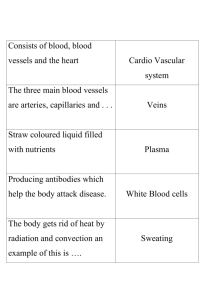
Chapter 03 - Lisle CUSD 202
advertisement
Chapter 27 Circulation Chapter 27 Circulatory System Basics Fluid—blood Channels—vessels A pump—the heart 2 Chapter 27 Types of Circulatory Systems Open • Open space within the body cavity—hemocoel • Arthropods (insects, spiders, and crustaceans) • Most mollusks (snails and clams) Closed • Confined blood in continuous vascular network • Pumping heart – Some invertebrates (earthworm, cephalopod mollusks) – All vertebrates 3 Chapter 27 Open & Closed Systems 4 The Evolution of the Vertebrate Heart (b) Amphibians (a) Fish Gill Reptiles” Capillaries Lung Capillaries Ventricle Chapter 27 (c) Mammals, Birds Lung Capillaries Atria Atriu m Ventricle Body Capillaries Body Capillaries Ventricles Body Capillaries 5 Vertebrate Circulatory System: Functions Chapter 27 Transport of O2 and CO2 Distribution of nutrients Transport of waste Distribution of hormones Regulation of body temperature Protection against blood loss and disease 6 Chapter 27 Mammal Circulatory System 7 Vertebrate Circulatory System: The Heart Chapter 27 Structure • Atria • Ventricles • Structural evolution among the vertebrates The cardiac cycle • Systole—period of ventricle contraction • Diastole—relaxation of all the chambers followed by contraction of the atria 8 Chapter 27 Heart - Human 9 Aorta Superior Vena Cava (from upper body) Pulmonary Artery (to right lung) Pulmonary Veins (from right lung) Right Atrium Atrioventricular Valve Right Ventricle Inferior Vena Cava (from lower body) 10 Chapter 27 Human Heart Pulmonary Artery (to left lung) Pulmonary Veins (from left lung) Left Atrium Atrioventricular Valve Left Ventricle Semilunar Valves Descending Aorta (to lower body) Chapter 27 11 The Cardiac Cycle Oxygenated blood from lungs Deoxygenated blood to lungs (c) Heart Relaxes; atria fill passively Oxygenated Deoxygenated blood from body blood to body (a) Atria Contract (b) Ventricles Contract Chapter 27 Cardiac Cycle 12 Chapter 27 Path of Blood Flow QuickTime™ and a Sorenson Video 3 decompressor are needed to see this picture. 13 Chapter 27 Measuring Blood Pressure 14 Chapter 27 The Structure of Cardiac Muscle 15 Chapter 27 16 Coordination of Heart Activity Atrioventricular and semilunar valves The sinoatrial node (SA node) The atrioventricular node (AV node) Influences on heart rate • Parasympathetic nervous system - decreases heart rate • Sympathetic nervous system - increases heart rate • Hormones Chapter 27 Sinoatrial Node Atrioventricular Node Excitable Fibers 17 The Heart’s Pacemaker and Its Connection s Chapter 27 Cardiac cycle 18 Chapter 27 Stab Wound - Heart 19 Chapter 27 Composition of Blood 20 Chapter 27 21 Blood Cells Red blood cells—erythrocytes (RBCs) • 99% of the total cellular component in the blood • Carry O2 bound to hemoglobin from lungs to tissue • Buffer CO2 carried from the tissues White blood cells—leukocytes (WBCs) • 1% of the total cellular component of blood • Five white blood cell type Platelets • Cellular fragments from megakaryocyte in the bone marrow • Function in blood clotting Chapter 27 Blood Smear Neurtophil Red Blood Cell Lymphocyte White Cell Platelet 22 Chapter 27 Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) Red Cells Made in the bone marrow Destroyed in the liver Stored in the spleen Heme + Globin + Iron = Hemoglobin Anemia = Lack of red blood cells 23 Chapter 27 24 Hemoglobin Polypeptide Chains Heme Group RBCs RBC Regulation by Negative Feedback Chapter 27 Oxygen deficiency Stimulates Erythropoietin production by kidneys Stimulates Red blood cell production in bone marrow Inhibits Restored oxygen level Causes 25 Chapter 27 26 White Blood Cells - Platelets White Blood Cells Made in the Bone Marrow Programmed in the lymph glands and thymus glands Platelets Made in the bone marrow A White Blood Cell Attacks Bacteria Chapter 27 27 Macrophage Bacteria Pseudopodia Chapter 27 The Production of Platelets 28 Chapter 27 Blood Clotting Ruptured Platelet Thromboplastin B L O O D prothrombin Fibrinogen Thrombin Fibrin 29 Chapter 27 Blood Clotting (a) 30 Chapter 27 Blood Clotting (b) Fibrin Network Platelets Trapped RBCs 31 Chapter 27 32 Blood Vessels Arteries and arterioles • Thick walled, elastic to withstand high pressure • Carry blood away from the heart Capillaries • Tiniest vessels; thin, single-cell wall for easy diffusion • Exchange of materials between blood & body cells Venules and veins • Thin-walled vessels surrounded smooth muscle • Low resistance to blood flow • Return blood to the heart Chapter 27 Blood Vessels Smooth Muscle Vein Artery 33 Chapter 27 Distribution of Blood Flow Regulated by muscular walls of arterioles Influenced by: • Autonomic nerves • Hormones • Other chemicals released from nearby tissues 34 The Human Circulatory System Chapter 27 Carotid Artery Jugular Vein Aorta Superior Vena Cava Heart Inferior Vena Cava 35 Chapter 27 Femoral Artery Femoral Vein 36 Precapillary Capillaries Interconnections & Sphincters Chapter 27 Structures Blood Vessels Arteriole Venule Conn. Tissue Muscle Conn. Tissue Artery Endothelium Vein 37 Valves Direct Flow of Blood in Veins Skeletal muscles help return blood to heart Valves prevent backflow Chapter 27 38 Chapter 27 The Lymphatic System Structure • Complex network of thin-walled vessels • In proximity to the capillary network • Composed of cells with openings between them that act as one-way valves Functions • Removal of excess fluid • Transport of fats from the intestine • Cellular body defenses 39 Tonsil Superior Vena Cava Heart Thoracic Duct Lymph Vessels Thoracic Duct enters vena cava Chapter 27 40 Lymphatic System Thymus Spleen Valve Lymphocytes Lymph Node Lymph Fluid Chapter 27 Lymph conducted to larger lymph vessels Capillaries leak plasma to form interstitial fluid 41 Lymph Capillary Structure Interstitial fluid enters lymph vessels PlaquesChapter 27 42 Clog Arteries Chapter 27 Normal Artery - Plaque 43 Chapter 27 The End