Chapter 15 - Cengage Learning
advertisement

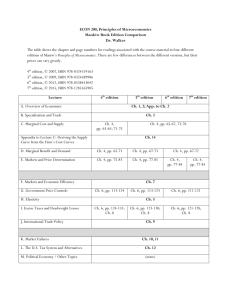
CHAPTER 15 Human Resource Management in virtual organisations For use with Human Resource Management in South Africa 4e by Grobler, Wärnich et al ISBN: 1408019515 © 2010 Cengage Learning Chapter outcomes • Define the concept "virtual organisation" • Identify three forms of virtual work arrangements • List the advantages and disadvantages for the company and employee when implementing the telecommuting work arrangement • List the characteristics which truly identify a virtual team • List three types of virtual teams For use with Human Resource Management in South Africa 4e by Grobler, Wärnich et al ISBN: 1408019515 © 2010 Cengage Learning Chapter outcomes (continued) • Discuss the advantages and disadvantages when using technology such as e-mail, bulletin boards, audio and video conferencing • Discuss the role of the HR professional within the virtual organisation • Discuss issues relating to job analysis practices within the virtual work environment • Discuss issues relating to a number of HR practices within the virtual work environment • Explain how the traditional and virtual organisation differs For use with Human Resource Management in South Africa 4e by Grobler, Wärnich et al ISBN: 1408019515 © 2010 Cengage Learning Technology has: • Prompted changes in company structures (eg. virtual organisation) • Modified work arrangements (eg. virtual team) • Influenced how people are managed (eg. virtual workplace) For use with Human Resource Management in South Africa 4e by Grobler, Wärnich et al ISBN: 1408019515 © 2010 Cengage Learning Virtual organisation defined • Virtual organisations are multi-site, multi-organisational and dynamic. At the macro level, a virtual organisation consists of a grouping of units of different companies (eg. other businesses, consultants, contractors) that have joined in an alliance to exploit complementary skills, in pursuing common strategic objectives For use with Human Resource Management in South Africa 4e by Grobler, Wärnich et al ISBN: 1408019515 © 2010 Cengage Learning Virtual organisation (continued) • Virtual organisations are characterised as those organisations in which the ongoing relationships with partners are salient • Core business activities are reduced, leaving the partners to focus on some of the key business functions • Core (or central organisation) is connected with the partners through technology • Virtual organisations tend to be characterised as flexible, and their structure as transitory and fluid • Many definitions of the concept tend to see groups as important. Some appear to see virtual teams as a sufficient condition for an organisation to be called a virtual organisation For use with Human Resource Management in South Africa 4e by Grobler, Wärnich et al ISBN: 1408019515 © 2010 Cengage Learning The virtual workplace • Telecommuting • Frontline model • Cyberlink model – Virtual teams: • Group must have some charter for working together • Group must be interdependent • Group must be committed to working together • Group must be accountable as a unit to someone or something in the bigger organisation For use with Human Resource Management in South Africa 4e by Grobler, Wärnich et al ISBN: 1408019515 © 2010 Cengage Learning The virtual workplace (continued) • Cyberlink model (continued) – Types of virtual teams: • Project teams • Service teams • Process teams – Why virtual teams? – Cost benefits of implementing virtual teams – Complexity of virtual teamworking – Technology for virtual teams For use with Human Resource Management in South Africa 4e by Grobler, Wärnich et al ISBN: 1408019515 © 2010 Cengage Learning Factors that contribute to the complexity of virtual teamworking • • • • • Number of team members Number of different languages spoken in the team Number or organisations represented in the team Number of time zones within the group Technical systems implemented For use with Human Resource Management in South Africa 4e by Grobler, Wärnich et al ISBN: 1408019515 © 2010 Cengage Learning HRM practices in virtual organisations • Virtual HR departments • The role of the HR professional in the virtual organisation • HR practices in virtual organisations – JA – Participants – Methods of data collection – Types of data and level of analysis For use with Human Resource Management in South Africa 4e by Grobler, Wärnich et al ISBN: 1408019515 © 2010 Cengage Learning HRM practices in virtual organisations (continued) • HR practices in virtual organisations (continued) – Staffing – Recruitment – Selection – T&D – E-learning – PA – Compensation – Negotiation For use with Human Resource Management in South Africa 4e by Grobler, Wärnich et al ISBN: 1408019515 © 2010 Cengage Learning Important skills and competencies needed in virtual organisations Shared sense of purpose