Cells
advertisement

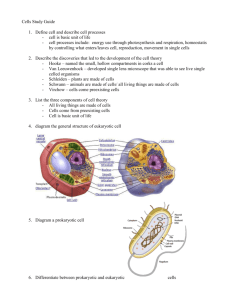
Agenda 10/14 Bellwork (back) Lab report- review format, time to type, get peer feedback, due Thursday Cell organelle flashcards- due Thursday Agenda 10/15- CP Biology Bellwork- MCAS questions New Information: Viruses, cell structure and function Activity: finish flashcards HW- finish lab report (and flashcards, if needed) Agenda 10/16- Honors Biology Bellwork- MCAS questions New Information: Viruses, cell structure and function Activity: cell analogy worksheet (due Fri) Viruses Generally not considered living things because they lack cell structure and cannot reproduce on their own. Millions or more, very diverse Viruses Protein shell, DNA or RNA, some have a lipid layer Insert into cells, some enter lysogenic cycle (viral DNA inserts into cell’s DNA), then escape via lysis (bursting of the cell) Viral Infections Two rotaviruses: the one on the right is coated with antibodies that stop its attaching to cells and infecting them Cells Amoeba Proteus Plant Stem Bacteria Red Blood Cell Nerve Cell Outline Cell Theory Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Organelles Containing DNA Endosymbiosis Plant Cells Animal Cells Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing cell. Cells come from other cells. Characteristics of All Cells Genetic material- DNA Prokaryotes: circular; free-floating Eukaryotes: linear; located in the nucleus Cytoplasm fills cell interior (aka cytosol) Cell membrane encloses the cell Ribosomes- site of protein production Cytoskeleton- support, transport, etc Prokaryotic Cells Simplest organisms, smaller in size Cytoplasm Cell Membrane DNA (circular) Ribosomes Cytoskeleton Cell Wall (peptidoglycan), some with capsulesprotection NO NUCLEUS but have a nucleoidpart of cytoplasm where DNA is found and chemical reactions take place NO membranebound organelles All unicellular Prokaryotic Cells Some use flagellum for locomotion (also present in some eukaryotes) threadlike structures protruding from cell surface; function= movement Generalized Prokaryotic Cell (no nucleus; all bacteria are prokaryotes) Ribosome Cell Membrane Cell Wall Flagellum Pilus DNA (circular) Generalized Eukaryotic Cellhas a nucleus and organelles; includes all plant, animal, fungi, protozoa cells Eukaryotic Cells Nucleus Membrane-bound organelles Linear DNA- in nucleus Ribosomes Cell Membrane Cell Wall (in SOME, not all) plants- cellulose, fungi- chitin NOT IN ANIMAL CELLS! Cytoskeleton Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote Smaller No nucleus- freefloating circular DNA Cell walls No membranebound organelles Ribosomes Cytoskeleton Larger Nucleus with linear DNA Cell walls in some (plants, fungi) Membrane-bound organelles Ribosomes Cytoskeleton Agenda 10/17- Honors Biology Bellwork- finish page, turn in Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote Cell structure review (flashcards) Cell lab HW- finish lab; start coloring (due Tuesday)- colors are posted on website (cardozabio.weebly.com) 1. Cell Membrane (aka plasma membrane) Made of lipids and proteins Holds in the cytoplasm, helps maintain cell’s homeostasis Controls what enters/leaves cell Lipid bilayer Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function 2. Nucleus Nickname: “The Control Center” Function: holds the DNA, controls cell activities 3. Nucleolus: dark spot in the middle of the nucleus; makes ribosomal RNA Nucleus bound by two phospholipid bilayer membranes nuclear envelope- has nuclear pores to control what enters/leaves Nucleus Chromosomes DNA of eukaryotes is divided into linear chromosomes. exist as strands of chromatin, except during cell division 4. Cytoplasm (aka cytosol) Clear jelly-like material between cell membrane and nucleus Helps keep cell shape Contains the organelles 5. Cytoskeleton Network of protein fibers supporting cell shape and anchoring organelles Actin filaments Microtubules cell movement Centrioles- organize cell division Intermediate filaments Cytoskeleton Animal Cell Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Ribosomes Cell Membrane Section 7-2 Go to Section: Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells 6. Endoplasmic Reticulum Network