Cell Organelles - SD43 Teacher Sites
advertisement

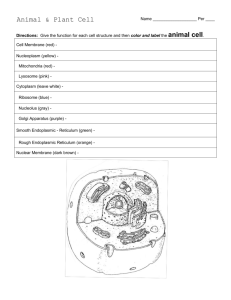
2013-2014 Cell Station Cards Station #1 – Make your own Flashcards 1. Each student should cut words and definitions out 2. Match each word with the definition. 3. Check your results with those of your station partners. 4. Glue together word and definition to make flashcards. 5. Quiz each other based on the parts of the cell and their functions if you have time remaining. Station #2 - Cell Theory 1 – Watch the clip The Wacky History of Cell Theory – Answer the questions on your worksheet. (also on next slide) Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow Vow -- Cell Is the Basic Building Block of Life Scientists Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow have studied living organisms for several years. With the help of the microscope they have determined that all living things are made of cells. According to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, these cells seem to be the basic structural units within organisms. The two scientists also note that the well-being of the organism depends on the well-being of its cells. Due to the numerous and varied experiments and studies they have conducted, Schleiden and Schwann are confident in their hypothesis and have laid out the points in what they call the cell theory. Schleiden and Schwann have incorporated into the cell theory experimental observations and conclusions of the famous scientist Rudolf Virchow, who has observed that cells reproduce themselves. Station #2 - Cell Theory Some facts that may help you Cell Theory: All living things are composed of cells Are basic units of living things. New cells arise only from preexisting cells. Microscopes revealed the presence of cells and show their detailed structure. Animal and Plant cells contain organelles Organelles are “little organs”: small bodies that have a specific structure and function Station #3 Prokaryotic Cells vs. Eukaryotic Cell 1. Complete the questions on your worksheet based on the information below 2. As you go through the organelle stations, complete the T chart – see how much you can complete now. Are extremely small Do not have a nucleus Have a cell wall with or without peptidoglycan Lack membrane bound organelles Bacteria are prokaryotic cells Are larger cells There is a nucleus present Cellulose cell wall (plants only) or chitin (fungi only) Contain many organelles Have larger ribosomes Everything except bacteria Station #3 – Plant vs. Animal 1. Fill in the blanks on your worksheet 2. Using your prior knowledge to complete a Venn Diagram 3. Watch this Plant Clip and add to your Venn Diagram Cell wall made of cellulose Have no cell wall Have 1 large central vacuole Have many small vacuoles Contain Chloroplasts No chloroplasts Station 4 – Watch The BrainPop 1.Watch the BrainPop on Cells Video 2.Take the Quiz 3.Record your Quiz Score on your worksheet Station 5 – Plant and Animal Cell 1.Label Each Cell Station #6 - Organelles Complete the notes for each organelle on your worksheet Lysosome - The Garbage Storage Bin Structure Round organelle surrounded by a membrane Function Contains digestive enzymes that are used to Breakdown macromolecules into small molecules the cell can use digest invading cells or to destroy the cell if it needs to be replaced (so it’s also called a Suicide Bag!) Vacuoles - Storage Tank Structure Membrane enclosed sacs for storage. Function Stores materials such as water, salts, proteins and carbohydrates Important Info Plant cells contain one large central vacuole which provides support in the form of Turgor Pressure Centrioles- the ushers Structure Paired structures located near nucleus Only visible when cell is ready to divide Function Helps organize cell division Important Info Not found in plant cells Mitochondria: The Powerhouse Structure Usually oval, with a double membrane Inner membrane (cristae) within outer membrane….inside is called the matrix. Function Site of respiration, where ATP is made in both plants and animals Important Info Found in large numbers in cells requiring lots of energy. Powerhouse of the cell Chloroplasts - The Bakery Structure Small , flattened structure found in plants. Surrounded by double membrane; has inner membranes inside (thylakoid membranes) Contain chlorophyll Function Site of photosynthesis (Change light energy into glucose ) The Nucleus- The Brain of The Cell Structure Large organelle surrounded by a nuclear membrane Contains pores Functions Contains the DNA (chromosomes) and nucleolus Controls cell’s activities Nucleolus makes RNA Ribosomes- The Factories Structure Very small organelle Can be free floating or can be attached to the ER Function Site where proteins made (protein synthesis) Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) -The highway of the cell Structure System of membranes (channels and tubular canals) enclosing a fluid filled space Surface covered with ribosomes Function Transports proteins which have been made in the ribosomes Smooth ER No ribosomes present Makes and transports lipids. Detoxify drugs in the liver. & Rough ER Ribosomes are attached Makes proteins for the cell to export Modifies the content Forms vesicles then carries contents to the Golgi The Golgi Apparatus - The UPS Structure Group of smooth endoplasmic reticulum that have flattened sacs Vesicles are often seen at the edges Functions Modifies, sorts and packages substances that are produced by cells (mainly proteins and glycoproteins) Makes lysosomes Cell Membrane : Gatekeeper of the Cell Also called the plasma membrane Structure Found on the surface of animal cells and just inside cell wall of plants Made of proteins and lipids Functions Regulates what goes into and out of the cell Also provides protection and support Has receptor molecules to respond to chemicals Cell Wall: Supporter of Plant Cells Structure A rigid structure that surrounds plant cells. Made mainly of cellulose (a carbohydrate) Functions Supports and strengthens plant cells Plant cells have a cell wall in addition to a cell membrane. The Cytoskeleton- The Backbone Structure Supporting structure and transport system Network of protein filaments Function Helps the cell to keep it’s shape Also helps cell move using things called microfilaments and microtubules Station #7 – Matching Worksheet Complete the Parts of the cell – Matching worksheet Station #8 – Cell Analogy 1. Complete the analogy of the cell worksheet Station #9 – Cell Investigation 1. 2. 3. 4. Go to the website below and look at the variety of organelles. Ensure to look at both plant and animal cells. Inside A Cell Bonus Site to check out Bonus Site 12. Plant Cell (Top) – pg. 175 Nucleolus Nucleus Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Nuclear envelope Ribosome (free) Rough endoplasmic reticulum Ribosome (attached) Golgi apparatus Cell wall Cell membrane Chloroplast Mitochondrion Vacuole 12. Animal Cell (Bottom) – pg. 175 Nucleolus Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Nucleus Nuclear envelope Rough endoplasmic reticulum Ribosome (free) Cell membrane Ribosome (attached) Centrioles Mitochondrion Golgi apparatus (On the back) Bacteria Cell – pg. 472 Peptidoglycan Cell Wall Flagellum Cell Membrane DNA Ribosomes Pili