Operating guidelines Team level Analysing & solving problems Conflict management etc. Dealing with change Managing alignment Flexibility Co-ordinating activities Adaptability Emotional control Individual Willingness to learn etc. Managers Encourage continuous learning Managing through technology etc. For use with Human Resource Management in South Africa 4e by Grobler, Wärnich et al ISBN: 1408019515 © 2010 Cengage Learning Advantages of e-learning • • • • • • • Self-paced: trainees can proceed on their own time Is interactive, tapping multiple trainee senses Allows for consistency in the delivery of training Enables scoring of exercises/assessments and the appropriate feedback Incorporates built-in guidance and help for trainees to use when needed Is relatively easy for trainers to update content Can be used to enhance instructor-led training For use with Human Resource Management in South Africa 4e by Grobler, Wärnich et al ISBN: 1408019515 © 2010 Cengage Learning Disadvantages of e-learning • • • • • • • May cause trainee anxiety Not all trainees may be ready for e-learning Not all trainees may have easy and uninterrupted access to computers Not appropriate for all training content (eg. leadership, cultural change) Requires significant upfront cost and investment No significantly greater learning evidenced in research studies Requires significant top management support to be successful For use with Human Resource Management in South Africa 4e by Grobler, Wärnich et al ISBN: 1408019515 © 2010 Cengage Learning A model of virtual negotiation characteristics Possible 3rd party Party A Party B Individual differences Individual differences Personality, distributive vs integrative, sensitivity vs nonverbals, comfort with technology Personality, distributive vs integrative, sensitivity vs nonverbals, comfort with technology Negotiation dynamics Personal disclosure, entrenchment, flaming, ethics Negotiation dynamics Communication media Personal disclosure, entrenchment, flaming, ethics Synchronicity, message misinterpretation, message content, information richness For use with Human Resource Management in South Africa 4e by Grobler, Wärnich et al ISBN: 1408019515 © 2010 Cengage Learning Attributes of virtual and traditional organisations • • • • • • Streamlined Flexible Focused Communication Hyper time Organisation structure • Management of work & workers • Career path • Information • Office building • Professionalism • Customer relations For use with Human Resource Management in South Africa 4e by Grobler, Wärnich et al ISBN: 1408019515 © 2010 Cengage Learning Summary • • • • There is a fast-growing interest in another way of working which combines changes, in technical and organisational systems of choice. This is virtual working and by extension virtual teams. Different types of teams within the virtual organisation can be found namely: project, service and process teams. The key for any company at the outset of a virtual teamworking implementation is to be technologically aware and open, not technologically deterministic and closed. Success of virtual teams will not come from tight managerial control, this inhibits the extent of the interactions within the network. For use with Human Resource Management in South Africa 4e by Grobler, Wärnich et al ISBN: 1408019515 © 2010 Cengage Learning Summary • • • The team will benefit most from acknowledging the fact that they are all individuals, and then drawing on their individual strengths to create a microcosm within the wider organisation that embodies shared culture and operating principle that they believe will enable them to deliver the best results as a team. Virtual organisations will need to adapt their recruiting processes to the changing skill base and nature of the labour pool from which they are recruiting. For the virtual organisation with its geographically dispersed global labour pools the traditional idea of candidates having onsite testing batteries and interviews is not practical. For use with Human Resource Management in South Africa 4e by Grobler, Wärnich et al ISBN: 1408019515 © 2010 Cengage Learning Summary • • • The virtual organisation's geographically dispersed supervisors, peers and subordinates offer a unique environment for understanding, performance evaluation, monitoring the employee's outputs may be a way of making performance evaluations work under these conditions. In the area of compensation the following methods may be used in the virtual environment, person-based systems, broadbanding and classification. While the process of negotiation has been written about extensively, little has been done regarding this activity in the virtual environment. This environment will dictate new rules for negotiating. For use with Human Resource Management in South Africa 4e by Grobler, Wärnich et al ISBN: 1408019515 © 2010 Cengage Learning