of canals running through cell: cellular highway- moves materials around cell 2 Types: - Rough ER: Rough appearance because it has ribosomes Function: helps make proteins, that’s why it has ribosomes - Smooth ER: NO ribosomes Function: makes fats or lipids; detoxifying 7. Ribosomes Function: make proteins Found in all cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic Ribosomes are composed of two subunits that join and attach to messenger RNA. site of protein synthesis assembled in nucleoli Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Go to Section: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function 8. Golgi Complex Nickname: “The shippers” Function: packages, modifies, and transports materials to different location inside/outside of the cell Appearance: stack of pancakes 9. Vacuoles Liquid-filled membrane sacs, store food water, minerals “warehouses” of the cell Plants: one central one, helps maintain cell shape Animals: a few, small ones Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function 10. Lysosomes: circular, but bigger than ribosomes Nickname: “Clean-up Crews” Function: to break down food and waste and to destroy old organelles 11. Centrioles Located near nucleus in pairs Help organize cell division In animal, not plant cells Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function 12. Mitochondria- has own DNA Nickname: “The Powerhouse” Function: Energy production (cellular respiration) Breaks down food to make ATP ATP: is the major fuel for all cell activities that require energy 13. Cilia and Flagella Function: movement Cilia: short, hair-like projections; move with beating action Flagella: longer, tail-like structure; move with whiplike action Animal Cell Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Ribosomes Cell Membrane Mitochondria Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Bodies Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Now let’s talk about structures found in PLANT Cells, but not animal cells!! Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Section 7-2 Plant Cell Vacuole Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Large Central Vacuole Function: stores water and some nutrients This is what makes lettuce crisp When there is no water, the plant wilts Found in some animal cells, but small Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Plant Cell Section 7-2 Vacuole Chloroplasts Cell Membrane Go to Section: 14. Chloroplasts found only in plants, some protists Function: traps energy from the sun to produce food for the plant cell (photosynthesis) A type of plastid (organelle that stores plant pigments)- Green in color because of chlorophyll, which is a green pigment Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Plant Cell Section 7-2 Vacuole Chloroplasts Cell Membrane Cell Wall Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function 15. Cell Wall Function: provides support and protection to the cell membrane Found outside the cell membrane in plant cells, fungi, some bacteria and protists Plant Cell Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Plant Animal 3 Domains, 6 Kingdoms of Life Domains Kingdoms Archaea Archaebacteria Bacteria Eubacteria Eukarya Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Classification of Life- 6 Kingdoms 1. Eubacteria: 2. Prokaryotic bacteria Unicellular or colonial Heterotroph or Photosynthetic Ex. E. coli Archaebacteria: Prokaryotic bacteria, extreme environments Unicellular or colonial Chemosynthetic (autotrophs) Classification of Life- 6 Kingdoms 3. Protists: mixed bag Unicellular or multicellular eukaryotes No true tissues/organs Some can photosynthesize, some are heterotrophs, some are both Ex. algae, diatoms, seaweed Classification of Life- 6 Kingdoms 4. Fungi: Unicellular or multicellular eukaryotes Decomposers or parasites Cell walls of chitin Ex. yeast, mushrooms, molds Classification of Life- 6 Kingdoms 5. Plantae: cell walls of cellulose Multicellular eukaryotes Possess true tissues/organs Photosynthetic, very few are also heterotrophs Ex. flowers, ferns, mosses Classification of Life- 6 Kingdoms 6. Animalia: Multicellular eukaryotes Complex organ systems Heterotrophs No cell walls (many)