-what are alternative choices? 3- Which drug has been associated with multiple treatment failures and is no longer recommended? 1. 2. 3. Pseudomonal infections are treated with a combination of an antipseudomonal betalactam (e.g., penicillin or cephalosporin) and an aminoglycoside. Carbapenems (e.g., imipenem, meropenem) with antipseudomonal quinolones may be used in conjunction with an aminoglycoside…. With the exception of cases involving febrile patients with neutropenia, in whom monotherapy with ceftazidime or a carbapenem (e.g., imipenem, meropenem) is used, a two drug regimen is recommended. Aminoglycosides have fallen to the wayside with newer generations of antibiotics. Other treatment options include, Zosyn®, primaxin, timentin, aztreonam (all as monotherapy) Angioedema associated with ACE-inhibitors has a predilection for which areas of the body? Lips, tongue and laryngeal soft tissues Which medication is the most common cause of drug reaction? Penicillin (especially ampicillin) What is the treatment for a paronychia? Incision and drainage is the choice, along with an oral cephalosporin and warm soaks. The usual organism is S. aureus, sometimes with concomitant streptococcal infection. Local measures alone commonly fail. If the process extends under the nail, a portion of the nail must be removed. How does one treat a felon? Incision and drainage Regarding puncture wounds of the foot1- What is the major complication that can occur? 2- what is the usual causative organism if the puncture occurred through a shoe? 1. Osteomyelitis 2. Pseudomonas How is a skin abscess best treated in the ED? I & D. Antibiotics are not shown to be beneficial What are the limitations of pulse oximetry? In comparison to ABGs, a pulse-oximetry provides no information on pH or PCO2 levels, and only indirectly assesses adequacy of ventilation, the latter of which is important in at least two clinical situations: 1- During conscious sedation, monitoring ventilation is important to prevent hypoxia 2- A decrease in hemoglobin oxygen saturation may result if a patient is hypoventilated or has severe anemia (Hgb < 5mg/dL) Other limitations include severe vasoconstriction, excessive movement, interference with transfer through nail bed and alterations in hemoglobin (including carboxyhemoglobin and methemoglobin). In a Haz-Mat incident, decontamination is best performed in the _____ setting? Prehospital If a patient has a wound which requires suturing but the patient claims that he is allergic to lidocaine, what are the available options? 1. Use an ester such as procaine, tetracaine or benzocaine. 2. Observe the patient for 30 minutes to watch for a reaction. True or False: there is no significant difference in infection rates when using clean nonsterile gloves rather than sterile gloves in re[pairing uncomplicated lacerations. True* *2006 LLSA Reading